|
Neskowin Ghost Forest
The Neskowin Ghost Forest is the remnants of a Sitka spruce forest on the Oregon Coast of the United States. The stumps were likely created when an earthquake of the Cascadia subduction zone abruptly lowered the trees, that were then covered by mud from landslides or debris from a tsunami. Many of the stumps are over 2,000 years old. The stumps were unearthed when turbulent storms swept away sand during the winter of 1997–1998. It is one of over thirty ghost forests along the Oregon and Washington Coast, though many appear as flat roots and not stumps. Most notably, Washington's ghost forest of red cedars was integral to the discovery of the Cascadia fault line. These ghost forests are evidence of significant, rapid changes in coastline – often due to seismic events such as the 1700 Cascadia earthquake. The stumps at Neskowin are 2,000 years old, according to carbon dating Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neskowin Ghost Forest - 2016
Neskowin is an unincorporated community in Tillamook County, Oregon, United States, along the Pacific Ocean between Cascade Head and Nestucca Bay. For statistical purposes, the United States Census Bureau has defined Neskowin as a census-designated place (CDP). The census definition of the area may not precisely correspond to local understanding of the area with the same name. The population of the CDP was 134 at the 2010 census, a decrease from 169 at the 2000 census. Geography Neskowin is located at (45.106502, -123.979306). According to the United States Census Bureau, the CDP has a total area of , all of it land. Demographics As of the census of 2000, there were 169 people, 94 households, and 47 families residing in the CDP. The population density was 117.3 people per square mile (45.3/km2). There were 408 housing units at an average density of 283.1 per square mile (109.4/km2). The racial makeup of the CDP was 94.08% White, 3.55% Native American, 0.59% Asian, 0.59% fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sitka Spruce
''Picea sitchensis'', the Sitka spruce, is a large, coniferous, evergreen tree growing to almost tall, with a trunk diameter at breast height that can exceed 5 m (16 ft). It is by far the largest species of spruce and the fifth-largest conifer in the world (behind Sequoiadendron giganteum, giant sequoia, Sequoia sempervirens, coast redwood, Agathis australis, kauri, and western red cedar), and the third-tallest conifer species (after coast redwood and Pseudotsuga menziesii var. menziesii, coast Douglas fir). The Sitka spruce is one of the few species List of superlative trees, documented to exceed in height. Its name is derived from the community of Sitka, Alaska, Sitka in southeast Alaska, where it is prevalent. Its range hugs the western coast of Canada and the US, continuing south into northernmost California. Description The Bark (botany), bark is thin and scaly, flaking off in small, circular plates across. The inner bark is reddish-brown. The crown is broad c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oregon Coast
The Oregon Coast is a coastal region of the U.S. state of Oregon. It is bordered by the Pacific Ocean to its west and the Oregon Coast Range to the east, and stretches approximately from the California state border in the south to the Columbia River in the north. The region is not a specific geological, environmental, or political entity, and includes the Columbia River Estuary. The Oregon Beach Bill of 1967 allows free beach access to everyone. In return for a pedestrian easement and relief from construction, the bill eliminates property taxes on private beach land and allows its owners to retain certain beach land rights. Traditionally, the Oregon Coast is regarded as three distinct sub–regions: * The North Coast, which stretches from the Columbia River to Cascade Head. * The Central Coast, which stretches from Cascade Head to Reedsport. * The South Coast, which stretches from Reedsport to the Oregon–California border. The largest city is Coos Bay, population 16,700 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
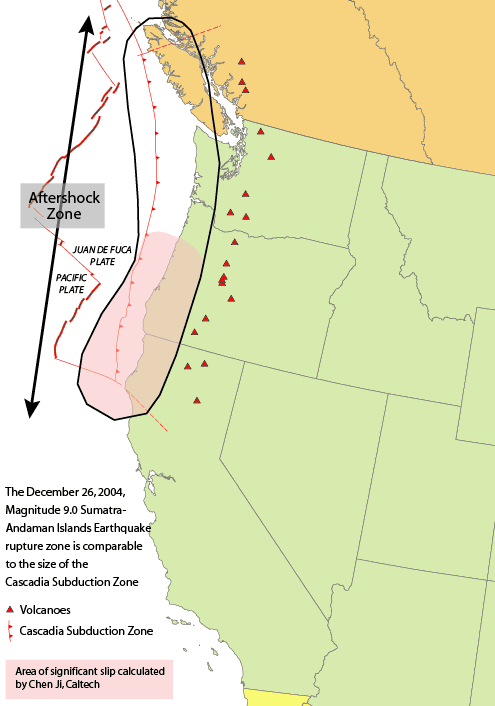
Cascadia Subduction Zone
The Cascadia subduction zone is a convergent plate boundary that stretches from northern Vancouver Island in Canada to Northern California in the United States. It is a very long, sloping subduction zone where the Explorer, Juan de Fuca, and Gorda plates move to the east and slide below the much larger mostly continental North American Plate. The zone varies in width and lies offshore beginning near Cape Mendocino, Northern California, passing through Oregon and Washington, and terminating at about Vancouver Island in British Columbia. The Explorer, Juan de Fuca, and Gorda plates are some of the remnants of the vast ancient Farallon Plate which is now mostly subducted under the North American Plate. The North American Plate itself is moving slowly in a generally southwest direction, sliding over the smaller plates as well as the huge oceanic Pacific Plate (which is moving in a northwest direction) in other locations such as the San Andreas Fault in central and southern Califo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
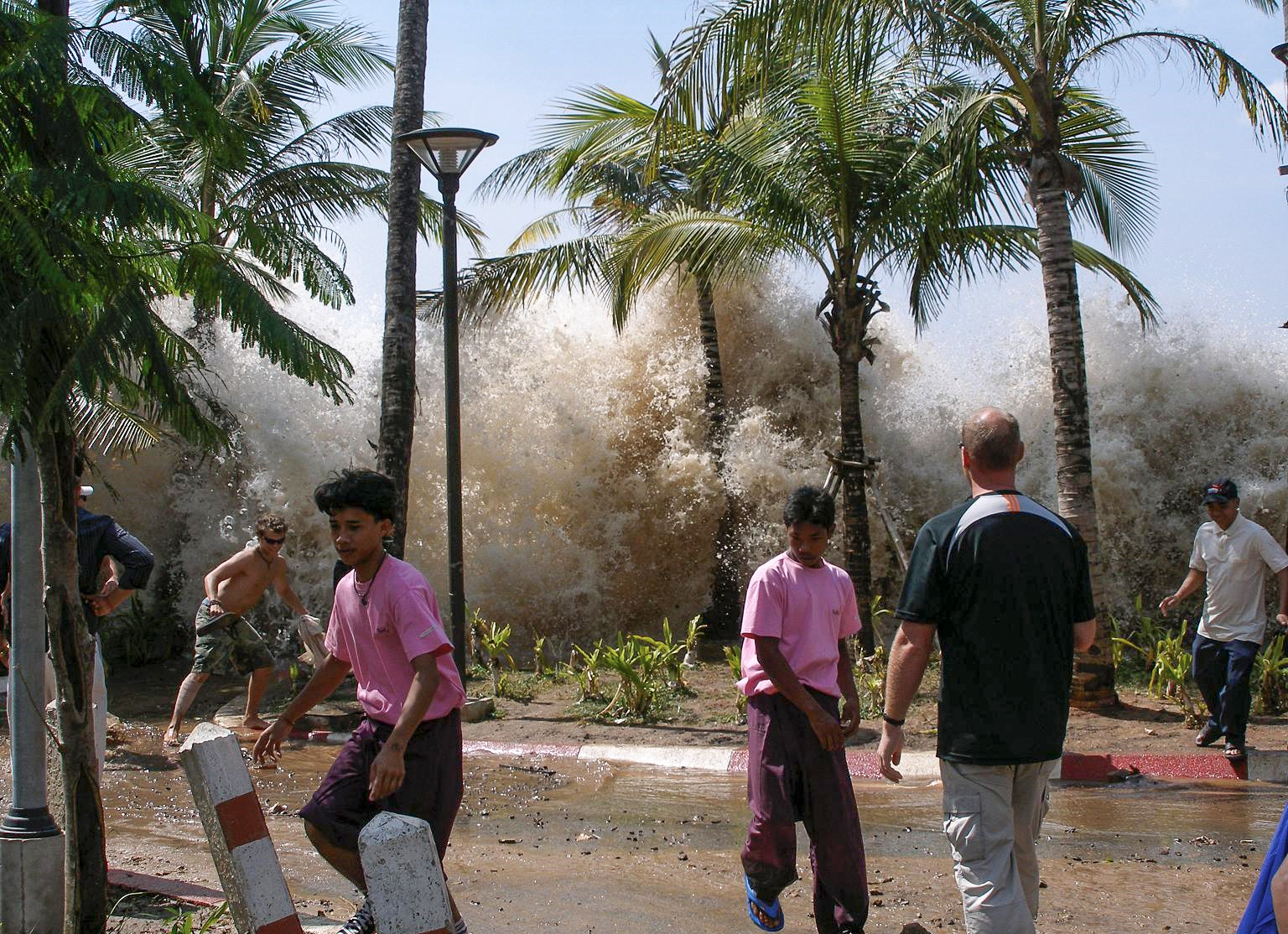
Tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explosions (including detonations, landslides, glacier calvings, meteorite impacts and other disturbances) above or below water all have the potential to generate a tsunami. Unlike normal ocean waves, which are generated by wind, or tides, which are in turn generated by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun, a tsunami is generated by the displacement of water from a large event. Tsunami waves do not resemble normal undersea currents or sea waves because their wavelength is far longer. Rather than appearing as a breaking wave, a tsunami may instead initially resemble a rapidly rising tide. For this reason, it is often referred to as a tidal wave, although this usage is not favoured by the scientific community because it might give ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghost Forest
Ghost forests are areas of dead trees in former forests, typically in coastal regions where rising sea levels or tectonic shifts have altered the height of a land mass. Forests located near the coast or estuaries may also be at risk of dying through saltwater poisoning, if invading seawater reduces the amount of freshwater that deciduous trees receive for sustenance. By looking at the stratigraphic record it is possible to reconstruct a series of events that lead to the creation of a ghost forest where, in a convergent plate boundary, there has been orogenic uplift, followed by earthquakes resulting in subsidence and tsunamis, altering the coast and creating a ghost forest. Formations Sea level changes When there is a change in sea level, coastal regions may become inundated with sea water. This can alter coastal areas and kill large areas of trees, leaving behind what is called a “ghost forest.” This type of ghost forest may develop in a variety of environments and in man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1700 Cascadia Earthquake
The 1700 Cascadia earthquake occurred along the Cascadia subduction zone on January 26, 1700, with an estimated moment magnitude of 8.7–9.2. The megathrust earthquake involved the Juan de Fuca Plate from mid-Vancouver Island, south along the Pacific Northwest coast as far as northern California. The length of the fault rupture was about , with an average slip of . The earthquake caused a tsunami which struck the west coast of North America and the coast of Japan. Japanese tsunami records, along with reconstructions of the wave moving across the ocean, put the earthquake at about 9pm on the evening of 26 January 1700. Evidence The earthquake took place at about 21:00 Pacific Time on January 26, 1700 ( NS). Although there are no written records for the region from the time, the timing of the earthquake has been inferred from Japanese records of a tsunami that does not correlate with any other Pacific Rim quake. The Japanese records exist primarily in the modern-day Iwate Pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon. The method was developed in the late 1940s at the University of Chicago by Willard Libby. It is based on the fact that radiocarbon () is constantly being created in the Earth's atmosphere by the interaction of cosmic rays with atmospheric nitrogen. The resulting combines with atmospheric oxygen to form radioactive carbon dioxide, which is incorporated into plants by photosynthesis; animals then acquire by eating the plants. When the animal or plant dies, it stops exchanging carbon with its environment, and thereafter the amount of it contains begins to decrease as the undergoes radioactive decay. Measuring the amount of in a sample from a dead plant or animal, such as a piece of wood or a fragment of bone, provides information that can be used to calc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proposal Rock (Oregon)
Proposal Rock is an island off the coast of the U.S. state of Oregon, in Tillamook County, near the community of Neskowin. The island is named for a local legend of a sea captain taking his beloved there to propose to her.Ralph Friedman, ''In Search of Western Oregon'' (1990), p. 40. The proposal was from Charley Gage to Della Page sometime around 1900. Della's mother, Sarah, then dubbed it Proposal Rock to mark the occasion. Proposal Rock was originally called “Schlock” by the Native Americans who first lived there. See also *Neskowin Ghost Forest The Neskowin Ghost Forest is the remnants of a Sitka spruce forest on the Oregon Coast of the United States. The stumps were likely created when an earthquake of the Cascadia subduction zone abruptly lowered the trees, that were then covered by mu ... References External links * Pacific islands of Oregon Landforms of Tillamook County, Oregon Uninhabited islands of Oregon {{TillamookCountyOR-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neskowin Beach State Recreation Site
Neskowin Beach State Recreation Site is a state park in Tillamook County, Oregon, United States, administered by the Oregon Parks and Recreation Department. See also * List of Oregon state parks *Neskowin Ghost Forest *Neskowin, Oregon References External links * State parks of Oregon Beaches of Oregon Landforms of Oregon Oregon Swimming venues in Oregon Tourist attractions in Oregon Oregon Oregon () is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundar ... Parks in Tillamook County, Oregon Landforms of Tillamook County, Oregon {{TillamookCountyOR-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |