|
Nick (DNA)
A nick is a discontinuity in a double stranded DNA molecule where there is no phosphodiester bond between adjacent nucleotides of one strand typically through damage or enzyme action. Nicks allow DNA strands to untwist during replication, and are also thought to play a role in the DNA mismatch repair mechanisms that fix errors on both the leading and lagging daughter strands.Williams JS, Kunkel TA. Ribonucleotides in DNA: Origins, repair and consequences. DNA repair. 2014;19:27-37. doi:10.1016/j.dnarep.2014.03.029 Formation of nicks The diagram shows the effects of nicks on intersecting DNA in a twisted plasmid. Nicking can be used to dissipate the energy held up by intersecting states. The nicks allow the DNA to take on a circular shape.Chao Ji, Lingyun Zhang, and Pengye Wang,Configuration Transitions of Free Circular DNA System Induced by Nicks" Journal of Nanomaterials, vol. 2015, Article ID 546851, 7 pages, 2015. doi:10.1155/2015/546851 Nicked DNA can be the result of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphodiester Bond
In chemistry, a phosphodiester bond occurs when exactly two of the hydroxyl groups () in phosphoric acid react with hydroxyl groups on other molecules to form two ester bonds. The "bond" involves this linkage . Discussion of phosphodiesters is dominated by their prevalence in DNA and RNA, but phosphodiesters occur in other biomolecules, e.g. acyl carrier proteins. Phosphodiester bonds make up the backbones of DNA and RNA. The phosphate is attached to the 5' carbon. The 3' carbon of one sugar is bonded to the 5' phosphate of the adjacent sugar. Specifically, the phosphodiester bond links the 3' carbon atom of one sugar molecule and the 5' carbon atom of another (hence the name, 3', 5' phosphodiester linkage). These saccharide groups are derived from deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA. Phosphodiesters are negatively charged at pH 7. Repulsion between these negative charges influences the conformation of the polynucleic acids. The negative charge attracts histones, metal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okazaki Fragments
Okazaki fragments are short sequences of DNA nucleotides (approximately 150 to 200 base pairs long in eukaryotes) which are synthesized discontinuously and later linked together by the enzyme DNA ligase to create the lagging strand during DNA replication. They were discovered in the 1960s by the Japanese molecular biologists Reiji and Tsuneko Okazaki, along with the help of some of their colleagues. During DNA replication, the double helix is unwound and the complementary strands are separated by the enzyme DNA helicase, creating what is known as the DNA replication fork. Following this fork, DNA primase and DNA polymerase begin to act in order to create a new complementary strand. Because these enzymes can only work in the 5’ to 3’ direction, the two unwound template strands are replicated in different ways. One strand, the leading strand, undergoes a continuous replication process since its template strand has 3’ to 5’ directionality, allowing the polymerase assem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Recombination
Genetic recombination (also known as genetic reshuffling) is the exchange of genetic material between different organisms which leads to production of offspring with combinations of traits that differ from those found in either parent. In eukaryotes, genetic recombination during meiosis can lead to a novel set of genetic information that can be further passed on from parents to offspring. Most recombination occurs naturally and can be classified into two types: (1) ''interchromosomal'' recombination, occurring through independent assortment of alleles whose loci are on different but homologous chromosomes (random orientation of pairs of homologous chromosomes in meiosis I); & (2) ''intrachromosomal'' recombination, occurring through crossing over. During meiosis in eukaryotes, genetic recombination involves the pairing of homologous chromosomes. This may be followed by information transfer between the chromosomes. The information transfer may occur without physical exchange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack the energy to ionize atoms, it can cause chemical reactions and causes many substances to glow or fluoresce. Consequently, the chemical and biological effects of UV are greater than simple heating effects, and many practical applications of UV radiation derive from its interactions with organic molecules. Short-wave ultraviolet light damages DNA and sterilizes surfaces with which it comes into contac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type I Topoisomerase
In molecular biology Type I topoisomerases are enzymes that cut one of the two strands of double-stranded DNA, relax the strand, and reanneal the strand. They are further subdivided into two structurally and mechanistically distinct topoisomerases: type IA and type IB. * Type IA topoisomerases change the linking number of a circular DNA strand by units of strictly 1. * Type IB topoisomerases change the linking number by multiples of 1 (n). Historically, type IA topoisomerases are referred to as prokaryotic topo I, while type IB topoisomerases are referred to as eukaryotic topoisomerase. This distinction, however, no longer applies as type IA and type IB topoisomerases exist in all domains of life. Functionally, these subclasses perform very specialized functions. Prokaryotic topoisomerase I (topo IA) can only relax negative supercoiled DNA, whereas eukaryotic topoisomerase I (topo IB) can introduce positive supercoils, separating the DNA of daughter chromosomes after DNA r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritance. This is essential for cell division during growth and repair of damaged tissues, while it also ensures that each of the new cells receives its own copy of the DNA. The cell possesses the distinctive property of division, which makes replication of DNA essential. DNA is made up of a double helix of two complementary strands. The double helix describes the appearance of a double-stranded DNA which is thus composed of two linear strands that run opposite to each other and twist together to form. During replication, these strands are separated. Each strand of the original DNA molecule then serves as a template for the production of its counterpart, a process referred to as semiconservative replication. As a result of semi-conservativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topoisomerase
DNA topoisomerases (or topoisomerases) are enzymes that catalyze changes in the topological state of DNA, interconverting relaxed and supercoiled forms, linked (catenated) and unlinked species, and knotted and unknotted DNA. Topological issues in DNA arise due to the intertwined nature of its double-helical structure, which, for example, can lead to overwinding of the DNA duplex during DNA replication and transcription. If left unchanged, this torsion would eventually stop the DNA or RNA polymerases involved in these processes from continuing along the DNA helix. A second topological challenge results from the linking or tangling of DNA during replication. Left unresolved, links between replicated DNA will impede cell division. The DNA topoisomerases prevent and correct these types of topological problems. They do this by binding to DNA and cutting the sugar-phosphate backbone of either one (type I topoisomerases) or both (type II topoisomerases) of the DNA strands. This transien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from ''in vitro'' experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to ''in vitro'' experiments, '' in vivo'' studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, and whole plants. Definition ''In vitro'' ( la, in glass; often not italicized in English usage) studies are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
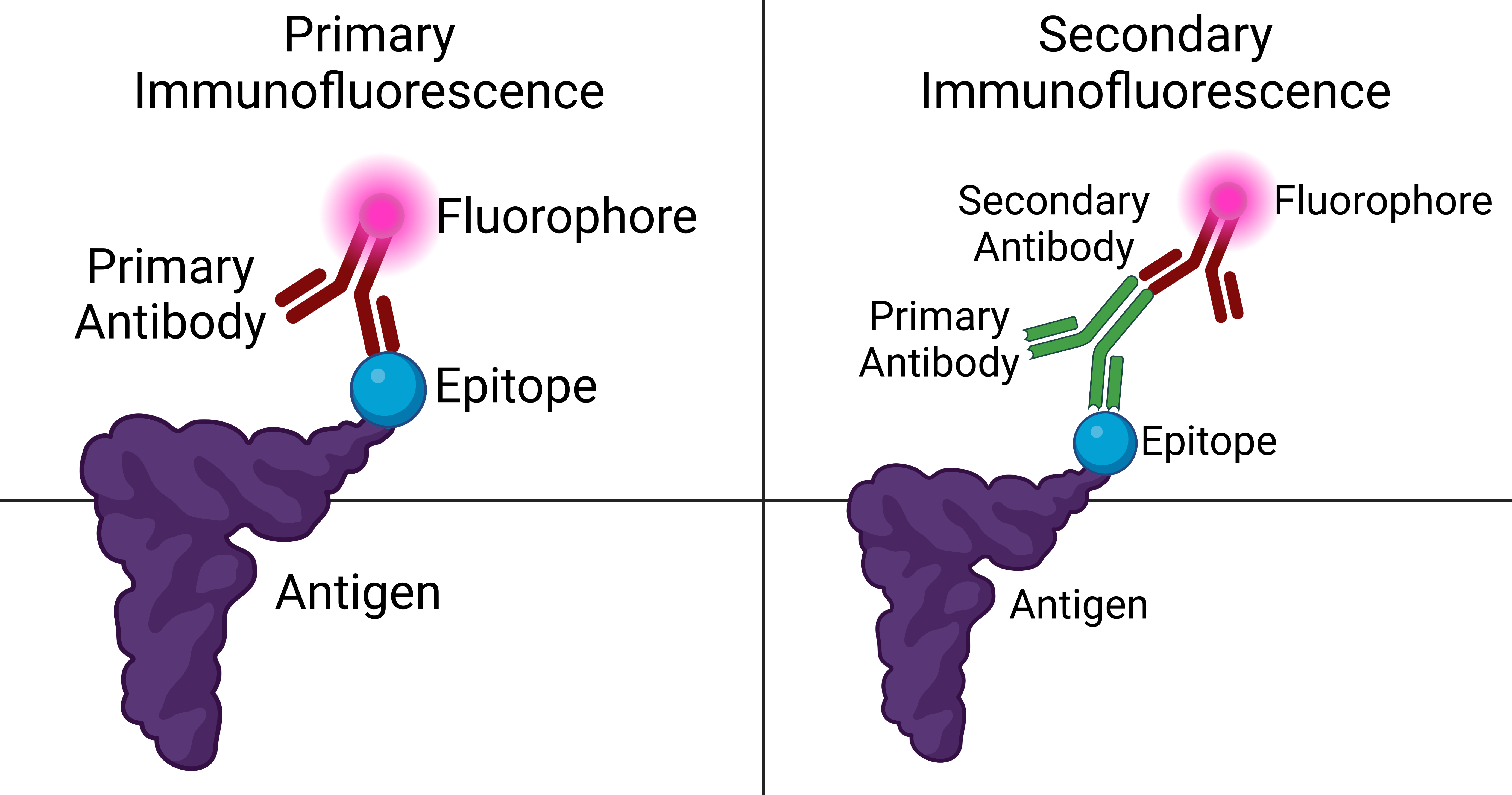
Immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence is a technique used for light microscopy with a fluorescence microscope and is used primarily on microbiological samples. This technique uses the specificity of antibodies to their antigen to target fluorescent dyes to specific biomolecule targets within a cell, and therefore allows visualization of the distribution of the target molecule through the sample. The specific region an antibody recognizes on an antigen is called an epitope. There have been efforts in epitope mapping since many antibodies can bind the same epitope and levels of binding between antibodies that recognize the same epitope can vary. Additionally, the binding of the fluorophore to the antibody itself cannot interfere with the immunological specificity of the antibody or the binding capacity of its antigen. Immunofluorescence is a widely used example of immunostaining (using antibodies to stain proteins) and is a specific example of immunohistochemistry (the use of the antibody-antigen re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Ligase
DNA ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, () that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. It plays a role in repairing single-strand breaks in duplex DNA in living organisms, but some forms (such as DNA ligase IV) may specifically repair double-strand breaks (i.e. a break in both complementary strands of DNA). Single-strand breaks are repaired by DNA ligase using the complementary strand of the double helix as a template, with DNA ligase creating the final phosphodiester bond to fully repair the DNA. DNA ligase is used in both DNA repair and DNA replication (see '' Mammalian ligases''). In addition, DNA ligase has extensive use in molecular biology laboratories for recombinant DNA experiments (see '' Research applications''). Purified DNA ligase is used in gene cloning to join DNA molecules together to form recombinant DNA. Enzymatic mechanism The mechanism of DNA ligase is to form two cova ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Polymerase
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create two identical DNA duplexes from a single original DNA duplex. During this process, DNA polymerase "reads" the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones. These enzymes catalyze the chemical reaction : deoxynucleoside triphosphate + DNAn pyrophosphate + DNAn+1. DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the three prime (3')-end of a DNA strand, one nucleotide at a time. Every time a cell divides, DNA polymerases are required to duplicate the cell's DNA, so that a copy of the original DNA molecule can be passed to each daughter cell. In this way, genetic information is passed down from generation to generation. Before replication can take place, an enzyme called helicase unwinds the DNA molecule from its t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nick Translation
Nick translation (or head translation), developed in 1977 by Peter Rigby and Paul Berg, is a tagging technique in molecular biology in which DNA Polymerase I is used to replace some of the nucleotides of a DNA sequence with their labeled analogues, creating a tagged DNA sequence which can be used as a probe in fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) or blotting techniques. It can also be used for radiolabeling. This process is called nick translation because the DNA to be processed is treated with DNAase to produce single-stranded "nicks". This is followed by replacement in nicked sites by DNA polymerase I, which elongates the 3' hydroxyl terminus, removing nucleotides by 5'-3' exonuclease activity, replacing them with dNTPs. To radioactively label a DNA fragment for use as a probe in blotting procedures, one of the incorporated nucleotides provided in the reaction is radiolabeled in the ''alpha'' phosphate position. Similarly, a fluorophore can be attached instead for fluo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |