|
Nicholas Christofilos
Nicholas Constantine Christofilos ( el, Νικόλαος Χριστοφίλου; December 16, 1916 – September 24, 1972) was a Greek physicist. The Christofilos effect, a type of electromagnetic shielding, is named after him. Career Christofilos was born in Boston, Massachusetts and raised in Greece. He attended the National Technical University of Athens at age 18, and graduated with a degree in Electrical and Mechanical Engineering in 1938. He remained in Greece during World War II, working for an Athens elevator maintenance company during the Nazi occupation. He later founded his own elevator company. During all of this, he maintained an amateur interest in accelerator physics and high-energy particle physics, and studied German and American texts on the subjects extensively. In 1946 he independently developed ideas for a synchrotron and in 1949 he conceived the strong-focusing principle. Rather than publishing in a journal he submitted a patent application in the US an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to the northeast. The Aegean Sea lies to the east of the Geography of Greece, mainland, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Sea of Crete and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Greece has the longest coastline on the Mediterranean Basin, featuring List of islands of Greece, thousands of islands. The country consists of nine Geographic regions of Greece, traditional geographic regions, and has a population of approximately 10.4 million. Athens is the nation's capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city, followed by Thessaloniki and Patras. Greece is considered the cradle of Western culture, Western civilization, being the birthplace of Athenian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) is a federal research facility in Livermore, California, United States. The lab was originally established as the University of California Radiation Laboratory, Livermore Branch in 1952 in response to the detonation of the first atomic bomb by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. It later became autonomous in 1971 and was designated a national laboratory in 1981. A federally funded research and development center, Lawrence Livermore Lab is primarily funded by the U.S. Department of Energy and it is managed privately and operated by Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC (a partnership of the University of California), Bechtel, BWX Technologies, AECOM, and Battelle Memorial Institute in affiliation with the Texas A&M University System. In 2012, the laboratory had the synthetic chemical element livermorium (element 116) named after it. Overview LLNL is self-described as a "premier research and development institution for sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elliott Cresson Medal
The Elliott Cresson Medal, also known as the Elliott Cresson Gold Medal, was the highest award given by the Franklin Institute. The award was established by Elliott Cresson, life member of the Franklin Institute, with $1,000 granted in 1848. The endowed award was to be "for some discovery in the Arts and Sciences, or for the invention or improvement of some useful machine, or for some new process or combination of materials in manufactures, or for ingenuity skill or perfection in workmanship." The medal was first awarded in 1875, 21 years after Cresson's death. The Franklin Institute continued awarding the medal on an occasional basis until 1998 when they reorganized their endowed awards under one umbrella, The Benjamin Franklin Awards. A total of 268 Elliott Cresson Medals were given out during the award's lifetime. See also * List of engineering awards * List of physics awards This list of physics awards is an index to articles about notable awards for physics. The list ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Sanguine
Project Sanguine was a U.S. Navy project, proposed in 1968 for communication with submerged submarines using extremely low frequency (ELF) radio waves. The originally proposed system, hardened to survive a nuclear attack, would have required a giant antenna covering two fifths of the state of Wisconsin. Because of protests and potential environmental impact, the proposed system was never implemented. A smaller, less hardened system called Project ELF consisting of two linked ELF transmitters located at Clam Lake, Wisconsin and Republic, Michigan was built beginning in 1982 and operated from 1989 until 2004. The system transmitted at a frequency of 76 Hz. At ELF frequencies the bandwidth of the transmission is very small, so the system could only send short coded text messages at a very low data rate. These signals were used to summon specific vessels to the surface to receive longer operational orders by ordinary radio or satellite communication. Proposed system The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground Dipole
In radio communication, a ground dipole, also referred to as an earth dipole antenna, transmission line antenna, and in technical literature as a horizontal electric dipole (HED), is a huge, specialized type of radio antenna that radiates extremely low frequency (ELF) electromagnetic waves. It is the only type of transmitting antenna that can radiate practical amounts of power in the frequency range of 3 Hz to 3 kHz, commonly called ELF waves. A ground dipole consists of two ground electrodes buried in the earth, separated by tens to hundreds of kilometers, linked by overhead transmission lines to a power plant transmitter located between them. Alternating current electricity flows in a giant loop between the electrodes through the ground, radiating ELF waves, so the ground is part of the antenna. To be most effective, ground dipoles must be located over certain types of underground rock formations. The idea was proposed by U.S. Dept. of Defense physicist Nicholas Chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
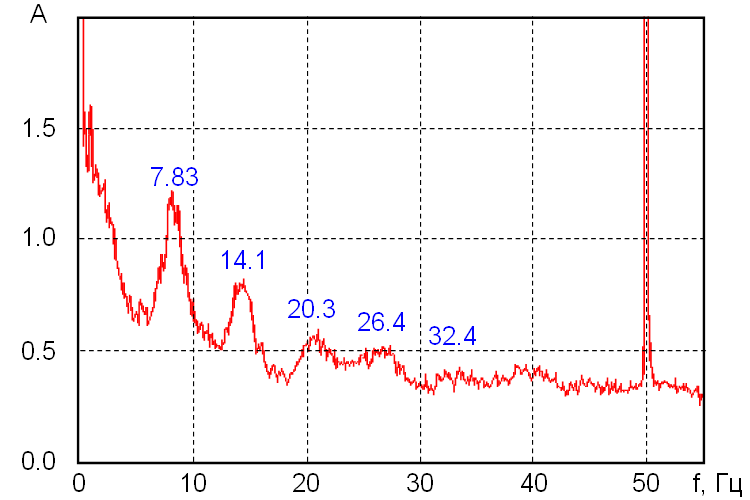
Extremely Low Frequency
Extremely low frequency (ELF) is the ITU designation for electromagnetic radiation ( radio waves) with frequencies from 3 to 30 Hz, and corresponding wavelengths of 100,000 to 10,000 kilometers, respectively. In atmospheric science, an alternative definition is usually given, from 3 Hz to 3 kHz.Liemohn, Michael W. and A. A. CHAN,Unraveling the Causes of Radiation Belt Enhancements". EOS, TRANSACTIONS, AMERICAN GEOPHYSICAL UNION, Volume 88, Number 42, 16 October 2007, pages 427-440. Republished by NASA and accessed online, 8 February 2010. Adobe File, page 2. In the related magnetosphere science, the lower frequency electromagnetic oscillations (pulsations occurring below ~3 Hz) are considered to lie in the ULF range, which is thus also defined differently from the ITU radio bands. ELF radio waves are generated by lightning and natural disturbances in Earth's magnetic field, so they are a subject of research by atmospheric scientists. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICBM
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons can also be delivered with varying effectiveness, but have never been deployed on ICBMs. Most modern designs support multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), allowing a single missile to carry several warheads, each of which can strike a different target. Russia, the United States, China, France, India, the United Kingdom, and North Korea are the only countries known to have operational ICBMs. Early ICBMs had limited precision, which made them suitable for use only against the largest targets, such as cities. They were seen as a "safe" basing option, one that would keep the deterrent force close to home where it would be difficult to attack. Attacks against military targets (especially hardened ones) still demanded th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Artificial Radiation Belts
Artificial radiation belts are radiation belts that have been created by high-altitude nuclear explosions. The table above only lists those high-altitude nuclear explosions for which a reference exists in the open (unclassified) English-language scientific literature to persistent artificial radiation belts resulting from the explosion. The Starfish Prime radiation belt had, by far, the greatest intensity and duration of any of the artificial radiation belts. The Starfish Prime radiation belt damaged the United Kingdom Satellite Ariel 1 and the United States satellites, Traac, Transit 4B, Injun I and Telstar I. It also damaged the Soviet satellite Cosmos V. All of these satellites failed completely within several months of the Starfish detonation. Telstar I lasted the longest of the satellites damaged by the Starfish Prime radiation, with its complete failure occurring on February 21, 1963. In Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory report ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-altitude Nuclear Explosion
High-altitude nuclear explosions are the result of nuclear weapons testing within the upper layers of the Earth's atmosphere and in outer space. Several such tests were performed at high altitudes by the United States and the Soviet Union between 1958 and 1962. The Partial Test Ban Treaty was passed in October 1963, ending atmospheric and exoatmospheric nuclear tests. The Outer Space Treaty of 1967 banned the stationing of nuclear weapons in space, in addition to other weapons of mass destruction. The Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty of 1996 prohibits all nuclear testing; whether over- or underground, underwater or in the atmosphere. EMP generation The strong electromagnetic pulse (EMP) that results has several components. In the first few tenths of nanoseconds, about a tenth of a percent of the weapon yield appears as powerful gamma rays with energies of one to three mega-electron volts (MeV, a unit of energy). The gamma rays penetrate the atmosphere and collide with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
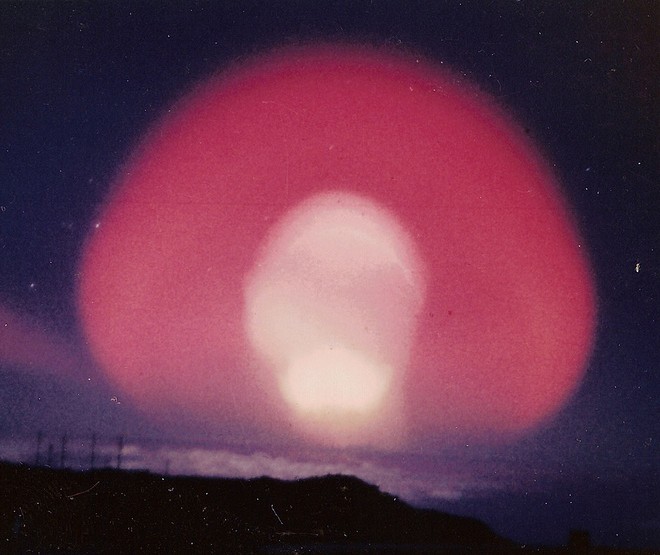
Operation Argus
Operation Argus was a series of United States low-yield, high-altitude nuclear weapons tests and missile tests secretly conducted from 27 August to 9 September 1958 over the South Atlantic Ocean. The tests were performed by the Defense Nuclear Agency. The tests were to study the Christofilos effect, which suggested it was possible to defend against Soviet nuclear missiles by exploding a small number of nuclear bombs high over the South Pacific. This would create a disk of electrons over the United States that would fry the electronics on the Soviet warheads as they descended. It was also possible to use the effect to blind Soviet radars, meaning that any Soviet missile-based ABM system would be unable to attack the US counterstrike. The tests demonstrated that the effect did indeed occur, but also revealed that it dissipated too rapidly to be very effective. Papers on the topic were published the next year, focusing on the events as purely scientific endeavors. Objectives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JASON Defense Advisory Group
JASON is an independent group of elite scientists which advises the United States government on matters of science and technology, mostly of a sensitive nature. The group was created in the aftermath of the Sputnik launch as a way to reinvigorate the idea of having the nation's preeminent scientists help the government with defense problems, similar to the way that scientists helped in World War II but with a new and younger generation. It was established in 1960 and has somewhere between 30 and 60 members. Its work first gained public notoriety as the source of the Vietnam War's McNamara Line electronic barrier. Although most of its research is military-focused, JASON also produced early work on the science of global warming and acid rain. Current unclassified research interests include health informatics, cyberwarfare, and renewable energy. Activities For administrative purposes, JASON's activities are run through the MITRE Corporation, a not-for-profit corporation in McLe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |