|
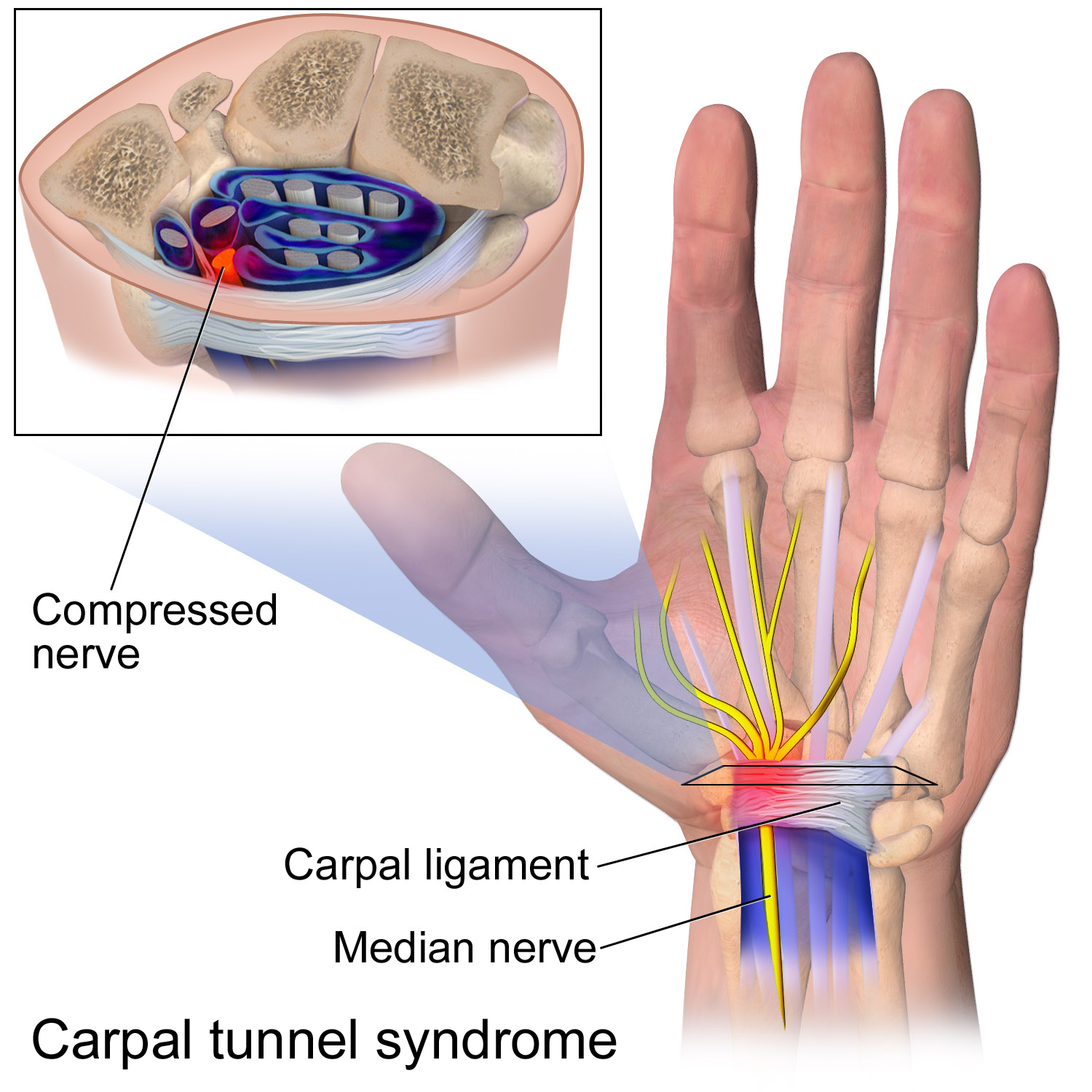
Nerve Glide
Nerve glide, also known as nerve flossing or nerve stretching, is an exercise that stretches nerves. It facilitates the smooth and regular movement of peripheral nerves in the body. It allows the nerve to glide freely along with the movement of the joint and relax the nerve from compression. Nerve gliding cannot proceed with injuries or inflammations as the nerve is trapped by the tissue surrounding the nerve near the joint. Thus, nerve gliding exercise is widely used in rehabilitation programs and during the post-surgical period. Radial, median, sciatic, and ulnar nerves require nerve gliding exercise during the rehabilitation period. The most common conditions that require nerve gliding exercise are carpal tunnel syndrome, cubital tunnel syndrome, radial neuropathy, and so on. Therapists prescribe different nerve gliding exercises in order to maximize the effects by correctly diagnosing the symptoms. Patients feel less pain when there is stretch in nerves, and there should ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system. A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses called action potentials that are transmitted along each of the axons to peripheral organs or, in the case of sensory nerves, from the periphery back to the central nervous system. Each axon, within the nerve, is an extension of an individual neuron, along with other supportive cells such as some Schwann cells that coat the axons in myelin. Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the endoneurium. The axons are bundled together into groups called fascicles, and each fascicle is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the perineurium. Finally, the entire nerve is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the epineurium. Nerve cells (often called neurons) are f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sciatica
Sciatica is pain going down the leg from the lower back. This pain may go down the back, outside, or front of the leg. Onset is often sudden following activities like heavy lifting, though gradual onset may also occur. The pain is often described as shooting. Typically, symptoms are only on one side of the body. Certain causes, however, may result in pain on both sides. Lower back pain is sometimes present. Weakness or numbness may occur in various parts of the affected leg and foot. About 90% of sciatica is due to a spinal disc herniation pressing on one of the lumbar or sacral nerve roots. Spondylolisthesis, spinal stenosis, piriformis syndrome, pelvic tumors, and pregnancy are other possible causes of sciatica. The straight-leg-raising test is often helpful in diagnosis. The test is positive if, when the leg is raised while a person is lying on their back, pain shoots below the knee. In most cases medical imaging is not needed. However, imaging may be obtained if bowel or blad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Range Of Motion
Range of motion (or ROM), is the linear or angular distance that a moving object may normally travel while properly attached to another. It is also called range of travel (or ROT), particularly when talking about mechanical devices and in mechanical engineering fields. For example, a sound volume control knob. As used in the biomedical field and by weightlifters, range of motion refers to the distance and direction a joint can move between the flexed position and the extended position. The act of attempting to increase this distance through therapeutic exercises (range of motion therapy—stretching from flexion to extension for physiological gain) is also sometimes called range of motion. Measuring range of motion Each specific joint has a normal range of motion that is expressed in degrees. The reference values for the normal ROM in individuals differ slightly depending on age and gender. For example, as an individual ages, they typically lose a small amount of ROM. Analog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, patient education, physical intervention, rehabilitation, disease prevention, and health promotion. Physical therapists are known as physiotherapists in many countries. In addition to clinical practice, other aspects of physical therapist practice include research, education, consultation, and health administration. Physical therapy is provided as a primary care treatment or alongside, or in conjunction with, other medical services. In some jurisdictions, such as the United Kingdom, physical therapists have the authority to prescribe medication. Overview Physical therapy addresses the illnesses or injuries that limit a person's abilities to move and perform functional activities in their daily lives. PTs use an individual's history and physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-level Laser Therapy
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT), cold laser therapy, or photobiomodulation (PBM) is a form of medicine that applies low-level (low-power) lasers or light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to the surface of the body. Whereas high-power lasers are used in laser medicine to cut or destroy tissue, it is claimed that application of low-power lasers relieves pain or stimulates and enhances cell function. The effects appear to be limited to a specified set of wavelengths, and administering LLLT below the dose range does not appear to be effective. Mechanism Research is ongoing about the mechanism of LLLT. The effects of LLLT appear to be limited to a specified set of wavelengths of laser, and administering LLLT below the dose range does not appear to be effective. Photochemical reactions are well known in biological research, and LLLT make use of the first law in photochemistry ( Grotthuss-Draper law): light must be absorbed by a chemical substance in order for a photochemical reaction to take p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Stretching
Stretching is a form of physical exercise in which a specific muscle or tendon (or muscle group) is deliberately flexed or stretched in order to improve the muscle's felt elasticity and achieve comfortable muscle tone. The result is a feeling of increased muscle control, flexibility, and range of motion. Stretching is also used therapeutically to alleviate cramps and to improve function in daily activities by increasing range of motion. In its most basic form, stretching is a natural and instinctive activity; it is performed by humans and many other animals. It can be accompanied by yawning. Stretching often occurs instinctively after waking from sleep, after long periods of inactivity, or after exiting confined spaces and areas. Not only vertebrates (mammals and birds), but also spiders were found to exhibit stretching in 2021. Increasing flexibility through stretching is one of the basic tenets of physical fitness. It is common for athletes to stretch before (for warming up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static Stretching
Stretching is a form of physical exercise in which a specific muscle or tendon (or muscle group) is deliberately flexed or stretched in order to improve the muscle's felt elasticity and achieve comfortable muscle tone. The result is a feeling of increased muscle control, flexibility, and range of motion. Stretching is also used therapeutically to alleviate cramps and to improve function in daily activities by increasing range of motion. In its most basic form, stretching is a natural and instinctive activity; it is performed by humans and many other animals. It can be accompanied by yawning. Stretching often occurs instinctively after waking from sleep, after long periods of inactivity, or after exiting confined spaces and areas. Not only vertebrates (mammals and birds), but also spiders were found to exhibit stretching in 2021. Increasing flexibility through stretching is one of the basic tenets of physical fitness. It is common for athletes to stretch before (for warming up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue is found in between other tissues everywhere in the body, including the nervous system. The three meninges, membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord are composed of connective tissue. Most types of connective tissue consists of three main components: elastic and collagen fibers, ground substance, and cells. Blood, and lymph are classed as specialized fluid connective tissues that do not contain fiber. All are immersed in the body water. The cells of connective tissue include fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells and leucocytes. The term "connective tissue" (in German, ''Bindegewebe'') was introduced in 1830 by Johannes Peter Müller. The tissue was already recognized as a distinct class in the 18th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough, high-tensile-strength band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It is able to transmit the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system without sacrificing its ability to withstand significant amounts of tension. Tendons are similar to ligaments; both are made of collagen. Ligaments connect one bone to another, while tendons connect muscle to bone. Structure Histologically, tendons consist of dense regular connective tissue. The main cellular component of tendons are specialized fibroblasts called tendon cells (tenocytes). Tenocytes synthesize the extracellular matrix of tendons, abundant in densely packed collagen fibers. The collagen fibers are parallel to each other and organized into tendon fascicles. Individual fascicles are bound by the endotendineum, which is a delicate loose connective tissue containing thin collagen fibrils and elastic fibres. Groups of fascicles are bounded by the epitenon, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamstring
In human anatomy, a hamstring () is any one of the three posterior thigh muscles in between the hip and the knee (from medial to lateral: semimembranosus, semitendinosus and biceps femoris). The hamstrings are susceptible to injury. In quadrupeds, the hamstring is the single large tendon found behind the knee or comparable area. Criteria The common criteria of any hamstring muscles are: # Muscles should originate from ischial tuberosity. # Muscles should be inserted over the knee joint, in the tibia or in the fibula. # Muscles will be innervated by the tibial branch of the sciatic nerve. # Muscle will participate in flexion of the knee joint and extension of the hip joint. Those muscles which fulfill all of the four criteria are called true hamstrings. The adductor magnus reaches only up to the adductor tubercle of the femur, but it is included amongst the hamstrings because the tibial collateral ligament of the knee joint morphologically is the degenerated tendon of this muscl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elbow Flexion
The elbow is the region between the arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa (also called the chelidon, or the elbow pit), and the lateral and the medial epicondyles of the humerus. The elbow joint is a hinge joint between the arm and the forearm; more specifically between the humerus in the upper arm and the radius and ulna in the forearm which allows the forearm and hand to be moved towards and away from the body. The term ''elbow'' is specifically used for humans and other primates, and in other vertebrates forelimb plus joint is used. The name for the elbow in Latin is ''cubitus'', and so the word cubital is used in some elbow-related terms, as in ''cubital nodes'' for example. Structure Joint The elbow joint has three different portions surrounded by a common joint capsule. These are joints between the three bones of the elbow, the humerus of the upper arm, and the radius and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulnar Nerve Entrapment
Ulnar nerve entrapment is a condition where the ulnar nerve becomes physically trapped or pinched, resulting in pain, numbness, or weakness, primarily affecting the little finger and ring finger of the hand. Entrapment may occur at any point from the spine at cervical vertebra C7 to the wrist; the most common point of entrapment is in the elbow (Cubital tunnel syndrome). Prevention is mostly through correct posture and avoiding repetitive or constant strain (e.g. "cell phone elbow"). Treatment is usually conservative, including medication, activity modification, and exercise, but may sometimes include surgery. Prognosis is generally good, with mild to moderate symptoms often resolving spontaneously. Signs and symptoms In general, ulnar neuropathy will result in symptoms in a specific anatomic distribution, affecting the little finger, the ulnar half of the ring finger, and the intrinsic muscles of the hand. The specific symptoms experienced in the characteristic distribution d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |