ICBM on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a
 The first practical design for an ICBM grew out of Nazi Germany's V-2 rocket program. The liquid-fueled V-2, designed by Wernher von Braun and his team, was widely used by Nazi Germany from mid-1944 until March 1945 to bomb British and Belgian cities, particularly Antwerp and London.
Under ''Projekt Amerika,'' von Braun's team developed the A9/10 ICBM, intended for use in bombing New York and other American cities. Initially intended to be guided by radio, it was changed to be a piloted craft after the failure of Operation Elster. The second stage of the A9/A10 rocket was tested a few times in January and February 1945.
After the war, the US executed Operation Paperclip, which took von Braun and hundreds of other leading German scientists to the United States to develop
The first practical design for an ICBM grew out of Nazi Germany's V-2 rocket program. The liquid-fueled V-2, designed by Wernher von Braun and his team, was widely used by Nazi Germany from mid-1944 until March 1945 to bomb British and Belgian cities, particularly Antwerp and London.
Under ''Projekt Amerika,'' von Braun's team developed the A9/10 ICBM, intended for use in bombing New York and other American cities. Initially intended to be guided by radio, it was changed to be a piloted craft after the failure of Operation Elster. The second stage of the A9/A10 rocket was tested a few times in January and February 1945.
After the war, the US executed Operation Paperclip, which took von Braun and hundreds of other leading German scientists to the United States to develop
 The US initiated ICBM research in 1946 with the RTV-A-2 Hiroc project. This was a three-stage effort with the ICBM development not starting until the third stage. However, funding was cut after only three partially successful launches in 1948 of the second stage design, used to test variations on the V-2 design. With overwhelming air superiority and truly intercontinental bombers, the newly forming US Air Force did not take the problem of ICBM development seriously. Things changed in 1953 with the Soviet testing of their first thermonuclear weapon, but it was not until 1954 that the
The US initiated ICBM research in 1946 with the RTV-A-2 Hiroc project. This was a three-stage effort with the ICBM development not starting until the third stage. However, funding was cut after only three partially successful launches in 1948 of the second stage design, used to test variations on the V-2 design. With overwhelming air superiority and truly intercontinental bombers, the newly forming US Air Force did not take the problem of ICBM development seriously. Things changed in 1953 with the Soviet testing of their first thermonuclear weapon, but it was not until 1954 that the
 In 1991, the United States and the Soviet Union agreed in the
In 1991, the United States and the Soviet Union agreed in the
''
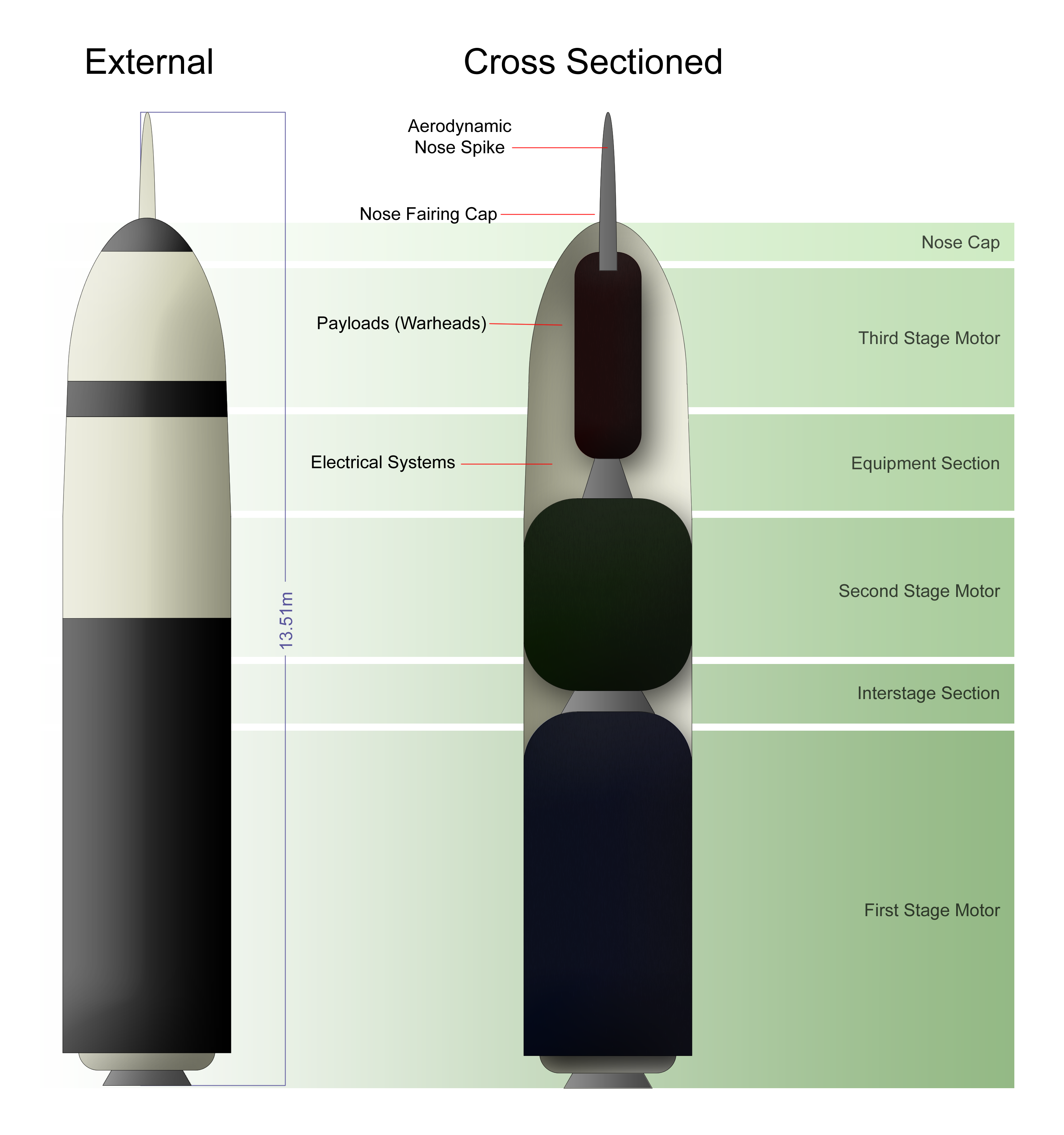 Modern ICBMs typically carry
Modern ICBMs typically carry  After launch, a booster pushes the missile and then falls away. Most modern boosters are solid-fueled rocket motors, which can be stored easily for long periods of time. Early missiles used liquid-fueled rocket motors. Many liquid-fueled ICBMs could not be kept fueled all the time as the cryogenic fuel liquid oxygen boiled off and caused ice formation, and therefore fueling the rocket was necessary before launch. This procedure was a source of significant operational delay, and might allow the missiles to be destroyed by enemy counterparts before they could be used. To resolve this problem the United Kingdom invented the missile silo that protected the missile from a
After launch, a booster pushes the missile and then falls away. Most modern boosters are solid-fueled rocket motors, which can be stored easily for long periods of time. Early missiles used liquid-fueled rocket motors. Many liquid-fueled ICBMs could not be kept fueled all the time as the cryogenic fuel liquid oxygen boiled off and caused ice formation, and therefore fueling the rocket was necessary before launch. This procedure was a source of significant operational delay, and might allow the missiles to be destroyed by enemy counterparts before they could be used. To resolve this problem the United Kingdom invented the missile silo that protected the missile from a
 Russia, the United States, China, North Korea and India are the only countries currently known to possess land-based ICBMs; Israel has also tested ICBMs but is currently not open about actual deployment.
Russia, the United States, China, North Korea and India are the only countries currently known to possess land-based ICBMs; Israel has also tested ICBMs but is currently not open about actual deployment.
 The United States currently operates 405 ICBMs in three USAF bases. The only model deployed is
The United States currently operates 405 ICBMs in three USAF bases. The only model deployed is  The Russian Strategic Rocket Forces have 286 ICBMs able to deliver 958 nuclear warheads: 46 silo-based R-36M2 (SS-18), 30 silo-based UR-100N (SS-19), 36 mobile RT-2PM "Topol" (SS-25), 60 silo-based RT-2UTTH "Topol M" (SS-27), 18 mobile RT-2UTTH "Topol M" (SS-27), 84 mobile RS-24 "Yars" (SS-29), and 12 silo-based RS-24 "Yars" (SS-29).
China has developed several long-range ICBMs, like the DF-31. The Dongfeng 5 or
The Russian Strategic Rocket Forces have 286 ICBMs able to deliver 958 nuclear warheads: 46 silo-based R-36M2 (SS-18), 30 silo-based UR-100N (SS-19), 36 mobile RT-2PM "Topol" (SS-25), 60 silo-based RT-2UTTH "Topol M" (SS-27), 18 mobile RT-2UTTH "Topol M" (SS-27), 84 mobile RS-24 "Yars" (SS-29), and 12 silo-based RS-24 "Yars" (SS-29).
China has developed several long-range ICBMs, like the DF-31. The Dongfeng 5 or  Missile was test-fired for the second time on 15 September 2013. On 31 January 2015, India conducted a third successful test flight of the Agni-V from the Abdul Kalam Island facility. The test used a canisterised version of the missile, mounted over a Tata truck. On 15 December 2022, first night trial of Agni-V was successfully carried out by SFC from Abdul Kalam Island, Odisha. The missile is now 20 percent lighter because the use of composite materials rather than steel material. The range has been increased to 7,000 km.
Missile was test-fired for the second time on 15 September 2013. On 31 January 2015, India conducted a third successful test flight of the Agni-V from the Abdul Kalam Island facility. The test used a canisterised version of the missile, mounted over a Tata truck. On 15 December 2022, first night trial of Agni-V was successfully carried out by SFC from Abdul Kalam Island, Odisha. The missile is now 20 percent lighter because the use of composite materials rather than steel material. The range has been increased to 7,000 km.
"Rockets and people"
– B. E. Chertok, M: "mechanical engineering", 1999. . * "Testing of rocket and space technology – the business of my life" Events and facts – A.I. Ostashev, Korolyov, 2001
Bibliography 1996–2004
* "Nesterenko" series Lives of great people – Authors: Gregory Sukhina A., Ivkin, Vladimir Ivanovich, publishing house "Young guard" in 2015, .
Missile Threat: A Project of the Center for Strategic and International Studies">Missile Threat: A Project of the Center for Strategic and International Studies
{{DEFAULTSORT:Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Ballistic missiles">* Missiles">Ballistic_missiles.html" ;"title="Intercontinental ballistic missiles"> Ballistic missiles">* Missiles Soviet inventions
 An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile
A ballistic missile is a type of missile that uses projectile motion to deliver warheads on a target. These weapons are guided only during relatively brief periods—most of the flight is unpowered. Short-range ballistic missiles stay within ...
with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary in ...
weapons can also be delivered with varying effectiveness, but have never been deployed on ICBMs. Most modern designs support multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle
A multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRV) is an exoatmospheric ballistic missile payload containing several warheads, each capable of being aimed to hit a different target. The concept is almost invariably associated with in ...
s (MIRVs), allowing a single missile to carry several warheads, each of which can strike a different target. Russia, the United States, China, France, India, the United Kingdom, and North Korea are the only countries known to have operational ICBMs.
Early ICBMs had limited precision, which made them suitable for use only against the largest targets, such as cities. They were seen as a "safe" basing option, one that would keep the deterrent force close to home where it would be difficult to attack. Attacks against military targets (especially hardened ones) still demanded the use of a more precise, manned bomber
A bomber is a military combat aircraft designed to attack ground and naval targets by dropping air-to-ground weaponry (such as bombs), launching aerial torpedo, torpedoes, or deploying air-launched cruise missiles. The first use of bombs dropped ...
. Second- and third-generation designs (such as the LGM-118 Peacekeeper) dramatically improved accuracy to the point where even the smallest point targets can be successfully attacked.
ICBMs are differentiated by having greater range and speed than other ballistic missiles: intermediate-range ballistic missile
An intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM) is a ballistic missile with a range of 3,000–5,500 km (1,864–3,418 miles), between a medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) and an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM). Classifying ba ...
s (IRBMs), medium-range ballistic missile
A medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) is a type of ballistic missile with medium range, this last classification depending on the standards of certain organizations. Within the U.S. Department of Defense, a medium-range missile is defined by ...
s (MRBMs), short-range ballistic missiles (SRBMs) and tactical ballistic missiles (TBMs). Short and medium-range ballistic missiles are known collectively as the theatre ballistic missiles.
History
World War II
IRBM
An intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM) is a ballistic missile with a range of 3,000–5,500 km (1,864–3,418 miles), between a medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) and an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM). Classifying b ...
s, ICBMs, and launchers for the US Army.
This technology was predicted by US Army General Hap Arnold, who wrote in 1943:
Cold War
After World War II, the Americans and the Soviets started rocket research programs based on the V-2 and other German wartime designs. Each branch of the US military started its own programs, leading to considerable duplication of effort. In the Soviet Union, rocket research was centrally organized although several teams worked on different designs. In the Soviet Union, early development was focused on missiles able to attack European targets. That changed in 1953, when Sergei Korolyov was directed to start development of a true ICBM able to deliver newly developed hydrogen bombs. Given steady funding throughout, the R-7 developed with some speed. The first launch took place on 15 May 1957 and led to an unintended crash from the site. The first successful test followed on 21 August 1957; the R-7 flew over and became the world's first ICBM. The first strategic-missile unit became operational on 9 February 1959 at Plesetsk in north-west Russia. It was the same R-7 launch vehicle that placed the first artificial satellite in space,Sputnik
Sputnik 1 (; see § Etymology) was the first artificial Earth satellite. It was launched into an elliptical low Earth orbit by the Soviet Union on 4 October 1957 as part of the Soviet space program. It sent a radio signal back to Earth for t ...
, on 4 October 1957. The first human spaceflight
Human spaceflight (also referred to as manned spaceflight or crewed spaceflight) is spaceflight with a crew or passengers aboard a spacecraft, often with the spacecraft being operated directly by the onboard human crew. Spacecraft can also be ...
in history was accomplished on a derivative of R-7, Vostok, on 12 April 1961, by Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin. A heavily modernized version of the R-7 is still used as the launch vehicle for the Soviet/Russian Soyuz spacecraft
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraf ...
, marking more than 60 years of operational history of Sergei Korolyov's original rocket design.
 The US initiated ICBM research in 1946 with the RTV-A-2 Hiroc project. This was a three-stage effort with the ICBM development not starting until the third stage. However, funding was cut after only three partially successful launches in 1948 of the second stage design, used to test variations on the V-2 design. With overwhelming air superiority and truly intercontinental bombers, the newly forming US Air Force did not take the problem of ICBM development seriously. Things changed in 1953 with the Soviet testing of their first thermonuclear weapon, but it was not until 1954 that the
The US initiated ICBM research in 1946 with the RTV-A-2 Hiroc project. This was a three-stage effort with the ICBM development not starting until the third stage. However, funding was cut after only three partially successful launches in 1948 of the second stage design, used to test variations on the V-2 design. With overwhelming air superiority and truly intercontinental bombers, the newly forming US Air Force did not take the problem of ICBM development seriously. Things changed in 1953 with the Soviet testing of their first thermonuclear weapon, but it was not until 1954 that the Atlas missile
The SM-65 Atlas was the first operational intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) developed by the United States and the first member of the Atlas rocket family. It was built for the U.S. Air Force by the Convair Division of General Dyna ...
program was given the highest national priority. The Atlas A first flew on 11 June 1957; the flight lasted only about 24 seconds before the rocket exploded. The first successful flight of an Atlas missile to full range occurred 28 November 1958. The first armed version of the Atlas, the Atlas D, was declared operational in January 1959 at Vandenberg, although it had not yet flown. The first test flight was carried out on 9 July 1959, and the missile was accepted for service on 1 September. The Titan I was another US multistage ICBM, with a successful launch February 5, 1959 with Titan I A3. Unlike the Atlas, the Titan I was a two-stage missile, rather than three. The Titan was larger, yet lighter, than the Atlas. Due to the improvements in engine technology and guidance systems the Titan I overtook the Atlas.
The R-7 and Atlas each required a large launch facility, making them vulnerable to attack, and could not be kept in a ready state. Failure rates were very high throughout the early years of ICBM technology. Human spaceflight programs ( Vostok, Mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
, Voskhod, Gemini, etc.) served as a highly visible means of demonstrating confidence in reliability, with successes translating directly to national defense implications. The US was well behind the Soviets in the Space Race and so US President John F. Kennedy increased the stakes with the Apollo program, which used Saturn rocket technology that had been funded by President Dwight D. Eisenhower.
These early ICBMs also formed the basis of many space launch systems. Examples include R-7, Atlas, Redstone, Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
, and Proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron mass ...
, which was derived from the earlier ICBMs but never deployed as an ICBM. The Eisenhower administration supported the development of solid-fueled missiles such as the LGM-30 Minuteman, Polaris
Polaris is a star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Minor. It is designated α Ursae Minoris ( Latinized to ''Alpha Ursae Minoris'') and is commonly called the North Star or Pole Star. With an apparent magnitude that ...
and Skybolt. Modern ICBMs tend to be smaller than their ancestors, due to increased accuracy and smaller and lighter warheads, and use solid fuels, making them less useful as orbital launch vehicles.
The Western view of the deployment of these systems was governed by the strategic theory of mutual assured destruction. In the 1950s and 1960s, development began on anti-ballistic missile
An anti-ballistic missile (ABM) is a surface-to-air missile designed to counter ballistic missiles (missile defense). Ballistic missiles are used to deliver nuclear, chemical, biological, or conventional warheads in a ballistic flight traj ...
systems by both the Americans and Soviets. Such systems were restricted by the 1972 Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty. The first successful ABM test was conducted by the Soviets in 1961, which later deployed a fully operational system defending Moscow in the 1970s (see Moscow ABM system).
The 1972 SALT treaty froze the number of ICBM launchers of both the Americans and the Soviets at existing levels and allowed new submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
-based SLBM launchers only if an equal number of land-based ICBM launchers were dismantled. Subsequent talks, called SALT II, were held from 1972 to 1979 and actually reduced the number of nuclear warheads held by the US and Soviets. SALT II was never ratified by the US Senate, but its terms were honored by both sides until 1986, when the Reagan administration "withdrew" after it had accused the Soviets of violating the pact.
In the 1980s, President Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
launched the Strategic Defense Initiative
The Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI), derisively nicknamed the "''Star Wars'' program", was a proposed missile defense system intended to protect the United States from attack by ballistic strategic nuclear weapons (intercontinental ballistic ...
as well as the MX and Midgetman ICBM programs.
China developed a minimal independent nuclear deterrent entering its own cold war after an ideological split with the Soviet Union beginning in the early 1960s. After first testing a domestic built nuclear weapon in 1964, it went on to develop various warheads and missiles. Beginning in the early 1970s, the liquid fuelled DF-5
The Dongfeng 5 () or DF-5 is a second-generation two stage Chinese intercontinental ballistic missile. It has a length of 32.6 m and a diameter of 3.35 m. It weighs in at 183,000 kilograms and it has an estimated range of 12,000 to 15,000 kilome ...
ICBM was developed and used as a satellite launch vehicle in 1975. The DF-5, with a range of —long enough to strike the Western United States and the Soviet Union—was silo deployed, with the first pair in service by 1981 and possibly twenty missiles in service by the late 1990s. China also deployed the JL-1
The Julang-1 (, also known as the JL-1; NATO reporting name CSS-N-3) was China's first generation nuclear submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM). According to a US Department of Defense report in 2011, the operational status of the JL-1 was ...
Medium-range ballistic missile
A medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) is a type of ballistic missile with medium range, this last classification depending on the standards of certain organizations. Within the U.S. Department of Defense, a medium-range missile is defined by ...
with a reach of aboard the ultimately unsuccessful type 92 submarine.
Post-Cold War
 In 1991, the United States and the Soviet Union agreed in the
In 1991, the United States and the Soviet Union agreed in the START I
START I (Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty) was a bilateral treaty between the United States and the Soviet Union on the reduction and the limitation of strategic offensive arms. The treaty was signed on 31 July 1991 and entered into force on 5 De ...
treaty to reduce their deployed ICBMs and attributed warheads.
, all five of the nations with permanent seats on the United Nations Security Council have operational long-range ballistic missile systems; Russia, the United States, and China also have land-based ICBMs (the US missiles are silo-based, while China and Russia have both silo and road-mobile ( DF-31, RT-2PM2 Topol-M missiles).
Israel is believed to have deployed a road mobile nuclear ICBM, the Jericho III, which entered service in 2008; an upgraded version is in development.
India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
successfully test fired Agni V, with a strike range of more than on 19 April 2012, claiming entry into the ICBM club. The missile's actual range is speculated by foreign researchers to be up to with India having downplayed its capabilities to avoid causing concern to other countries. On 15 December 2022, first night trial of Agni-V was successfully carried out by SFC from Abdul Kalam Island, Odisha. The missile is now 20 percent lighter because the use of composite materials rather than steel material. The range has been increased to 7,000 km.
By 2012 there was speculation by some intelligence agencies that North Korea is developing an ICBM. North Korea successfully put a satellite into space on 12 December 2012 using the Unha-3 rocket. The United States claimed that the launch was in fact a way to test an ICBM. (See Timeline of first orbital launches by country.) In early July 2017, North Korea claimed for the first time to have tested successfully an ICBM capable of carrying a large thermonuclear warhead.
In July 2014, China announced the development of its newest generation of ICBM, the Dongfeng-41 ( DF-41), which has a range of 12,000 kilometres (7,500 miles), capable of reaching the United States, and which analysts believe is capable of being outfitted with MIRV technology.
Most countries in the early stages of developing ICBMs have used liquid propellants, with the known exceptions being the India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
n Agni-V, the planned but cancelled South African RSA-4 ICBM, and the now in service Israeli Jericho III.
The RS-28 SarmatНовую тяжелую ракету "Сармат" будут делать в Красноярске''
Rossiyskaya Gazeta
' (russian: Российская газета, lit. Russian Gazette) is a Russian newspaper published by the Government of Russia. The daily newspaper serves as the official government gazette of the Government of the Russian Federation, publishi ...
'', 2 February 2015. (Russian: РС-28 Сармат; NATO reporting name
NATO reporting names are code names for military equipment from Russia, China, and historically, the Eastern Bloc (Soviet Union and other nations of the Warsaw Pact). They provide unambiguous and easily understood English words in a uniform manne ...
: SATAN 2), is a Russian liquid-fueled, MIRV-equipped, super-heavy thermonuclear armed intercontinental ballistic missile in development by the Makeyev Rocket Design Bureau
The JSC Makeyev Design Bureau (russian: ГРЦ Макеева; also known as Makeyev OKB) is a Russian missile design company located in Miass, Russia.
Established in December 1947 as SKB-385 in Zlatoust (see Zlatoust Machine-Building Plant), th ...
from 2009, intended to replace the previous R-36 missile. Its large payload would allow for up to 10 heavy warheads or 15 lighter ones or up to 24 hypersonic glide vehicles Yu-74, or a combination of warheads and massive amounts of countermeasures designed to defeat anti-missile systems; it was announced by the Russian military as a response to the US Prompt Global Strike.
Flight phases
The following flight phases can be distinguished: * boost phase: 3 to 5 minutes; it is shorter for asolid-fuel rocket
A solid-propellant rocket or solid rocket is a rocket with a rocket engine that uses solid propellants ( fuel/oxidizer). The earliest rockets were solid-fuel rockets powered by gunpowder; they were used in warfare by the Arabs, Chinese, Persian ...
than for a liquid-propellant rocket
A liquid-propellant rocket or liquid rocket utilizes a rocket engine that uses liquid rocket propellant, liquid propellants. Liquids are desirable because they have a reasonably high density and high Specific impulse, specific impulse (''I''sp). T ...
; depending on the trajectory chosen, typical burnout speed is , up to ; altitude at the end of this phase is typically .
* midcourse phase: approx. 25 minutes – sub-orbital spaceflight with a flightpath being a part of an ellipse
In mathematics, an ellipse is a plane curve surrounding two focal points, such that for all points on the curve, the sum of the two distances to the focal points is a constant. It generalizes a circle, which is the special type of ellipse i ...
with a vertical major axis; the apogee
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion.
General description
There are two apsides in any el ...
(halfway through the midcourse phase) is at an altitude of approximately ; the semi-major axis
In geometry, the major axis of an ellipse is its longest diameter: a line segment that runs through the center and both foci, with ends at the two most widely separated points of the perimeter. The semi-major axis (major semiaxis) is the long ...
is between ; the projection of the flightpath on the Earth's surface is close to a great circle
In mathematics, a great circle or orthodrome is the circular intersection of a sphere and a plane passing through the sphere's center point.
Any arc of a great circle is a geodesic of the sphere, so that great circles in spherical geomet ...
, slightly displaced due to earth rotation during the time of flight; the missile may release several independent warheads and penetration aids, such as metallic-coated balloons, aluminum chaff
Chaff (; ) is the dry, scaly protective casing of the seeds of cereal grains or similar fine, dry, scaly plant material (such as scaly parts of flowers or finely chopped straw). Chaff is indigestible by humans, but livestock can eat it. In a ...
, and full-scale warhead decoys.
* reentry/terminal phase (starting at an altitude of ): 2 minutes – impact is at a speed of up to (for early ICBMs less than ); see also maneuverable reentry vehicle.
ICBMs usually use the trajectory which optimizes range for a given amount of payload (the ''minimum-energy trajectory''); an alternative is a depressed trajectory
A ballistic missile is a type of missile that uses projectile motion to deliver warheads on a target. These weapons are guided only during relatively brief periods—most of the flight is unpowered. Short-range ballistic missiles stay within the ...
, which allows less payload, shorter flight time, and has a much lower apogee.
Modern ICBMs
 Modern ICBMs typically carry
Modern ICBMs typically carry multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle
A multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRV) is an exoatmospheric ballistic missile payload containing several warheads, each capable of being aimed to hit a different target. The concept is almost invariably associated with in ...
s (''MIRVs''), each of which carries a separate nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
* Nuclear ...
warhead, allowing a single missile to hit multiple targets. MIRV was an outgrowth of the rapidly shrinking size and weight of modern warheads and the Strategic Arms Limitation Treaties ( SALT I and SALT II), which imposed limitations on the number of launch vehicles. It has also proved to be an "easy answer" to proposed deployments of anti-ballistic missile
An anti-ballistic missile (ABM) is a surface-to-air missile designed to counter ballistic missiles (missile defense). Ballistic missiles are used to deliver nuclear, chemical, biological, or conventional warheads in a ballistic flight traj ...
(ABM) systems: It is far less expensive to add more warheads to an existing missile system than to build an ABM system capable of shooting down the additional warheads; hence, most ABM system proposals have been judged to be impractical. The first operational ABM systems were deployed in the United States during the 1970s. The Safeguard ABM facility, located in North Dakota, was operational from 1975 to 1976. The Soviets deployed their ABM-1 Galosh system around Moscow in the 1970s, which remains in service. Israel deployed a national ABM system based on the Arrow missile in 1998, but it is mainly designed to intercept shorter-ranged theater ballistic missiles, not ICBMs. The Alaska-based United States national missile defense system attained initial operational capability in 2004.
ICBMs can be deployed from multiple platforms:
* in missile silos, which offer some protection from military attack (including, the designers hope, some protection from a nuclear first strike First strike most commonly refers to:
* Pre-emptive nuclear strike
* Pre-emptive war
First strike may also refer to:
* ''First Strike'' (1996 film), also known as ''Jackie Chan's First Strike'' or ''Police Story 4: First Strike'', an action movie ...
)
* on submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
s: submarine-launched ballistic missile
A submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) is a ballistic missile capable of being launched from submarines. Modern variants usually deliver multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), each of which carries a nuclear warhead ...
s (SLBMs); most or all SLBMs have the long range of ICBMs (as opposed to IRBMs)
* on heavy trucks; this applies to one version of the Topol which may be deployed from a self-propelled mobile launcher
In the military, vehicles such as trucks or tractor units can be used to transport or launch missiles (rockets with warheads), essentially a form of rocket artillery.
History
The missile vehicle may be a self-propelled unit or the missile hold ...
, capable of moving through roadless terrain, and launching a missile from any point along its route
* mobile launchers on rails; this applies, for example, to РТ-23УТТХ "Молодец" ( RT-23UTTH "Molodets" – SS-24 "Scalpel")
The last three kinds are mobile and therefore hard to find.
During storage, one of the most important features of the missile is its serviceability. One of the key features of the first computer-controlled ICBM, the Minuteman missile, was that it could quickly and easily use its computer to test itself.
 After launch, a booster pushes the missile and then falls away. Most modern boosters are solid-fueled rocket motors, which can be stored easily for long periods of time. Early missiles used liquid-fueled rocket motors. Many liquid-fueled ICBMs could not be kept fueled all the time as the cryogenic fuel liquid oxygen boiled off and caused ice formation, and therefore fueling the rocket was necessary before launch. This procedure was a source of significant operational delay, and might allow the missiles to be destroyed by enemy counterparts before they could be used. To resolve this problem the United Kingdom invented the missile silo that protected the missile from a
After launch, a booster pushes the missile and then falls away. Most modern boosters are solid-fueled rocket motors, which can be stored easily for long periods of time. Early missiles used liquid-fueled rocket motors. Many liquid-fueled ICBMs could not be kept fueled all the time as the cryogenic fuel liquid oxygen boiled off and caused ice formation, and therefore fueling the rocket was necessary before launch. This procedure was a source of significant operational delay, and might allow the missiles to be destroyed by enemy counterparts before they could be used. To resolve this problem the United Kingdom invented the missile silo that protected the missile from a first strike First strike most commonly refers to:
* Pre-emptive nuclear strike
* Pre-emptive war
First strike may also refer to:
* ''First Strike'' (1996 film), also known as ''Jackie Chan's First Strike'' or ''Police Story 4: First Strike'', an action movie ...
and also hid fuelling operations underground.
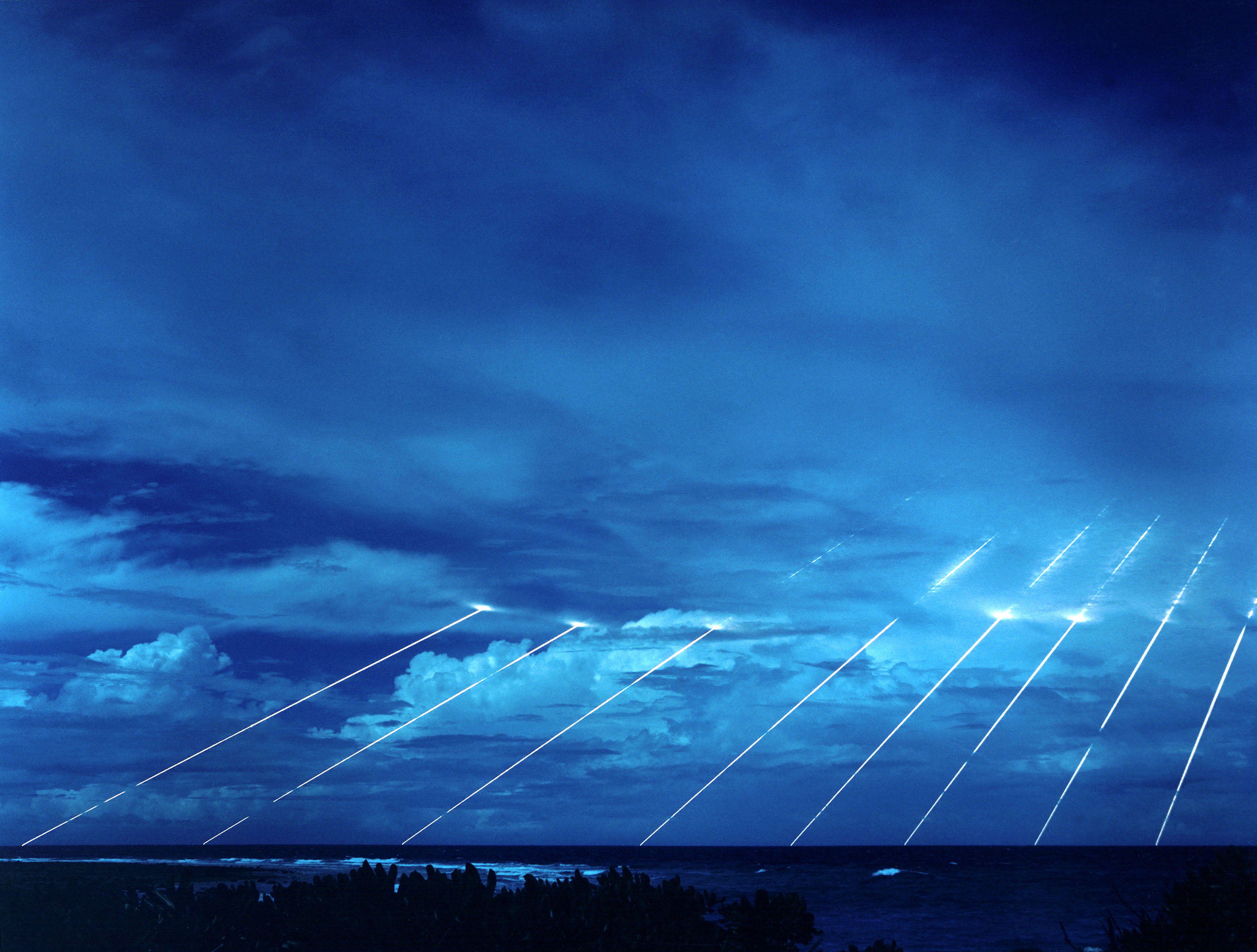
Once the booster falls away, the remaining "bus" releases several warheads, each of which continues on its own unpowered ballistic trajectory, much like an artillery shell or cannonball. The warhead is encased in a cone-shaped reentry vehicle and is difficult to detect in this phase of flight as there is no rocket exhaust or other emissions to mark its position to defenders. The high speeds of the warheads make them difficult to intercept and allow for little warning, striking targets many thousands of kilometers away from the launch site (and due to the possible locations of the submarines: anywhere in the world) within approximately 30 minutes.
Many authorities say that missiles also release aluminized balloons, electronic noise-makers, and other items intended to confuse interception devices and radars.
As the nuclear warhead reenters the Earth's atmosphere its high speed causes compression of the air, leading to a dramatic rise in temperature which would destroy it if it were not shielded in some way. As a result, warhead components are contained within an aluminium honeycomb substructure, sheathed in a pyrolytic carbon-epoxy
Epoxy is the family of basic components or cured end products of epoxy resins. Epoxy resins, also known as polyepoxides, are a class of reactive prepolymers and polymers which contain epoxide groups. The epoxide functional group is also coll ...
synthetic resin composite material heat shield. Warheads are also often radiation-hardened (to protect against nuclear armed ABMs or the nearby detonation of friendly warheads), one neutron-resistant material developed for this purpose in the UK is three-dimensional quartz phenolic
Three-dimensional quartz phenolic (3DQP) is a phenolic-based material composed of a quartz cloth material impregnated with a phenolic resin and hot-pressed. When cured, 3DQP can be machined in the same way as metals and is tough and fire-resistant. ...
.
Circular error probable
In the military science of ballistics, circular error probable (CEP) (also circular error probability or circle of equal probability) is a measure of a weapon system's precision. It is defined as the radius of a circle, centered on the mean, wh ...
is crucial, because halving the circular error probable decreases the needed warhead energy by a factor of four. Accuracy is limited by the accuracy of the navigation system and the available geodetic information.
Strategic missile systems are thought to use custom integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
s designed to calculate navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navigation, ...
al differential equations thousands to millions of FLOPS
In computing, floating point operations per second (FLOPS, flops or flop/s) is a measure of computer performance, useful in fields of scientific computations that require floating-point calculations. For such cases, it is a more accurate meas ...
in order to reduce navigational errors caused by calculation alone. These circuits are usually a network of binary addition circuits that continually recalculate the missile's position. The inputs to the navigation circuit are set by a general-purpose computer according to a navigational input schedule loaded into the missile before launch.
One particular weapon developed by the Soviet Unionthe Fractional Orbital Bombardment Systemhad a partial orbital trajectory, and unlike most ICBMs its target could not be deduced from its orbital flight path. It was decommissioned in compliance with arms control agreements, which address the maximum range of ICBMs and prohibit orbital or fractional-orbital weapons. However, according to reports, Russia is working on the new Sarmat ICBM which leverages Fractional Orbital Bombardment concepts to use a Southern polar approach instead of flying over the northern polar regions. Using that approach, it is theorized, avoids the American missile defense batteries in California and Alaska.
New development of ICBM technology are ICBMs able to carry hypersonic glide vehicles as a payload
Payload is the object or the entity which is being carried by an aircraft or launch vehicle. Sometimes payload also refers to the carrying capacity of an aircraft or launch vehicle, usually measured in terms of weight. Depending on the nature of ...
such as RS-28 Sarmat.
Specific ICBMs
Land-based ICBMs

 Russia, the United States, China, North Korea and India are the only countries currently known to possess land-based ICBMs; Israel has also tested ICBMs but is currently not open about actual deployment.
Russia, the United States, China, North Korea and India are the only countries currently known to possess land-based ICBMs; Israel has also tested ICBMs but is currently not open about actual deployment.
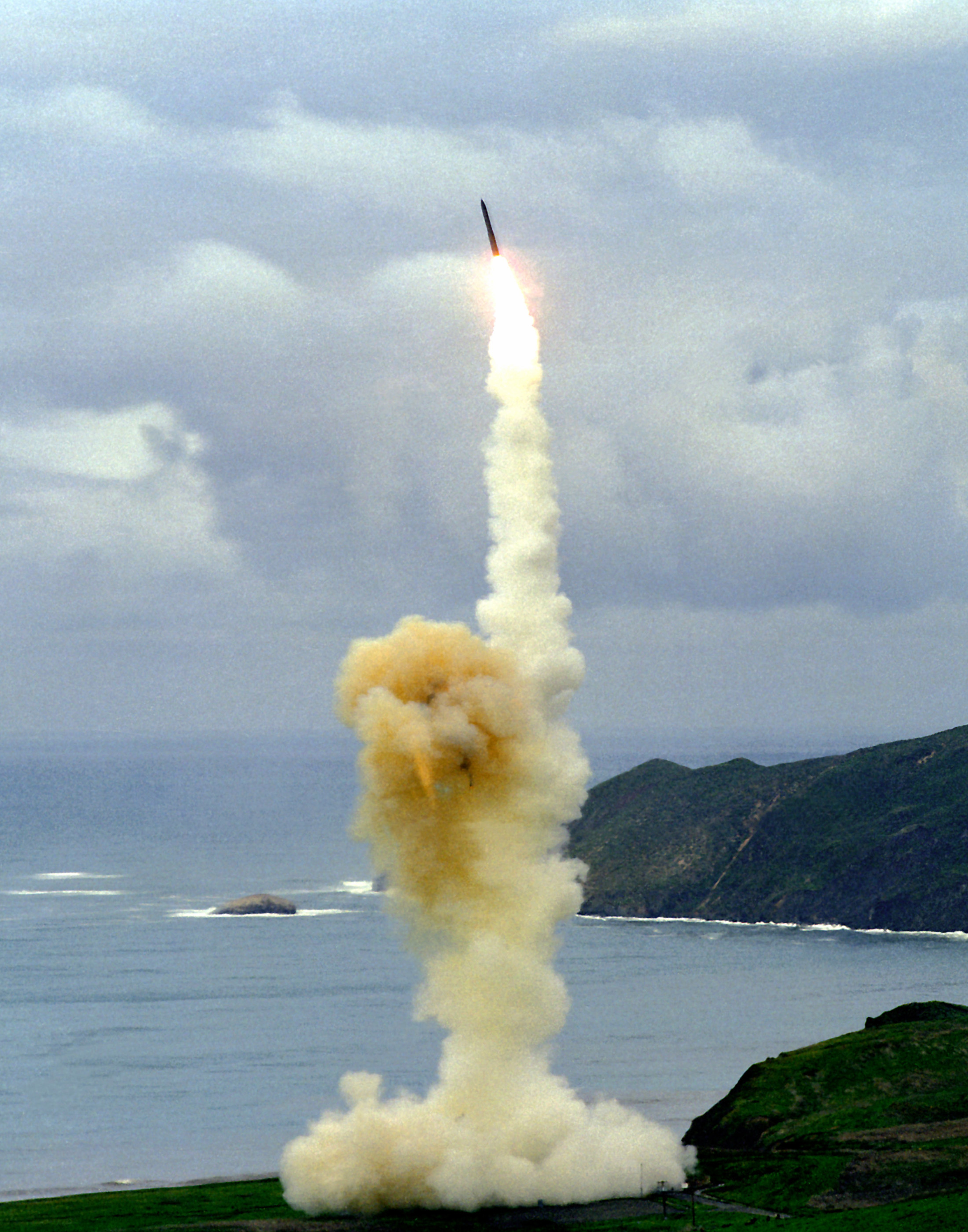
 The United States currently operates 405 ICBMs in three USAF bases. The only model deployed is
The United States currently operates 405 ICBMs in three USAF bases. The only model deployed is LGM-30G Minuteman-III
The LGM-30 Minuteman is an American land-based intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) in service with the Air Force Global Strike Command. , the LGM-30G Minuteman III version is the only land-based ICBM in service in the United States and re ...
. All previous USAF Minuteman II missiles were destroyed in accordance with START II
START II (Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty) was a bilateral treaty between the United States and Russia on the Reduction and Limitation of Strategic Offensive Arms. It was signed by US President George H. W. Bush and Russian President Boris Yelts ...
, and their launch silos have been sealed or sold to the public. The powerful MIRV-capable Peacekeeper missiles were phased out in 2005.
 The Russian Strategic Rocket Forces have 286 ICBMs able to deliver 958 nuclear warheads: 46 silo-based R-36M2 (SS-18), 30 silo-based UR-100N (SS-19), 36 mobile RT-2PM "Topol" (SS-25), 60 silo-based RT-2UTTH "Topol M" (SS-27), 18 mobile RT-2UTTH "Topol M" (SS-27), 84 mobile RS-24 "Yars" (SS-29), and 12 silo-based RS-24 "Yars" (SS-29).
China has developed several long-range ICBMs, like the DF-31. The Dongfeng 5 or
The Russian Strategic Rocket Forces have 286 ICBMs able to deliver 958 nuclear warheads: 46 silo-based R-36M2 (SS-18), 30 silo-based UR-100N (SS-19), 36 mobile RT-2PM "Topol" (SS-25), 60 silo-based RT-2UTTH "Topol M" (SS-27), 18 mobile RT-2UTTH "Topol M" (SS-27), 84 mobile RS-24 "Yars" (SS-29), and 12 silo-based RS-24 "Yars" (SS-29).
China has developed several long-range ICBMs, like the DF-31. The Dongfeng 5 or DF-5
The Dongfeng 5 () or DF-5 is a second-generation two stage Chinese intercontinental ballistic missile. It has a length of 32.6 m and a diameter of 3.35 m. It weighs in at 183,000 kilograms and it has an estimated range of 12,000 to 15,000 kilome ...
is a 3-stage liquid fuel ICBM and has an estimated range of 13,000 kilometers. The DF-5 had its first flight in 1971 and was in operational service 10 years later. One of the downsides of the missile was that it took between 30 and 60 minutes to fuel. The Dong Feng 31 (a.k.a. CSS-10) is a medium-range, three-stage, solid-propellant intercontinental ballistic missile, and is a land-based variant of the submarine-launched JL-2.
The DF-41 or CSS-X-10 can carry up to 10 nuclear warheads, which are MIRVs and has a range of approximately . The DF-41 deployed underground in Xinjiang, Qinghai, Gansu and Inner Mongolia. The mysterious underground subway ICBM carrier systems are called the " Underground Great Wall Project".
Israel is believed to have deployed a road mobile nuclear ICBM, the Jericho III, which entered service in 2008. It is possible for the missile to be equipped with a single nuclear warhead or up to three MIRV warheads. It is believed to be based on the Shavit space launch vehicle and is estimated to have a range of . In November 2011 Israel tested an ICBM believed to be an upgraded version of the Jericho III.
India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
has a series of ballistic missiles called Agni. On 19 April 2012, India successfully test fired its first Agni-V, a three-stage solid fueled missile, with a strike range of more than .  Missile was test-fired for the second time on 15 September 2013. On 31 January 2015, India conducted a third successful test flight of the Agni-V from the Abdul Kalam Island facility. The test used a canisterised version of the missile, mounted over a Tata truck. On 15 December 2022, first night trial of Agni-V was successfully carried out by SFC from Abdul Kalam Island, Odisha. The missile is now 20 percent lighter because the use of composite materials rather than steel material. The range has been increased to 7,000 km.
Missile was test-fired for the second time on 15 September 2013. On 31 January 2015, India conducted a third successful test flight of the Agni-V from the Abdul Kalam Island facility. The test used a canisterised version of the missile, mounted over a Tata truck. On 15 December 2022, first night trial of Agni-V was successfully carried out by SFC from Abdul Kalam Island, Odisha. The missile is now 20 percent lighter because the use of composite materials rather than steel material. The range has been increased to 7,000 km.
Submarine-launched ICBMs
Missile defense
An anti-ballistic missile is a missile which can be deployed to counter an incoming nuclear or non-nuclear ICBM. ICBMs can be intercepted in three regions of their trajectory: boost phase, mid-course phase or terminal phase. The United States, Russia, India, France, Israel, and China have now developed anti-ballistic missile systems, of which the Russian A-135 anti-ballistic missile system, the American Ground-Based Midcourse Defense and the Indian Prithvi Defence Vehicle Mark-II are the only systems having the capability to intercept and shoot down ICBMs carryingnuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
* Nuclear ...
, chemical, biological
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary in ...
, or conventional warheads.
See also
*Bernard Schriever
Bernard Adolph Schriever (14 September 1910 – 20 June 2005), also known as Bennie Schriever, was a United States Air Force general who played a major role in the Air Force's space and ballistic missile programs.
Born in Bremen, Germany, Sch ...
* DEFCON
* Dense Pack
* Emergency Action Message
In the United States military's strategic nuclear weapon nuclear command and control (NC2) system, an Emergency Action Message (EAM) is a preformatted message that directs nuclear-capable forces to execute specific Major Attack Options (MAOs) o ...
* High-alert nuclear weapon A high-alert nuclear weapon commonly refers to a launch-ready ballistic missile that is armed with a nuclear warhead whose launch can be ordered (through the National Command Authority (United States), National Command Authority) and executed (via a ...
* ICBM address
ICBM (intercontinental ballistic missile) address or missile address is hacker slang for one's longitude and latitude (preferably to seconds-of-arc accuracy) when placed in a signature or another publicly available file.
Origin
The form that u ...
* List of states with nuclear weapons
* Nuclear disarmament
* Nuclear navy
* Nuclear warfare
* Submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
* Throw-weight
* Universal Rocket
References
Further reading
* J. K. Golovanov, M., "Korolev: Facts and myths", Nauka, 1994, ."Rockets and people"
– B. E. Chertok, M: "mechanical engineering", 1999. . * "Testing of rocket and space technology – the business of my life" Events and facts – A.I. Ostashev, Korolyov, 2001
Bibliography 1996–2004
* "Nesterenko" series Lives of great people – Authors: Gregory Sukhina A., Ivkin, Vladimir Ivanovich, publishing house "Young guard" in 2015, .
External links
Missile Threat: A Project of the Center for Strategic and International Studies">Missile Threat: A Project of the Center for Strategic and International Studies
{{DEFAULTSORT:Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Ballistic missiles">* Missiles">Ballistic_missiles.html" ;"title="Intercontinental ballistic missiles"> Ballistic missiles">* Missiles Soviet inventions