|
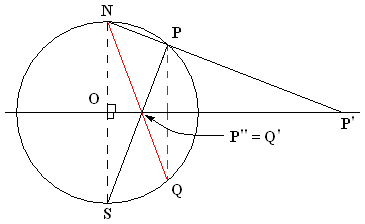
Nicolosi Globular Projection
The Nicolosi globular projection is a polyconic map projection invented about the year 1,000 by the Iranian polymath al-Biruni. As a circular representation of a hemisphere, it is called ''globular'' because it evokes a globe. It can only display one hemisphere at a time and so normally appears as a "double hemispheric" presentation in world maps. The projection came into use in the Western world starting in 1660, reaching its most common use in the 19th century. As a "compromise" projection, it preserves no particular properties, instead giving a balance of distortions. History Abū Rayḥān Muḥammad ibn Aḥmad Al-Bīrūnī, who was the foremost Muslim scholar of the Islamic Golden Age, invented the first recorded globular projection for use in celestial maps about the year 1000. Centuries later, as Europe entered its Age of Discovery, the demand for world maps increased rapidly, sparking a vast experimentation with diverse map projections. Globular projections were one cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
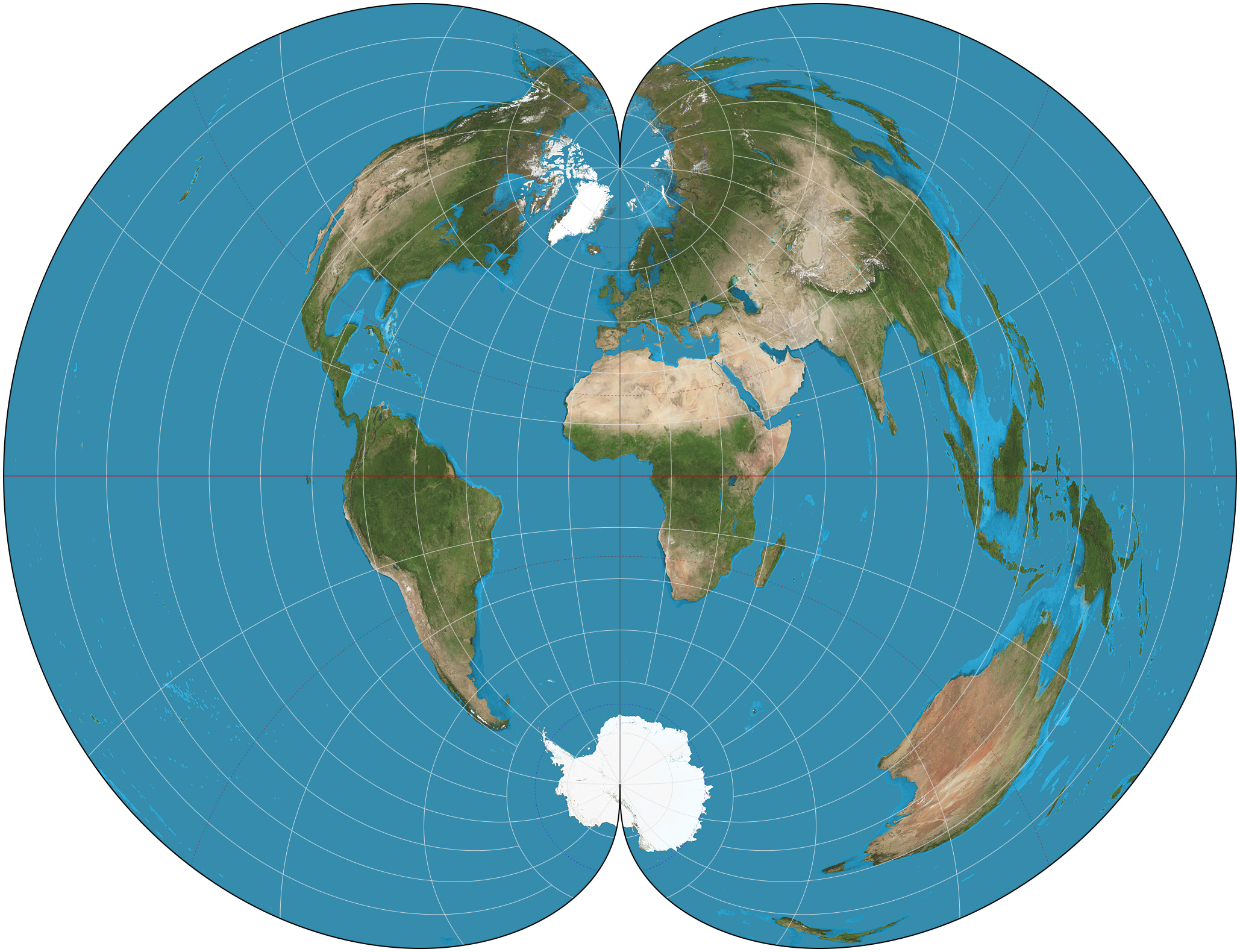
Nicolosi Globular Projections SW
Nicolosi ( scn, Niculùsi) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Catania in the Italian region Sicily, located about southeast of Palermo and about northwest of Catania. Nicolosi borders the following municipalities: Adrano, Belpasso, Biancavilla, Bronte, Castiglione di Sicilia, Maletto, Mascalucia, Pedara, Randazzo, Sant'Alfio, Zafferana Etnea. Twin towns — sister cities Nicolosi is twinned with: * Edremit, Turkey Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ... since 2010 References External links Official websiteUnofficial website Cities and towns in Sicily {{Sicily-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolosi Globular Projection Distortion
Nicolosi ( scn, Niculùsi) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Catania in the Italian region Sicily, located about southeast of Palermo and about northwest of Catania. Nicolosi borders the following municipalities: Adrano, Belpasso, Biancavilla, Bronte, Castiglione di Sicilia, Maletto, Mascalucia, Pedara, Randazzo, Sant'Alfio, Zafferana Etnea. Twin towns — sister cities Nicolosi is twinned with: * Edremit, Turkey Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ... since 2010 References External links Official websiteUnofficial website Cities and towns in Sicily {{Sicily-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyconic Projection Class
Polyconic can refer either to a class of map projections or to a specific projection known less ambiguously as the American polyconic projection. Polyconic as a class refers to those projections whose parallels are all non-concentric circular arcs, except for a straight equator, and the centers of these circles lie along a central axis. This description applies to projections in equatorial aspect. Polyconic projections Some of the projections that fall into the polyconic class are: *American polyconic projection—each parallel becomes a circular arc having true scale, the same scale as the central meridian *Latitudinally equal-differential polyconic projection *Rectangular polyconic projection *Van der Grinten projection—projects entire earth into one circle; all meridians and parallels are arcs of circles. * Nicolosi globular projection—typically used to project a hemisphere into a circle; all meridians and parallels are arcs of circles. A series of polyconic projections, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Projection
In cartography, map projection is the term used to describe a broad set of transformations employed to represent the two-dimensional curved surface of a globe on a plane. In a map projection, coordinates, often expressed as latitude and longitude, of locations from the surface of the globe are transformed to coordinates on a plane. Projection is a necessary step in creating a two-dimensional map and is one of the essential elements of cartography. All projections of a sphere on a plane necessarily distort the surface in some way and to some extent. Depending on the purpose of the map, some distortions are acceptable and others are not; therefore, different map projections exist in order to preserve some properties of the sphere-like body at the expense of other properties. The study of map projections is primarily about the characterization of their distortions. There is no limit to the number of possible map projections. More generally, projections are considered in several fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Biruni
Abu Rayhan Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Biruni (973 – after 1050) commonly known as al-Biruni, was a Khwarazmian Iranian in scholar and polymath during the Islamic Golden Age. He has been called variously the "founder of Indology", "Father of Comparative Religion", "Father of modern geodesy", and the first anthropologist. Al-Biruni was well versed in physics, mathematics, astronomy, and natural sciences, and also distinguished himself as a historian, chronologist, and linguist. He studied almost all the sciences of his day and was rewarded abundantly for his tireless research in many fields of knowledge. Royalty and other powerful elements in society funded Al-Biruni's research and sought him out with specific projects in mind. Influential in his own right, Al-Biruni was himself influenced by the scholars of other nations, such as the Greeks, from whom he took inspiration when he turned to the study of philosophy. A gifted linguist, he was conversant in Khwarezmian, Persian, Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globe
A globe is a spherical model of Earth, of some other celestial body, or of the celestial sphere. Globes serve purposes similar to maps, but unlike maps, they do not distort the surface that they portray except to scale it down. A model globe of Earth is called a terrestrial globe. A model globe of the celestial sphere is called a ''celestial globe''. A globe shows details of its subject. A terrestrial globe shows landmasses and water bodies. It might show nations and major cities and the network of latitude and longitude lines. Some have raised relief to show mountains and other large landforms. A celestial globe shows notable stars, and may also show positions of other prominent astronomical objects. Typically, it will also divide the celestial sphere into constellations. The word ''globe'' comes from the Latin word ''globus'', meaning "sphere". Globes have a long history. The first known mention of a globe is from Strabo, describing the Globe of Crates from about 150&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Age Of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafaring Europeans explored and colonized regions across the globe. The extensive overseas exploration, with the Portuguese and Spanish at the forefront, later joined by the Dutch, English, and French, emerged as a powerful factor in European culture, most notably the European encounter and colonization of the Americas. It also marks an increased adoption of colonialism as a government policy in several European states. As such, it is sometimes synonymous with the first wave of European colonization. European exploration outside the Mediterranean started with the maritime expeditions of Portugal to the Canary Islands in 1336, and later with the Portuguese discoveries of the Atlantic archipelagos of Madeira and Azores, the coast of West Afr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roger Bacon
Roger Bacon (; la, Rogerus or ', also '' Rogerus''; ), also known by the scholastic accolade ''Doctor Mirabilis'', was a medieval English philosopher and Franciscan friar who placed considerable emphasis on the study of nature through empiricism. In the early modern era, he was regarded as a wizard and particularly famed for the story of his mechanical or necromantic brazen head. He is sometimes credited (mainly since the 19th century) as one of the earliest European advocates of the modern scientific method, along with his teacher Robert Grosseteste. Bacon applied the empirical method of Ibn al-Haytham (Alhazen) to observations in texts attributed to Aristotle. Bacon discovered the importance of empirical testing when the results he obtained were different from those that would have been predicted by Aristotle. His linguistic work has been heralded for its early exposition of a universal grammar, and 21st-century re-evaluations emphasise that Bacon was essentially a medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
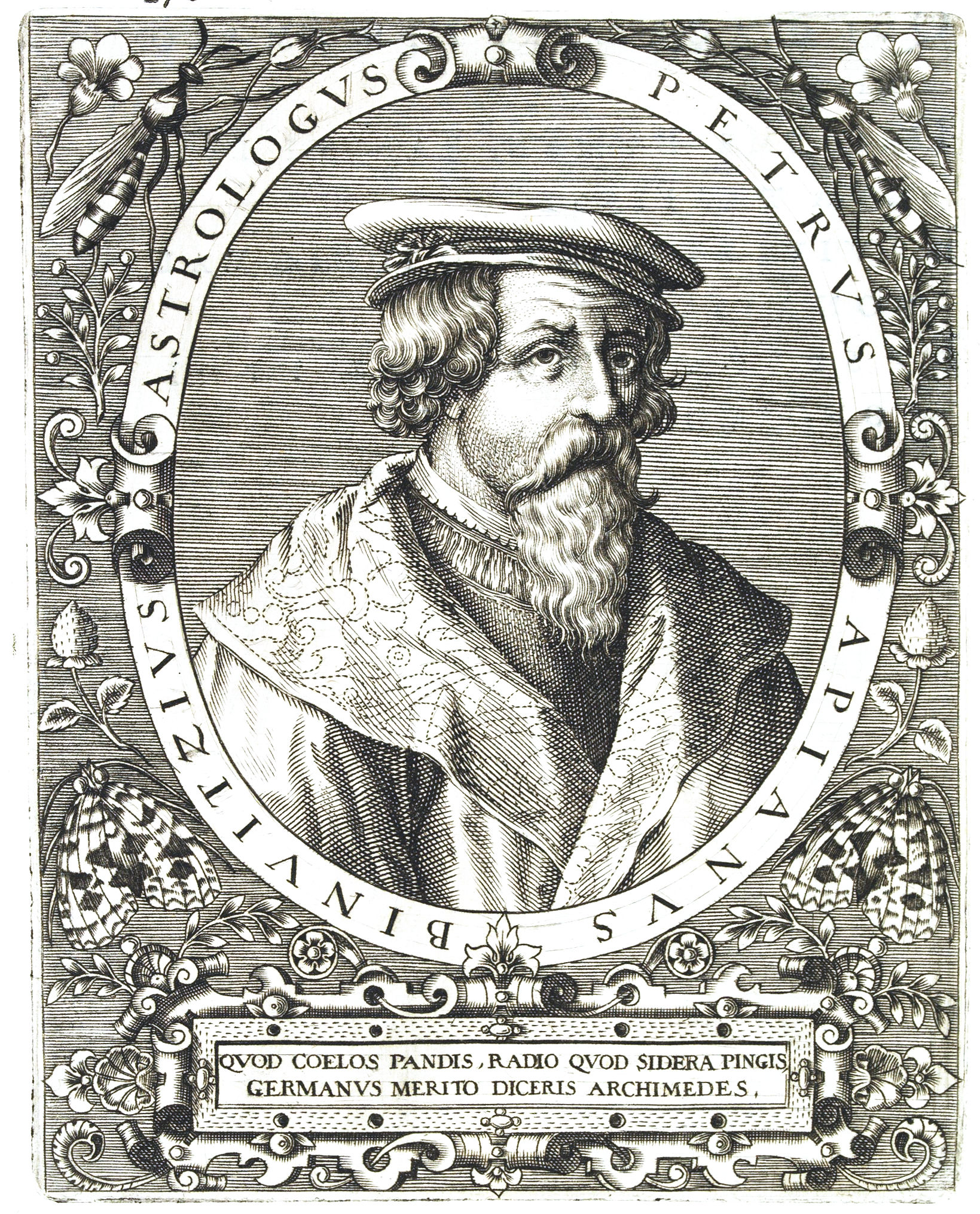
Petrus Apianus
Petrus Apianus (April 16, 1495 – April 21, 1552), also known as Peter Apian, Peter Bennewitz, and Peter Bienewitz, was a German humanist, known for his works in mathematics, astronomy and cartography. His work on "cosmography", the field that dealt with the earth and its position in the universe, was presented in his most famous publications, ''Astronomicum Caesareum'' (1540) and ''Cosmographicus liber'' (1524). His books were extremely influential in his time, with the numerous editions in multiple languages being published until 1609. The lunar crater '' Apianus'' and asteroid 19139 Apian are named in his honour. Life and work Apianus was born as Peter Bienewitz (or Bennewitz) in Leisnig in Saxony; his father, Martin, was a shoemaker. The family was relatively well off, belonging to the middle-class citizenry of Leisnig. Apianus was educated at the Latin school in Rochlitz. From 1516 to 1519 he studied at the University of Leipzig; during this time, he Latinized his na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georges Fournier (Jesuit)
Georges Fournier (31 August 1595 – 13 April 1652) was a French Jesuit priest, geographer and mathematician. Biography Fournier served as a naval military chaplain on a ship of the line, and acquired a strong knowledge of technical and naval matters. In 1642, he published the treaty ''Hydrographie'', where he attempted to provide a scientific foundation to the design of ships. Bertrand Gille, ''Histoire des techniques''. At the time, results like ''Couronne'' or HMS ''Sovereign of the Seas'' were obtained by empirical trials and errors. He also authored a ''Treaty of fortifications or military architecture, drawn from the most estimated places of our times, for fortifications'',Voir bibliographie et traité en ligne sur le site ''Architectura'' du Centre d'étu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovan Battista Nicolosi
Giovan Battista Nicolosi, D.D., was a Sicilian priest and geographer. Nicolosi proposed a new projection for the construction of the world map in two hemispheres, known today as the Nicolosi globular projection, in which the parallels and meridians are arcs of the circle and equidistant along the equator and central meridian. Biography Early life Giovan Battista Nicolosi was born in Paternò, on October 14, 1610, of poor parents. He was the second child in a family of ten siblings. In 1640 Nicolosi moved to Rome, where he devoted himself to the study of mathematics and geography and quickly gained favor with the city's most powerful families. In 1642, he published his ''Teorica del Globo Terrestre'' ("Theory of the Terrestrial Globe"), a small geographical treatise in which he adopts the tripartite division of the subject into mathematical, physical, and political geography, usually credited to Varenius. Although in his unpublished works he showed leanings towards the new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereographic Projection
In mathematics, a stereographic projection is a perspective projection of the sphere, through a specific point on the sphere (the ''pole'' or ''center of projection''), onto a plane (geometry), plane (the ''projection plane'') perpendicular to the diameter through the point. It is a smooth function, smooth, bijection, bijective function (mathematics), function from the entire sphere except the center of projection to the entire plane. It maps circle of a sphere, circles on the sphere to generalised circle, circles or lines on the plane, and is conformal map, conformal, meaning that it preserves angles at which curves meet and thus Local property, locally approximately preserves similarity (geometry), shapes. It is neither isometry, isometric (distance preserving) nor Equiareal map, equiareal (area preserving). The stereographic projection gives a way to representation (mathematics), represent a sphere by a plane. The metric tensor, metric induced metric, induced by the inverse s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)