|
Nichirō
Nichirō (日朗, 1245–1320) was a Buddhist disciple of Nichiren, the nephew of Nisshō. Nichirō agreed with Nisshō's defense of Nichiren as a Tendai reformer. He founded a practice hall that became part of Ikegami Honmon-ji, the site of Nichiren's death. His school is now part of Nichiren-shū is a combination of several schools ranging from four of the original Nichiren Buddhist schools that date back to Nichiren's original disciples, and part of the fifth: Overview The school is often referred to as the ''Minobu Sect'' due to .... Nichirō designated nine senior disciples. Among them were Nichizō and Nichiin. External links The Six Major Disciples of Nichiren 1245 births 1320 deaths Japanese Buddhist clergy Nichiren-shū Buddhist monks Nichiren Buddhism Kamakura period Buddhist clergy {{Japan-reli-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nichiren Buddhism
Nichiren Buddhism ( ja, 日蓮仏教), also known as Hokkeshū ( ja, 法華宗, meaning ''Lotus Sect'') is a branch of Mahayana Buddhism based on the teachings of the 13th-century Japanese Buddhist priest Nichiren (1222–1282) and is one of the Kamakura period schools. Its teachings derive from some 300–400 extant letters and treatises either authored by or attributed to Nichiren. Nichiren Buddhism generally sources its basic doctrine from the Lotus Sutra claiming that all sentient beings possess an internal Buddha-nature capable of attaining Buddhahood in the current life. There are three essential aspects to Nichiren Buddhism: # The faith in Nichiren's Gohonzon # The chanting of ''Namu Myoho Renge Kyo'' with varying recitations of the Lotus Sutra # The study of Nichiren's scriptural writings, called ''Gosho''. After his death, Nichiren left to both his senior disciples and lay followers the mandate to widely propagate the ''Gohonzon'' and chanting the '' Daimoku'' in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nichizō
Nichizō (日像, 1269–1342) was one of Nichirō's nine senior disciples (not to be confused with the six senior disciples of Nichiren). He was responsible for giving Nichiren Buddhism Nichiren Buddhism ( ja, 日蓮仏教), also known as Hokkeshū ( ja, 法華宗, meaning ''Lotus Sect'') is a branch of Mahayana Buddhism based on the teachings of the 13th-century Japanese Buddhist priest Nichiren (1222–1282) and is one of ... official imperial recognition in 1321. He was exiled twice while attempting to achieve this goal. External links * https://web.archive.org/web/20100612233710/http://nichirenscoffeehouse.net/Ryuei/HokkeShu_01.html 1269 births 1342 deaths Japanese Buddhist clergy Nichiren Buddhism Nichiren-shū Buddhist monks Kamakura period Buddhist clergy {{Japan-reli-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nichiin
Nichiin (日印, 1264 – January 20, 1329) was one of Nichirō's nine senior disciples (not to be confused with the six senior disciples of Nichiren). Along with his own disciple Nichijin (日陣) he is considered the founder of the Hokkeshū Jinmon Ryū subsect of Nichiren Buddhism. He was born in Teradomari in Echigo. He became a Tendai priest at the age of 8 and was sent to Kyoto at 16. He famously won a debate against Pure Land A pure land is the celestial realm of a buddha or bodhisattva in Mahayana Buddhism. The term "pure land" is particular to East Asian Buddhism () and related traditions; in Sanskrit the equivalent concept is called a buddha-field (Sanskrit ). Th ... Buddhists in 1319, and announced the Jinmon Ryū sect on October 12, 1321. 1264 births 1329 deaths Nichiren-shū Buddhist monks Kamakura period Buddhist clergy {{Japan-reli-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nichiren-shū
is a combination of several schools ranging from four of the original Nichiren Buddhist schools that date back to Nichiren's original disciples, and part of the fifth: Overview The school is often referred to as the ''Minobu Sect'' due to their prominence within the Mount Minobu area. The school's head temple, Kuon-ji, is located on Mount Minobu where Nichiren lived in seclusion and where he asked to be buried. Another significant temple of sect is the ''Ikegami Honmon-ji'' where Nichiren died. Accordingly, many of Nichiren's most important personal artifacts and writings preserved, also considered to be National Treasures of Japan are within their safekeeping. The sect is also known for its more open and tolerant views of other Buddhist traditions, even mixing or incorporating various mixed Buddhist beliefs and Shinto practices into their own Nichiren Buddhist aesthetics, most notably the use of various religious statues, the red stamping practice of Shuin for novelty, eso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
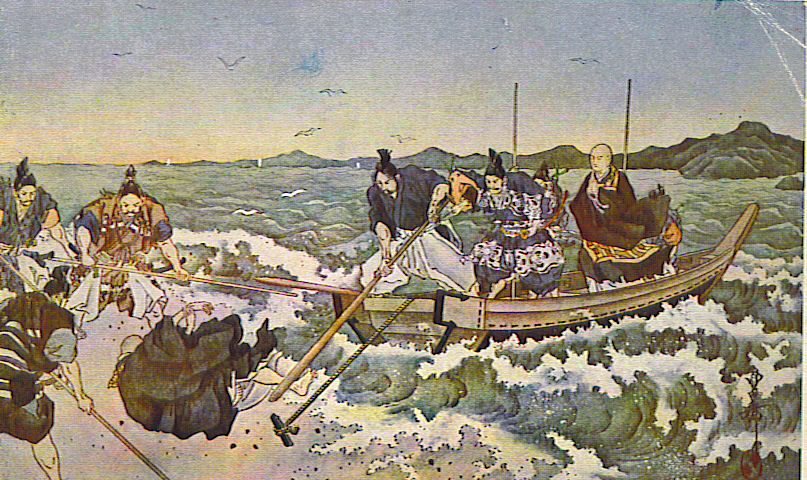
Nichiren
Nichiren (16 February 1222 – 13 October 1282) was a Japanese Buddhist priest and philosopher of the Kamakura period. Nichiren declared that the Lotus Sutra alone contains the highest truth of Buddhist teachings suited for the Third Age of Buddhism, insisting that the Sovereign of Japan and its people should support only this form of Buddhism and eradicate all others. He advocated the repeated recitation of its title, ''Nam(u)-myoho-renge-kyo'' as the only path to Buddhahood and held that Shakyamuni Buddha and all other Buddhist deities were extraordinary manifestations of a particular Buddha-nature termed ''Myoho-Renge'' that is equally accessible to all. He declared that believers of the Sutra must propagate it even under persecution. Nichiren was a prolific writer and his biography, temperament, and the evolution of his beliefs has been gleaned primarily from his own writings. He claimed the reincarnation of Jōgyō bodhisattva in a past life, and designated six seni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nisshō
was a Buddhist disciple of Nichiren and the uncle of Nichirō. He was the only disciple who was actually older than Nichiren himself. He was a Tendai , also known as the Tendai Lotus School (天台法華宗 ''Tendai hokke shū,'' sometimes just "''hokke shū''") is a Mahāyāna Buddhist tradition (with significant esoteric elements) officially established in Japan in 806 by the Japanese m ... priest in his youth, and after Nichiren's death he continued to claim that he was merely carrying out a reform of this sect. He founded Myōhokke-ji in 1284. His Hama-ha subsect continued to hold good relations with the Tendai sect. External links The Six Major Disciples of Nichiren 1236 births 1323 deaths Japanese Buddhist clergy Nichiren-shū Buddhist monks Nichiren Buddhism Kamakura period Buddhist clergy {{Japan-reli-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nichiren Exiled
Nichiren (16 February 1222 – 13 October 1282) was a Japanese Buddhist priest and philosopher of the Kamakura period. Nichiren declared that the Lotus Sutra alone contains the highest truth of Buddhist teachings suited for the Third Age of Buddhism, insisting that the Sovereign of Japan and its people should support only this form of Buddhism and eradicate all others. He advocated the repeated recitation of its title, ''Nam(u)-myoho-renge-kyo'' as the only path to Buddhahood and held that Shakyamuni Buddha and all other Buddhist deities were extraordinary manifestations of a particular Buddha-nature termed ''Myoho-Renge'' that is equally accessible to all. He declared that believers of the Sutra must propagate it even under persecution. Nichiren was a prolific writer and his biography, temperament, and the evolution of his beliefs has been gleaned primarily from his own writings. He claimed the reincarnation of Jōgyō bodhisattva in a past life, and designated six seni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nichiren-shū Buddhist Monks
is a combination of several schools ranging from four of the original Nichiren Buddhist schools that date back to Nichiren's original disciples, and part of the fifth: Overview The school is often referred to as the ''Minobu Sect'' due to their prominence within the Mount Minobu area. The school's head temple, Kuon-ji, is located on Mount Minobu where Nichiren lived in seclusion and where he asked to be buried. Another significant temple of sect is the ''Ikegami Honmon-ji'' where Nichiren died. Accordingly, many of Nichiren's most important personal artifacts and writings preserved, also considered to be National Treasures of Japan are within their safekeeping. The sect is also known for its more open and tolerant views of other Buddhist traditions, even mixing or incorporating various mixed Buddhist beliefs and Shinto practices into their own Nichiren Buddhist aesthetics, most notably the use of various religious statues, the red stamping practice of Shuin for novelty, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; " taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and the ; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ikegami Honmon-ji
is a temple of the Nichiren Shū south of Tokyo, erected where Nichiren is said to have died. Also Nichiren's disciple Nikkō spent the rest of his life at this temple. The temple grounds also include Nichiren Shū's administrative headquarters. A short walk from Ikegami Station (Tōkyū Ikegami Line) or Nishi-Magome Station (Toei Asakusa Line), Ikegami Honmon-ji contains a number of buildings, most of which have been reconstructed since the bombing of 15 March 1945. They include the Important Cultural Property designated five-storey pagoda built in 1608, the ''kyōzō'' (, repository of religious writings) built in 1784, and the ''hōtō'' (), built in 1781 where Nichiren was cremated. Other buildings have been rebuilt, or newly constructed, since 1945. Now in Ōta-ku, suburban Tokyo, Ikegami Honmon-ji was at some distance from the city until the mid-20th century. Basil Hall Chamberlain and W. B. Mason wrote of it in 1907: "Its fine situation and magnificent timbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; " taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tendai
, also known as the Tendai Lotus School (天台法華宗 ''Tendai hokke shū,'' sometimes just "''hokke shū''") is a Mahāyāna Buddhist tradition (with significant esoteric elements) officially established in Japan in 806 by the Japanese monk Saichō ( posthumously known as Dengyō Daishi). The Tendai school, which has been based on Mount Hiei since its inception, rose to prominence during the Heian period (794-1185). It gradually eclipsed the powerful ''Hossō'' school and competed with the rival Shingon school to become the most influential sect at the Imperial court. By the Kamakura period (1185-1333), Tendai had become one of the dominant forms of Japanese Buddhism, with numerous temples and vast landholdings. During the Kamakura period, various monks left Tendai (seeing it as corrupt) to establish their own "new" or "Kamakura" Buddhist schools such as Jōdo-shū, Nichiren-shū and Sōtō Zen. The destruction of the head temple of Enryaku-ji by Oda Nobunaga in 1571, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |