|
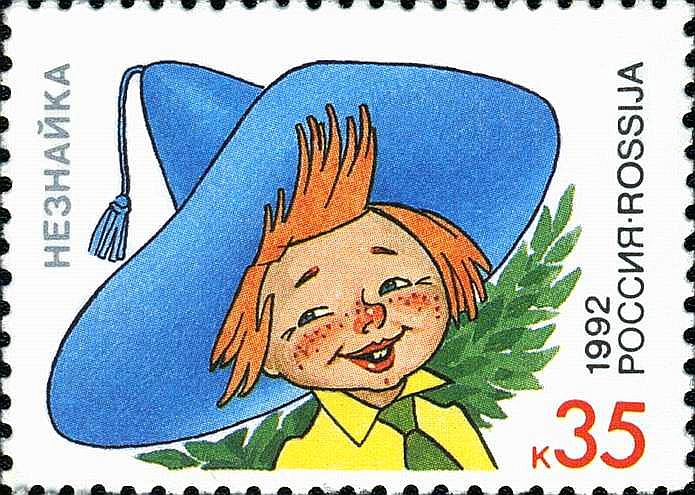
Neznaika On The Moon
Dunno, or Know-Nothing or Ignoramus (russian: Незнайка, ''Neznayka'' that is Don'tknowka (ka - the Russian suffix here for drawing up the whole name in a cheerful form); from the Russian phrase "" ("''ne znayu''", ''don't know'') is a character created by Soviet children's writer Nikolay Nosov. The idea of the character comes from the books of Palmer Cox. Dunno, recognized by his bright blue hat, canary-yellow trousers, orange shirt, and green tie, is the title character of Nosov's trilogy, '' The Adventures of Dunno and his Friends'' (1954), ''Dunno in Sun City'' (1958), and ''Dunno on the Moon'' (1966). There have been several movie adaptations of the books. Names His names are translated differently in various languages: * ar, الجاهل * az, Bilməz * bg, Незнайко * bn, আনাড়ি * cs, Neználek * german: Nimmerklug * he, בורבורי * es, Nosabenada * et, Totu * hi, Najanu * hu, Nemtudomka * hy, Անգետիկը * ka, ნეზნ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neznaika Friends Cover
Dunno, or Know-Nothing or Ignoramus (russian: Незнайка, ''Neznayka'' that is Don'tknowka (ka - the Russian suffix here for drawing up the whole name in a cheerful form); from the Russian phrase "" ("''ne znayu''", ''don't know'') is a character created by Soviet children's writer Nikolay Nosov. The idea of the character comes from the books of Palmer Cox. Dunno, recognized by his bright blue hat, canary-yellow trousers, orange shirt, and green tie, is the title character of Nosov's trilogy, '' The Adventures of Dunno and his Friends'' (1954), ''Dunno in Sun City'' (1958), and ''Dunno on the Moon'' (1966). There have been several movie adaptations of the books. Names His names are translated differently in various languages: * ar, الجاهل * az, Bilməz * bg, Незнайко * bn, আনাড়ি * cs, Neználek * german: Nimmerklug * he, בורבורי * es, Nosabenada * et, Totu * hi, Najanu * hu, Nemtudomka * hy, Անգետիկը * ka, ნეზნ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
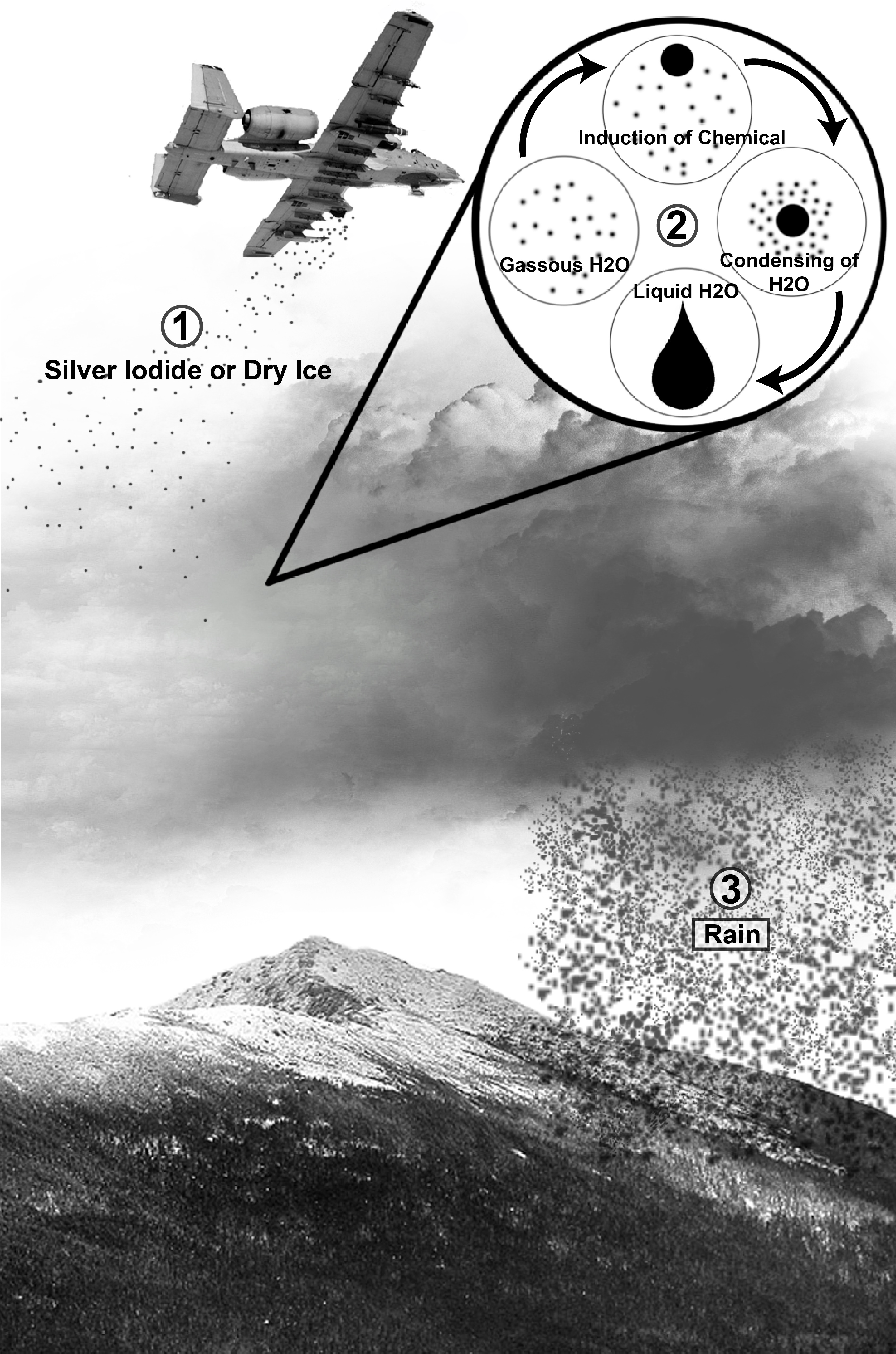
Cloud Seeding
Cloud seeding is a type of weather modification that aims to change the amount or type of precipitation that falls from clouds by dispersing substances into the air that serve as cloud condensation or ice nuclei, which alter the microphysical processes within the cloud. Its effectiveness is debated; some studies have suggested that it is "difficult to show clearly that cloud seeding has a very large effect." The usual objective is to increase precipitation (rain or snow), either for its own sake or to prevent precipitation from occurring in days afterward. Methodologies Salts The most common chemicals used for cloud seeding include silver iodide, potassium iodide and dry ice (solid carbon dioxide). Liquid propane, which expands into a gas, has also been used. This can produce ice crystals at higher temperatures than silver iodide. After promising research, the use of hygroscopic materials, such as table salt, is becoming more popular. When cloud seeding, increased snowfall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syrup
In cooking, a syrup (less commonly sirup; from ar, شراب; , beverage, wine and la, sirupus) is a condiment that is a thick, viscous liquid consisting primarily of a solution of sugar in water, containing a large amount of dissolved sugars but showing little tendency to deposit crystals. Its consistency is similar to that of molasses. The viscosity arises from the multiple hydrogen bonds between the dissolved sugar, which has many hydroxyl (OH) groups. Culinary syrup There are a range of syrups used in food production, including: * Agave syrup, made from agave stem * Cane syrup, made from sugar canes * Chocolate syrup * Corn syrup * Glucose syrup * Golden syrup, a by-product of refining crystallized sugar * High fructose corn syrup, widely used in the US * Maple syrup Common syrups A variety of beverages call for sweetening to offset the tartness of some juices used in the drink recipes. Granulated sugar does not dissolve easily in cold drinks or ethyl alcohol. Since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gusli
''Gusli'' ( rus, гусли, p=ˈɡuslʲɪ) is the oldest East Slavic multi-string plucked instrument, belonging to the zither family, due to its strings being parallel to its resonance board. Its roots lie in Veliky Novgorod in Novgorodian Rus'. It may have a connection to the Byzantine form of the Greek kithara, which in turn derived from the ancient lyre, or might have been imported from Western and Central Europe during the Middle Ages, when the zither had immense popularity. It has its relatives in Europe and throughout the world: kantele in Finland, kannel in Estonia, kanklės in Lithuania, kokles in Latvia, Zither in Germany, citera in the Czech Republic, psalterium in France and so on... Furthermore, the kanun has been found in Arabic countries, and the autoharp, in the United States. It is also related to such ancient instruments as Chinese gu zheng, which has a thousand-year history, and its Japanese relative koto. A stringed musical instrument called is listed as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Gogol
Nikolai Vasilyevich Gogol; uk, link=no, Мико́ла Васи́льович Го́голь, translit=Mykola Vasyliovych Hohol; (russian: Яновский; uk, Яновський, translit=Yanovskyi) ( – ) was a Russian novelist, short story writer and playwright of Ukrainian origin. Gogol was one of the first to use the technique of the grotesque, in works such as " The Nose", " Viy", "The Overcoat", and "Nevsky Prospekt". These stories, and others such as " Diary of a Madman", have also been noted for their proto-surrealist qualities. According to Viktor Shklovsky, Gogol's strange style of writing resembles the "ostranenie" technique of defamiliarization. His early works, such as ''Evenings on a Farm Near Dikanka'', were influenced by his Ukrainian upbringing, Ukrainian culture and folklore. His later writing satirised political corruption in the Russian Empire (''The Government Inspector'', '' Dead Souls''). The novel ''Taras Bulba'' (1835), the play ''Marriage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan The Fool
Ivan the Fool () or Ivan the Ninny is a lucky fool stock character who appears in Russian folklore, a very simple-minded, but, nevertheless, lucky young man. Ivan is described as a likeable fair-haired and blue-eyed youth. The approximate setting of Ivan the Fool's adventures is 15th- or 16th-century Russia. Ivan the Fool usually appears in stories either as a peasant or as the son of a poor family. He is usually the youngest of three brothers; his older siblings appear much smarter than he, but are sometimes unkind to and envious of him. In contrast to typical heroes, Ivan's simplicity and lack of guile turn out to help him in his adventures. For example, he listens to his heart rather than to his mind, and he easily forgets offence and endeavors to help others even at his own expense. His naivety, kindness, and daring help him fight villains, make friends, and win princesses' hearts, and ultimately he is rewarded with half a kingdom or some similar accomplishment. The mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folk Hero
A folk hero or national hero is a type of hero – real, fictional or mythological – with their name, personality and deeds embedded in the popular consciousness of a people, mentioned frequently in folk songs, folk tales and other folklore; and with modern trope status in literature, art and films. Overview Although some folk heroes are historical public figures, many are not. The lives of folk heroes are generally fictional, their characteristics and deeds often exaggerated to mythic proportions. The folk hero often begins life as a normal person, but is transformed into someone extraordinary by significant life events, often in response to social injustice, and sometimes in response to natural disasters. One major category of folk hero is the defender of the common people against the oppression or corruption of the established power structure. Members of this category of folk hero often, but not necessarily, live outside the law in some way. See also * List of folk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia Stamp 1992 No 17
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across eleven time zones and shares land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than any other country but China. It is the world's ninth-most populous country and Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and largest city is Moscow, the largest city entirely within Europe. Saint Petersburg is Russia's cultural centre and second-largest city. Other major urban areas include Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Nizhny Novgorod, and Kazan. The East Slavs emerged as a recognisable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries CE. Kievan Rus' arose as a state in the 9th century, and in 988, it adopted Orthodox Christianity from the Byzan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamprey
Lampreys (sometimes inaccurately called lamprey eels) are an ancient extant lineage of jawless fish of the order Petromyzontiformes , placed in the superclass Cyclostomata. The adult lamprey may be characterized by a toothed, funnel-like sucking mouth. The common name "lamprey" is probably derived from Latin , which may mean "stone licker" ( "to lick" + "stone"), though the etymology is uncertain. ''Lamprey'' is sometimes seen for the plural form. There are about 38 known extant species of lampreys and five known extinct species. Parasitic carnivorous species are the most well-known, and feed by boring into the flesh of other fish to suck their blood; but only 18 species of lampreys engage in this micropredatory lifestyle. Of the 18 carnivorous species, nine migrate from saltwater to freshwater to breed (some of them also have freshwater populations), and nine live exclusively in freshwater. All non-carnivorous forms are freshwater species. Adults of the non-carnivorous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dumping (pricing Policy)
Dumping, in economics, is a kind of injuring pricing, especially in the context of international trade. It occurs when manufacturers export a product to another country at a price below the normal price with an injuring effect. The objective of dumping is to increase market share in a foreign market by driving out competition and thereby create a monopoly situation where the exporter will be able to unilaterally dictate price and quality of the product. Trade treaties might include mechanisms to alleviate problems related to dumping, such as countervailing duty penalties and anti-dumping statutes. Overview A standard technical definition of dumping is the act of charging a lower price for the like product in a foreign market than the normal value of the product, for example the price of the same product in a domestic market of the exporter or in a third country market. This is often referred to as selling at less than "normal value" on the same level of trade in the ordinary cours ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quantities in seawater. The open ocean has about of solids per liter of sea water, a salinity of 3.5%. Salt is essential for life in general, and saltiness is one of the basic human tastes. Salt is one of the oldest and most ubiquitous food seasonings, and is known to uniformly improve the taste perception of food, including otherwise unpalatable food. Salting, brining, and pickling are also ancient and important methods of food preservation. Some of the earliest evidence of salt processing dates to around 6,000 BC, when people living in the area of present-day Romania boiled spring water to extract salts; a salt-works in China dates to approximately the same period. Salt was also prized by the ancient Hebrews, Greeks, Romans, Byzantines, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket
A rocket (from it, rocchetto, , bobbin/spool) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using the surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely from propellant carried within the vehicle; therefore a rocket can fly in the vacuum of space. Rockets work more efficiently in a vacuum and incur a loss of thrust due to the opposing pressure of the atmosphere. Multistage rockets are capable of attaining escape velocity from Earth and therefore can achieve unlimited maximum altitude. Compared with airbreathing engines, rockets are lightweight and powerful and capable of generating large accelerations. To control their flight, rockets rely on momentum, airfoils, auxiliary reaction engines, gimballed thrust, momentum wheels, deflection of the exhaust stream, propellant flow, spin, or gravity. Rockets for military and recreational uses date back to at least 13th-century China. Signific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)


