|
Neuburg (Freiburg Im Breisgau)
Neuburg is a quarter of the German city Freiburg im Breisgau. The district is located directly north of the old town with its numerous sights and includes the Schlossberg which is situated east of the city's historic center. Neuburg adjoins the district ''Oberau'' on wooded Schlossberg, as well as it adjoins Herdern in the north. On its western side, the district is cut off from Stühlinger by the tracks of the ''Rheintalbahn'' running from Mannheim to Basel. The district's name Neuburg is rarely used by Freiburg's inhabitants since Neuburg is split into two-halves by the major street Habsburger Street. The area east of Habsburger Street is commonly viewed as part of the district Herdern, whereas the area west of it is said to be part of the ''Institutsviertel'' (engl. institute district), which comprises the local University's Natural sciences department. History The first construction of houses in Neuburg started soon after the foundation of Freiburg in the 12th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freiburg Im Breisgau
Freiburg im Breisgau (; abbreviated as Freiburg i. Br. or Freiburg i. B.; Low Alemannic German, Low Alemannic: ''Friburg im Brisgau''), commonly referred to as Freiburg, is an independent city in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. With a population of about 230,000 (as of 31 December 2018), Freiburg is the List of cities in Baden-Württemberg by population, fourth-largest city in Baden-Württemberg after Stuttgart, Mannheim, and Karlsruhe. The population of the Freiburg metropolitan area was 656,753 in 2018. In the Southern Germany, south-west of the country, it straddles the Dreisam river, at the foot of the Schlossberg (Freiburg), Schlossberg. Historically, the city has acted as the hub of the Breisgau region on the western edge of the Black Forest in the Upper Rhine Plain. A famous old German university town, and Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Freiburg, archiepiscopal seat, Freiburg was incorporated in the early twelfth century and developed into a major commercial, intellectual, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Germany
Southern Germany () is a region of Germany which has no exact boundary, but is generally taken to include the areas in which Upper German dialects are spoken, historically the stem duchies of Bavaria and Swabia or, in a modern context, Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg and the southern parts of Hesse and Rhineland-Palatinate that were part of the Duchy of Franconia. German-speaking Switzerland, Austria, Liechtenstein, and South Tyrol are historically, culturally, and linguistically related to Southern Germany in many ways. Boundaries Southern Germany primarily contrasts with Northern Germany. The term mostly corresponds to those territories of modern Germany which did not form part of the North German Confederation in the nineteenth century. Between Northern and Southern Germany is the loosely defined area known as Central Germany (''Mitteldeutschland''), roughly corresponding to the areal of Central German dialects (Franconia, Thuringia, Saxony). The boundary between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cemetery
A cemetery, burial ground, gravesite or graveyard is a place where the remains of dead people are buried or otherwise interred. The word ''cemetery'' (from Greek , "sleeping place") implies that the land is specifically designated as a burial ground and originally applied to the Roman catacombs. The term ''graveyard'' is often used interchangeably with cemetery, but a graveyard primarily refers to a burial ground within a churchyard. The intact or cremated remains of people may be interred in a grave, commonly referred to as burial, or in a tomb, an "above-ground grave" (resembling a sarcophagus), a mausoleum, columbarium, niche, or other edifice. In Western cultures, funeral ceremonies are often observed in cemeteries. These ceremonies or rites of passage differ according to cultural practices and religious beliefs. Modern cemeteries often include crematoria, and some grounds previously used for both, continue as crematoria as a principal use long after the interment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Tigerfish
Operation Tigerfish was the military code name in World War II for the air raid on Freiburg in the evening of 27 November 1944 by the Royal Air Force with about 2,800 dead. The name ''Tigerfish'' goes back to Air Vice-Marshal Robert Saundby, an avid fisherman who codenamed all German cities "fitted" for carpet bombing with a ''Fish code''. Saundby was the deputy of Air Chief Marshal Arthur Harris, Air Officer Commanding-in-Chief of RAF Bomber Command. Background After Freiburg was mistakenly bombed by the German Luftwaffe on 10 May 1940 when 57 people were killed, the city remained spared from attacks until October 1943. For a long time, people in Freiburg had lived in the hope that they would not have to suffer a major attack. The city was classified only as air protection location category 2 in 1935. As a consequence, Freiburg had to make arrangements for adequate protection of the population by the construction of shelters and bunkers without getting any financial re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—most recently part of the Eastern Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Baden
The Grand Duchy of Baden (german: Großherzogtum Baden) was a state in the southwest German Empire on the east bank of the Rhine. It existed between 1806 and 1918. It came into existence in the 12th century as the Margraviate of Baden and subsequently split into the states of Baden-Durlach and Baden-Baden, which were reunified in 1771. It then became the much-enlarged Grand Duchy of Baden after the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire from 1803 to 1806 and was a sovereign country until it joined the German Empire in 1871. In 1918, it became part of the Weimar Republic as the Republic of Baden. Baden was bordered to the north by the Kingdom of Bavaria and the Grand Duchy of Hessen-Darmstadt; to the west, along most of its length, by the river Rhine, which separated Baden from the Bavarian Rhenish Palatinate and Alsace in modern France; to the south by Switzerland; and to the east by the Kingdom of Württemberg, the Principality of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen and Bavaria. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debris
Debris (, ) is rubble, wreckage, ruins, litter and discarded garbage/refuse/trash, scattered remains of something destroyed, or, as in geology, large rock fragments left by a melting glacier, etc. Depending on context, ''debris'' can refer to a number of different things. The first apparent use of the French word in English is in a 1701 description of the army of Prince Rupert upon its retreat from a battle with the army of Oliver Cromwell, in England. Disaster In disaster scenarios, tornadoes leave behind large pieces of houses and mass destruction overall. This debris also flies around the tornado itself when it is in progress. The tornado's winds capture debris it kicks up in its wind orbit, and spins it inside its vortex. The tornado's wind radius is larger than the funnel itself. Tsunamis and hurricanes also bring large amounts of debris, such as Hurricane Katrina in 2005 and Hurricane Sandy in 2012. Earthquakes rock cities to rubble debris. Geological In geology, debri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
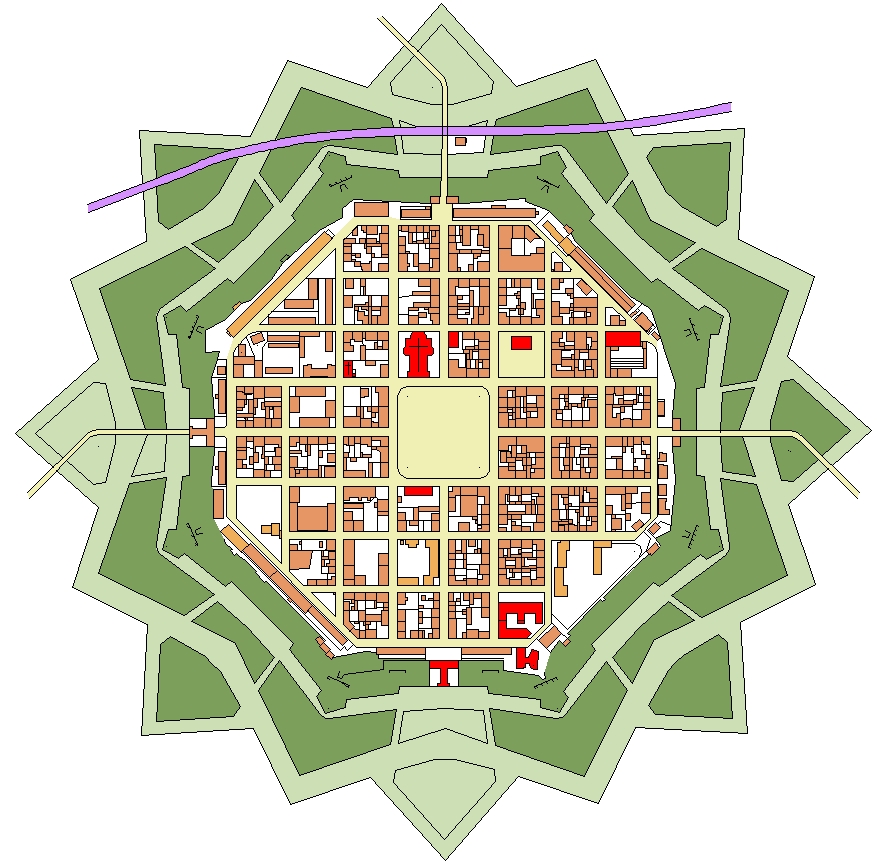
Neuf-Brisach
Neuf-Brisach ( or ; ; gsw-FR, Nei-Brisach) is a fortified town and commune of the department of Haut-Rhin in the French region of Alsace. The fortified town was intended to guard the border between France and the Holy Roman Empire and, subsequently, the German states. It was built after the Treaty of Ryswick in 1697 that resulted in France losing the town of Breisach, on the opposite bank of the Rhine. The town's name means ''New Breisach''. Today the town is a UNESCO World Heritage Site because of quintessential military fortifications and its testimony to the influence of Vauban on military architecture during the 17-19th centuries. History Work began on the fortified town in 1698, to plans drawn by Vauban, a military engineer at the service of Louis XIV. Vauban died in 1707 and this, his last work, was completed by Louis de Cormontaigne. The city's layout was that of an 'ideal city', as was popular at the time, with a regular square grid street pattern inside an octagonal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alsace
Alsace (, ; ; Low Alemannic German/ gsw-FR, Elsàss ; german: Elsass ; la, Alsatia) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine next to Germany and Switzerland. In 2020, it had a population of 1,898,533. Alsatian culture is characterized by a blend of Germanic and French influences. Until 1871, Alsace included the area now known as the Territoire de Belfort, which formed its southernmost part. From 1982 to 2016, Alsace was the smallest administrative ''région'' in metropolitan France, consisting of the Bas-Rhin and Haut-Rhin departments. Territorial reform passed by the French Parliament in 2014 resulted in the merger of the Alsace administrative region with Champagne-Ardenne and Lorraine to form Grand Est. On 1 January 2021, the departments of Bas-Rhin and Haut-Rhin merged into the new European Collectivity of Alsace but remained part of the region Grand Est. Alsatian is an Alemannic dialect closely related ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortification
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ("to make"). From very early history to modern times, defensive walls have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley civilization were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large stone walls had been built in Mycenaean Greece, such as the ancient site of Mycenae (famous for the huge stone blocks of its 'cyclopean' walls). A Greek '' phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison, and is the equivalent of the Roman castellum or English fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certain roads, passes, and borders. Though smaller than a real fortress, they act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sébastien Le Prestre De Vauban
Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban, Seigneur de Vauban, later Marquis de Vauban (baptised 15 May 163330 March 1707), commonly referred to as ''Vauban'' (), was a French military engineer who worked under Louis XIV. He is generally considered the greatest engineer of his time, and one of the most important in European military history. His principles for fortifications were widely used for nearly 100 years, while aspects of his offensive tactics remained in use until the mid-twentieth century. He viewed civilian infrastructure as closely connected to military effectiveness and worked on many of France's major ports, as well as projects like the Canal de la Bruche, which remain in use today. He founded the , whose curriculum was based on his publications on engineering design, strategy and training. His economic tract, , used statistics in support of his arguments, making it a precursor of modern economics. Later destroyed by royal decree, it contained radical proposals for a more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD 500), the Middle Ages (AD 500 to AD 1500), and the modern era (since AD 1500). The first early ..., lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle, famine, and disease, while some areas of what is now modern Germany experienced population declines of over 50%. Related conflicts include the Eighty Years' War, the War of the Mantuan Succession, the Franco-Spanish War (1635–1659), Franco-Spanish War, and the Portuguese Restoration War. Until the 20th century, historians generally viewed it as a continuation of the religious struggle initiated by the 16th-century Reformation within the Holy Roman Empire. The 1555 Peace of Augsburg atte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_4029.jpg)



.png)