|
Nicetas The Patrician
Saint Nicetas the Patrician ( gr, Νικήτας Πατρίκιος, Niketas Patrikios; 761/62 – 6 October 836) was a Byzantine monk and a fervent opponent of Byzantine Iconoclasm. He is usually identified with Nicetas Monomachos (Νικήτας Μονομάχος), a eunuch official and general from Paphlagonia active at the turn of the 9th century. He is honoured as a saint and a Confessor of the Faith by the Eastern Orthodox Church. His feast day is on 13 October. Early life and career Nicetas was born in Paphlagonia in 761/62, and his parents were probably named Gregory and Anna. Later tradition held that he was a descendant of Theodora (wife of Theophilos), Empress Theodora, the wife of Theophilos (emperor), Theophilos (). This is clearly impossible, but some sort of relation cannot be excluded. Another tradition records that he was also a relative of Empress Irene of Athens ().Banev (2003)Chapter 1/ref>Lilie (1996), pp. 37, 127. According to his hagiography, he was cas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
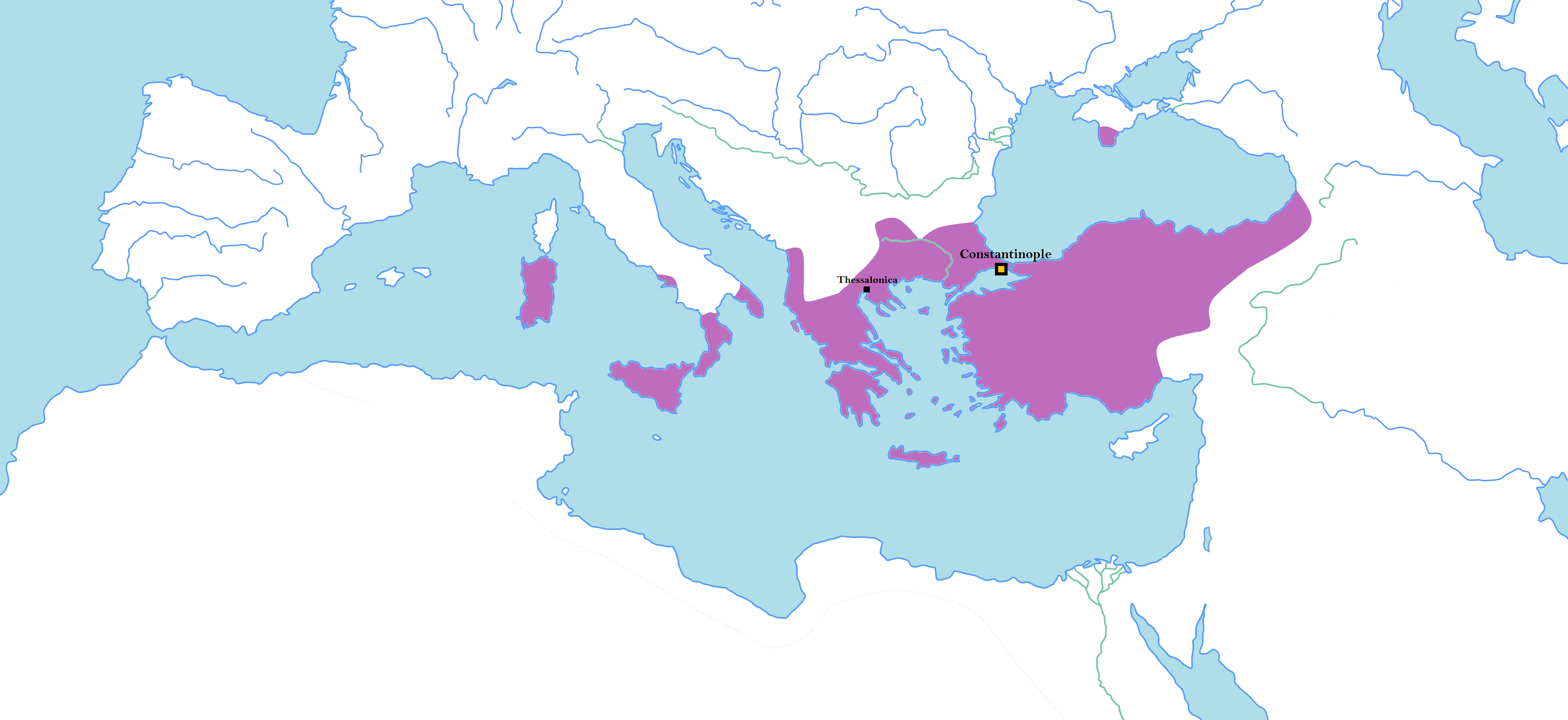
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theme (Byzantine District)
The themes or ( el, θέματα, , singular: , ) were the main military/administrative divisions of the middle Byzantine Empire. They were established in the mid-7th century in the aftermath of the Slavic invasion of the Balkans and Muslim conquests of parts of Byzantine territory, and replaced the earlier provincial system established by Diocletian and Constantine the Great. In their origin, the first themes were created from the areas of encampment of the field armies of the East Roman army, and their names corresponded to the military units that had existed in those areas. The theme system reached its apogee in the 9th and 10th centuries, as older themes were split up and the conquest of territory resulted in the creation of new ones. The original theme system underwent significant changes in the 11th and 12th centuries, but the term remained in use as a provincial and financial circumscription until the very end of the Empire. History Background During the late 6th and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Logothete
The ( gr, λογοθέτης τοῦ γενικοῦ, often called or simply (, 'the general ogothete), and usually rendered in English as the General Logothete, was in charge of the 'general financial ministry', the of the middle Byzantine Empire.. History and functions The was responsible for general taxation and revenue, and also served as a court for financial cases. As such, it broadly fulfilled the tasks of the earlier , although it was mostly derived from the "general department" of the praetorian prefecture. The first attested , the monk Theodotos, is mentioned in 692, but the post may have been instituted as early as 626. The bureau of the and its logothete remained one of the chief ministries for the entire middle Byzantine period (7th–12th centuries). During the Komnenian period, its importance declined, but recovered under the Angeloi. Following the sack of Constantinople in 1204 and the dissolution of the Byzantine Empire, the office of the was retained as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The islands are in the shallow Venetian Lagoon, an enclosed bay lying between the mouths of the Po River, Po and the Piave River, Piave rivers (more exactly between the Brenta (river), Brenta and the Sile (river), Sile). In 2020, around 258,685 people resided in greater Venice or the ''Comune di Venezia'', of whom around 55,000 live in the historical island city of Venice (''centro storico'') and the rest on the mainland (''terraferma''). Together with the cities of Padua, Italy, Padua and Treviso, Italy, Treviso, Venice is included in the Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area (PATREVE), which is considered a statistical metropolitan area, with a total population of 2.6 million. The name is derived from the ancient Adri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of the Adriatic Sea, stretching from the island of Rab in the north to the Bay of Kotor in the south. The Dalmatian Hinterland ranges in width from fifty kilometres in the north, to just a few kilometres in the south; it is mostly covered by the rugged Dinaric Alps. List of islands of Croatia, Seventy-nine islands (and about 500 islets) run parallel to the coast, the largest (in Dalmatia) being Brač, Pag (island), Pag, and Hvar. The largest city is Split, Croatia, Split, followed by Zadar and Šibenik. The name of the region stems from an Illyrians, Illyrian tribe called the Dalmatae, who lived in the area in classical antiquity. Later it became a Dalmatia (Roman province), Roman province, and as result a Romance languages, Romance culture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bithynia
Bithynia (; Koine Greek: , ''Bithynía'') was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor (present-day Turkey), adjoining the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, and the Black Sea. It bordered Mysia to the southwest, Paphlagonia to the northeast along the Pontic coast, and Phrygia to the southeast towards the interior of Asia Minor. Bithynia was an independent kingdom from the 4th century BC. Its capital Nicomedia was rebuilt on the site of ancient Astacus in 264 BC by Nicomedes I of Bithynia. Bithynia was bequeathed to the Roman Republic in 74 BC, and became united with the Pontus region as the province of Bithynia et Pontus. In the 7th century it was incorporated into the Byzantine Opsikion theme. It became a border region to the Seljuk Empire in the 13th century, and was eventually conquered by the Ottoman Turks between 1325 and 1333. Description Several major cities sat on the fertile shores of the Propontis (which is now known as Sea of Marma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastria Monastery
Sancaktar Hayrettin Mosque ( tr, Sancaktar Hayrettin Câmîi; also ''Sancaktar Hayrettin Mescidi'', where ''Mescit'' is the Turkish word for a small mosque, or ''Sancaktar Mescidi'') is part of a former Eastern Orthodox monastery converted into a mosque by the Ottomans. It is generally believed that the small building belonged to the Byzantine Monastery of Gastria ( el, , ''Monē tōn Gastríōn'', meaning "Monastery of the Vases"). The edifice is a minor example of Palaiologan architecture in Constantinople, and is important for historical reasons. Location The medieval structure, choked by artisan shops, lies in Istanbul, in the district of Fatih, in the neighborhood of Kocamustafapaşa (historically Samatya), on ''Teberdar Sokak'', about five hundred meters north east of the Kocamustafapaşa station of the suburban railway line between Sirkeci and Halkalı. History The origin of this building, which lies on the southern slope of the seventh hill of Constantinople and overl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staurakios
Staurakios or Stauracius ( gr, Σταυράκιος, links=no; early 790s – 11 January 812AD) was Byzantine emperor from 26 July to 2 October 811. He was born in the early 790s, probably between 791 and 793, to Nikephoros I and an unknown woman. Nikephoros seized the throne of the Byzantine Empire from Empress Irene in 802, and elevated Staurakios to co-emperor on 25 December 803. On 20 December 807, a bride show was held by Nikephoros to select a wife for Staurakios, which resulted in his marriage to Theophano of Athens, a kinswoman of Irene. Little else is known of him until he came to take the throne upon the death of Nikephroros. Staurakios took part in an invasion of the Bulgarian Khanate in 811, alongside his father and brother-in-law. Although initially successful, with the Byzantines laying siege to the Bulgarian capital of Pliska and defeating a relief force, they were soon ambushed by Khan Krum, and trapped in a small valley. The Bulgarians then attacked, startin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros I
Nikephoros I or Nicephorus I ( gr, Νικηφόρος; 750 – 26 July 811) was Byzantine emperor from 802 to 811. Having served Empress Irene as '' genikos logothetēs'', he subsequently ousted her from power and took the throne himself. In reference to his career before becoming emperor, he is sometimes surnamed "the Logothete" (ὁ Λογοθέτης) and "Genikos" or "Genicus" (ὁ Γενικός). Nikephoros pursued wars against the Arabs and Bulgarians, with mixed results; while invading Bulgaria he was defeated and killed at the Battle of Pliska. Background Sources outside the Byzantine context, including Michael the Syrian, al-Tabari, and Mas'udi, preserve the tradition that Nikephoros was of Ghassanid Arab origin. al-Tabari claims that he derived this information from Byzantine sources, but no surviving Byzantine chronicle makes explicit mention of the emperor's ethnic background. The modern scholar Paul Julius Alexander suggests that al-Tabari did transmit informat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine IX Monomachos
Constantine IX Monomachos ( grc-x-medieval, Κωνσταντῖνος Μονομάχος, translit=Kōnstantinos IX Monomachos; 1004 – 11 January 1055), reigned as Byzantine emperor from June 1042 to January 1055. Empress Zoë Porphyrogenita chose him as a husband and co-emperor in 1042, although he had been exiled for conspiring against her previous husband, Emperor Michael IV the Paphlagonian. The couple shared the throne with Zoë's sister Theodora Porphyrogenita. Zoë died in 1050, and Constantine continued his collaboration with Theodora until his own death five years later. Constantine waged wars against groups which included the Kievan Rus', the Pechenegs and, in the East, the rising Seljuq Turks. Despite the varying success of these campaigns, the Byzantine Empire largely retained the borders established after the conquests of Basil II, even expanding eastwards when Constantine annexed the wealthy Armenian kingdom of Ani. Constantine accordingly may be considered the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monomachos Family
Monomachos, Romanization of Greek, Latinized Monomachus ( el, Μονομάχος, , Lone Warrior), feminine form Monomachina (Μονομαχίνα), was the name of a Byzantine Empire, Byzantine aristocratic family active in the 10th–15th centuries and possibly even before that. The name, Monomachos, means “the gladiator” in Greek. It produced several officials and military commanders, as well as one emperor, Constantine IX Monomachos (). History The first occurrences of the name are unclear, and may refer to sobriquets rather to members of the family. An Byzantine Iconoclasm, iconoclast bishop of Nicomedia with the name is alluded to in the 9th-century hagiography of St. Joannicius, whereas a fervently anti-iconoclast official was Niketas Monomachos, Patrikios Niketas Monomachos during the early 9th century, who was later declared a saint. The family was said to have been ‘ancient’ but did not come to the fore until the 10th and 11th centuries: firstly with Pavlos M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)