|
Netherhall RUFC
Humberstone and Hamilton is an electoral ward and administrative division of the City of Leicester, England. It comprises the north-eastern Leicester suburbs of Humberstone, Humberstone Garden City, Hamilton and Netherhall. Geography Humberstone and Hamilton is bordered by the wards of Rushey Mead to the north, Charnwood to the east and Coleman and Thurncourt to the south. The ward borders the county of Leicestershire; in particular, the borough of Charnwood to the north and the district of Harborough to the east. The ward comprises the suburb of Humberstone in the west, Netherhall in the southeast and Hamilton to the northeast (which makes Hamilton the most northeasterly suburb of Leicester). History Name The ward takes its name from the historical village of Humberstone and the modern housing estate of Hamilton. The place-name 'Humberstone' is first attested in the Domesday Book of 1086, where it appears as 'Humerstane'. The name means 'Hunbeorht's stone'. The "Humber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leicester
Leicester ( ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, city, Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority and the county town of Leicestershire in the East Midlands of England. It is the largest settlement in the East Midlands. The city lies on the River Soar and close to the eastern end of the National Forest, England, National Forest. It is situated to the north-east of Birmingham and Coventry, south of Nottingham and west of Peterborough. The population size has increased by 38,800 ( 11.8%) from around 329,800 in 2011 to 368,600 in 2021 making it the most populous municipality in the East Midlands region. The associated Urban area#United Kingdom, urban area is also the 11th most populous in England and the List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, 13th most populous in the United Kingdom. Leicester is at the intersection of two railway lines: the Midland Main Line and the Birmingham to London Stansted Airport line. It is also at the confluence of the M1 motorway, M1/M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barkby Thorpe
Barkby Thorpe is a hamlet and civil parish in the Charnwood district of Leicestershire, England. The hamlet has a population of around 50, and is close to the Leicester urban sprawl in Thurmaston. Nearby villages are Barkby, Beeby and the abandoned village of Hamilton. The name Barkby has an Old Norse Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and t ... origin meaning "Barki's farm/settlement". References Hamlets in Leicestershire Civil parishes in Leicestershire Borough of Charnwood {{Leicestershire-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arriva Midlands East
Arriva Midlands East, is a bus company operating services in Leicestershire. It is a trading division of Arriva Midlands which is a subsidiary of Arriva plc which is itself owned by the government of Germany through Deutsche Bahn. History In September 1981 Midland Red East was formed with 181 buses operating from five depots in Derbyshire, Leicestershire, Lincolnshire and Nottinghamshire as part of the breakup of the Midland Red bus company, and in January 1984 was renamed Midland Fox.Midland Red Depots MidlandRed.net In 1987 it was privatised in a . Several smaller operators including Loughborough Bus & Coach Company were purchased and in 1989 it was sold to the Drawlane Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orchard Mead Academy
Orchard Mead Academy, previously known as Hamilton Community College, is a co-educational secondary school located in Leicester, England, taking children between the ages of eleven and sixteen.Hamilton Community College at dcsf.gov.uk (accessed 25 June 2008) The college became an academy on 1 September 2017, joining The Mead Educational Trust /(TMET) as a . The main school building dating from the 50s and 60s was replaced in 2014 as part of the |
Free School (England)
A free school in England is a type of academy established since 2010 under the Government's free school policy initiative. From May 2015, usage of the term was formally extended to include new academies set up via a local authority competition. Like other academies, free schools are non-profit-making, state-funded schools which are free to attend but which are mostly independent of the local authority. Description Like all academies, free schools are governed by non-profit charitable trusts that sign funding agreements with the Education Secretary. There are different model funding agreements for single academy trusts and multi academy trusts. It is possible for a local authority to sponsor a free school in partnership with other organisations, provided they have no more than a 19.9 per cent representation on the board of trustees. Studio schools and university technical colleges are both sub-types of free school. Policy creation and implementation Free schools were introd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikh
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism, Sikhism (Sikhi), a Monotheism, monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Sikh'' has its origin in the word ' (), meaning 'disciple' or 'student'. Male Sikhs generally have ''Singh'' ('lion'/'tiger') as their last name, though not all Singhs are necessarily Sikhs; likewise, female Sikhs have ''Kaur'' ('princess') as their last name. These unique last names were given by the Gurus to allow Sikhs to stand out and also as an act of defiance to India's caste system, which the Gurus were always against. Sikhs strongly believe in the idea of "Sarbat Da Bhala" - "Welfare of all" and are often seen on the frontline to provide humanitarian aid across the world. Sikhs who have undergone the ''Amrit Sanchar'' ('baptism by Khanda (Sikh symbol), Khanda'), an initiation ceremony, are from the day of thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tesco
Tesco plc () is a British multinational groceries and general merchandise retailer headquartered in Welwyn Garden City, England. In 2011 it was the third-largest retailer in the world measured by gross revenues and the ninth-largest in the world measured by revenues. It has shops in Ireland, the United Kingdom, the Czech Republic, Hungary and Slovakia. It is the market leader of groceries in the UK (where it has a market share of around 28.4%). Tesco has expanded globally since the early 1990s, with operations in 11 other countries in the world. The company pulled out of the US in 2013, but continues to see growth elsewhere. Since the 1960s, Tesco has diversified into areas such as the retailing of books, clothing, electronics, furniture, toys, petrol, software, financial services, telecoms and internet services. In the 1990s, Tesco re-positioned itself from being a downmarket high-volume low-cost retailer, attempting to attract a range of social groups with its low-cost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roughcast
Roughcast or pebbledash is a coarse plaster surface used on outside walls that consists of lime and sometimes cement mixed with sand, small gravel and often pebbles or shells. The materials are mixed into a slurry and are then thrown at the working surface with a trowel or scoop. The idea is to maintain an even spread, free from lumps, ridges or runs and without missing any background. Roughcasting incorporates the stones in the mix, whereas pebbledashing adds them on top. According to the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' Eleventh Edition (1910–1911), roughcast had been a widespread exterior coating given to the walls of common dwellings and outbuildings, but it was then frequently employed for decorative effect on country houses, especially those built using timber framing (half timber). Variety can be obtained on the surface of the wall by small pebbles of different colours, and in the Tudor period fragments of glass were sometimes embedded. Though it is an occasional home-de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Housing Cooperative
A housing cooperative, or housing co-op, is a legal entity, usually a cooperative or a corporation, which owns real estate, consisting of one or more residential buildings; it is one type of housing tenure. Housing cooperatives are a distinctive form of home ownership that have many characteristics that differ from other residential arrangements such as single family home ownership, condominiums and renting. The corporation is membership based, with membership granted by way of a share purchase in the cooperative. Each shareholder in the legal entity is granted the right to occupy one housing unit. A primary advantage of the housing cooperative is the pooling of the members' resources so that their buying power is leveraged; thus lowering the cost per member in all the services and products associated with home ownership. Another key element in some forms of housing cooperatives is that the members, through their elected representatives, screen and select who may live in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Workers Cooperative
A worker cooperative is a cooperative owned and self-managed by its workers. This control may mean a firm where every worker-owner participates in decision-making in a democratic fashion, or it may refer to one in which management is elected by every worker-owner who each have one vote. History Worker cooperatives rose to prominence during the Industrial Revolution as part of the labour movement. As employment moved to industrial areas and job sectors declined, workers began organizing and controlling businesses for themselves. Worker cooperatives were originally sparked by "critical reaction to industrial capitalism and the excesses of the industrial revolution." Some worker cooperatives were designed to "cope with the evils of unbridled capitalism and the insecurities of wage labor". The philosophy that underpinned the cooperative movement stemmed from the socialist writings of thinkers including Robert Owen and Charles Fourier. Robert Owen, considered by many as the father o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
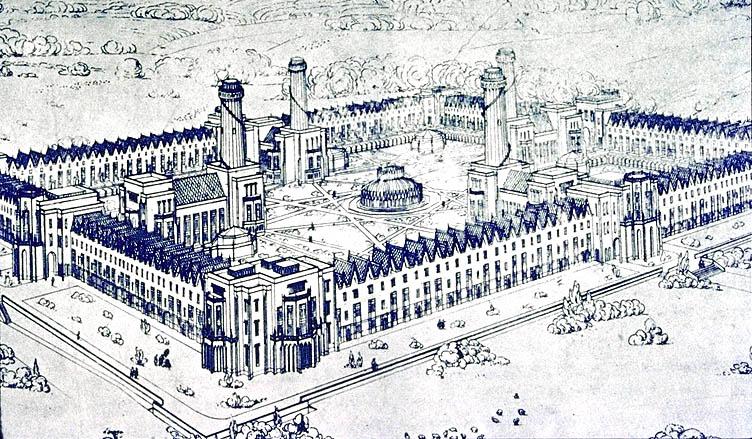
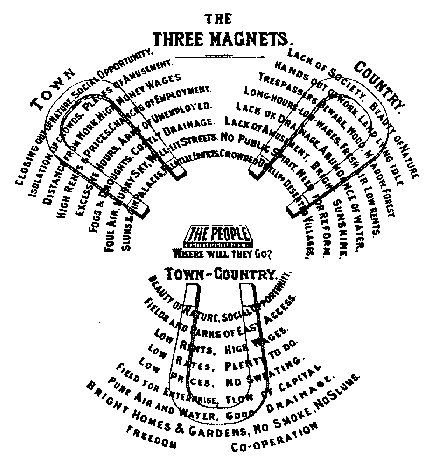
Garden City Movement
The garden city movement was a 20th century urban planning movement promoting satellite communities surrounding the central city and separated with greenbelts. These Garden Cities would contain proportionate areas of residences, industry, and agriculture. Ebenezer Howard first posited the idea in 1898 as a way to capture the primary benefits of the countryside and the city while avoiding the disadvantages presented by both. In the early 20th century, Letchworth, Brentham Garden Suburb and Welwyn Garden City were built in or near London according to Howard's concept and many other garden cities inspired by his model have since been built all over the world. History Conception Inspired by the utopian novel ''Looking Backward'' and Henry George's work ''Progress and Poverty'', Howard published the book '': a Peaceful Path to Real Reform'' in 1898 (which was reissued in 1902 as ''Garden Cities of To-morrow''). His idealised garden city would house 32,000 people on a site of , pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alabaster
Alabaster is a mineral or rock that is soft, often used for carving, and is processed for plaster powder. Archaeologists and the stone processing industry use the word differently from geologists. The former use it in a wider sense that includes varieties of two different minerals: the fine-grained massive type of gypsum and the fine-grained banded type of calcite.''More about alabaster and travertine'', brief guide explaining the different use of these words by geologists, archaeologists, and those in the stone trade. Oxford University Museum of Natural History, 2012/ref> Geologists define alabaster only as the gypsum type. Chemically, gypsum is a Water of crystallization, hydrous sulfur, sulfate of calcium, while calcite is a carbonate of calcium. The two types of alabaster have similar properties. They are usually lightly colored, translucent, and soft stones. They have been used throughout history primarily for carving decorative artifacts."Grove": R. W. Sanderson and Francis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |