|
Neofusicoccum Australe
''Neofusicoccum australe'' is a fungus species in the genus ''Neofusicoccum''. It is responsible for a grapevine trunk disease. A 2009 survey of endophytic fungi on woody species at two tuart woodlands of Southwest Australia (ecoregion), sampling acacia '' Acacia cochlearis'', '' A. rostellifera'', the sheoak ''Allocasuarina fraseriana'', peppermint ''Agonis flexuosa'', ''Banksia grandis'', ''Eucalyptus marginata'', sandalwood ''Santalum acuminatum'' and nominate species ''Corymbia calophylla'' (tuart), found around three quarters of isolates were taxa of the family Botryosphaeriaceae The Botryosphaeriaceae are a family of sac fungi (Ascomycetes), which is the type representative of the order Botryosphaeriales. According to a 2008 estimate, the family contains 26 genera and over 1500 species. Members of this order include not ..., eighty percent of which was this species. References External links * * Botryosphaeriaceae Fungi described in 2004 Grapevine trunk di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neofusicoccum
''Neofusicoccum'' is a genus of fungi in the family Botryosphaeriaceae. Species *''Neofusicoccum andinum'' *''Neofusicoccum arbuti'' *''Neofusicoccum australe'' *''Neofusicoccum carallia'' *''Neofusicoccum cordaticola'' *''Neofusicoccum corticosae'' *''Neofusicoccum eucalypticola'' *''Neofusicoccum eucalyptorum'' *''Neofusicoccum grevilleae'' *''Neofusicoccum kwambonambiense'' *''Neofusicoccum luteum'' *''Neofusicoccum macroclavatum'' *''Neofusicoccum mangiferae'' *''Neofusicoccum mediterraneum'' *''Neofusicoccum nonquaesitum'' *''Neofusicoccum occulatum'' *''Neofusicoccum parvum'' *''Neofusicoccum pennatisporum'' *''Neofusicoccum protearum'' *''Neofusicoccum ribis'' *''Neofusicoccum umdonicola'' *''Neofusicoccum viticlavatum'' *''Neofusicoccum vitifusiforme'' References External links * Botryosphaeriaceae Dothideomycetes genera {{Dothideomycetes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grapevine Trunk Disease
Grapevine trunk diseases (GTD) are the most destructive diseases of vineyards worldwide. Fungicides (such as sodium arsenite or 8-hydroxyquinoline, used to fight esca) with the potential to control GTD have been banned in Europe and there are no highly effective treatments available. Action to develop new strategies to fight these diseases are needed. The following fungal species are responsible for grapevine trunk diseases: * ''Botryosphaeria dothidea'' and other ''Botryosphaeria'' species, such as '' B. obtusa'', '' B. parva'' and '' B. australis'',Botryosphaeria spp. as grapevine trunk disease pathogens. Niekerk, J.M, P.H. Fourie, F. Halleen and P.W. Crous, Phytopathologia Mediterranea, 2006, volume 45, pages 43-54 * ''Cylindrocarpon'' spp., ''Ilyonectria'' spp., ''Dactylonectria'' spp. and ''Campylocarpon'' spp.Occurrence of grapevine trunk disease pathogens in rootstock mother plants in South Africa. P. H. Fourie and F. Halleen, Australasian Plant Pathology, June 2004, Volume 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endophytic
An endophyte is an endosymbiont, often a bacterium or fungus, that lives within a plant for at least part of its life cycle without causing apparent disease. Endophytes are ubiquitous and have been found in all species of plants studied to date; however, most of the endophyte/plant relationships are not well understood. Some endophytes may enhance host growth, nutrient acquisition and improve the plant's ability to tolerate abiotic stresses, such as drought and decrease biotic stresses by enhancing plant resistance to insects, pathogens and herbivores. Although endophytic bacteria and fungi are frequently studied, endophytic archaea are increasingly being considered for their role in plant growth promotion as part of the core microbiome of a plant. History Endophytes were first described by the German botanist Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link in 1809. They were thought to be plant parasitic fungi and they were later termed as "microzymas" by the French scientist Béchamp. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwest Australia (ecoregion)
Southwest Australia is a biogeographic region in Western Australia. It includes the Mediterranean-climate area of southwestern Australia, which is home to a diverse and distinctive flora and fauna. The region is also known as the Southwest Australia Global Diversity Hotspot, as well as Kwongan. Geography The region includes the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub ecoregions of Western Australia. The region covers 356,717 km2, consisting of a broad coastal plain 20-120 kilometres wide, transitioning to gently undulating uplands made up of weathered granite, gneiss and laterite. Bluff Knoll in the Stirling Range is the highest peak in the region, at 1,099 metres (3,606 ft) elevation. Desert and xeric shrublands lie to the north and east across the centre of Australia, separating Southwest Australia from the other Mediterranean and humid-climate regions of the continent. Climate The region has a wet-winter, dry-summer Mediterranean climate, one of five such regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acacia Cochlearis
''Acacia cochlearis'', commonly known as the rigid wattle, is a shrub of the genus ''Acacia'' and the subgenus ''Plurinerves''. It is native to an area along the coast from the Goldfields-Esperance to the Mid West regions of Western Australia. Description The bushy erect pungent shrub typically grows to a height of with branchlets that are ribbed, glabrous or sparsely appressed-puberulous with straight hairs. Stipules are present only on young fresh shoots. The trunk and branches have smooth green or brown bark. The leathery leaves have phyllodes or are sessile, patent to ascending, inequilateral basally, subulate-linear, elliptic in shape and straight to recurved. They are mostly in length and wide. It blooms from July to October and produces yellow flowers. The inflorescences are simple with 1–3 per axil and peduncles which are long, Heads are globular with a diameter, containing 30-50-flowers that have a deep golden color. The flowers are pollinated by many differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acacia Rostellifera
''Acacia rostellifera'', commonly known as summer-scented wattle or skunk tree, is a coastal tree or small tree in the family Fabaceae. Endemic to Western Australia, it occurs along the west coast as far north as Kalbarri in the Southwest Australia savanna ecoregion, and along the south coast as far east as Israelite Bay. The summer-scented wattle generally reproduces by suckers from underground stems. Because of this suckering, the species often forms thickets that exclude all other species. The tallest ''Acacia'' of its area, it can grow to 10 metres. Specimens above 3 metres are not often seen, however, as bushfires A wildfire, forest fire, bushfire, wildland fire or rural fire is an unplanned, uncontrolled and unpredictable fire in an area of combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identif ... occur often in its area. Fire burns the plants right to the ground, but the underground stem resprouts vigo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allocasuarina Fraseriana
''Allocasuarina fraseriana'', commonly known as western sheoak, common sheoak, WA sheoak. Fraser's sheoak or just sheoak, is a tree in the family Casuarinaceae. Endemic to Western Australia, it occurs near the coast in the south west corner of the State, from Jurien (30° S) to Albany (35° S). The Noongar peoples know the tree as kondil.condil, kulli or gulli. Description In ideal conditions, Western Sheoak grows to a height of about . Where exposed to salty coastal breezes, however, it is usually somewhat smaller. It usually has a diameter of at breast height. As with other ''Allocasuarina'' species, its "foliage" consists of slender green branchlets informally referred to as "needles" but more correctly termed cladodes. The cladodes are segmented, and the true leaves are tiny teeth encircling each joint. Male trees have small brown flower spikes at the end of branchlets. Flowering is prolific, giving male trees a rusty brown hue during flowering in late winter and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agonis Flexuosa
''Agonis flexuosa'' is a species of tree that grows in the south west of Western Australia. It is easily the most common of the ''Agonis'' species, and is one of the most recognisable trees of Western Australia, being commonly grown in parks and on road verges in Perth. The species is commonly known as Western Australian peppermint, Swan River peppermint or peppermint, and willow myrtle for its weeping habit. The Noongar peoples know the tree as Wanil, Wonnow, Wonong or Wannang. Description ''A. flexuosa'' occurs mainly as a small and robust tree, usually less than 10 metres tall, although it may grow to 15 metres. It has fibrous brown bark, long narrow dull-green leaves, and tightly clustered inflorescences of small white flowers in the axes. It grows in a weeping habit, and looks remarkably like the weeping willow from a distance. Leaves are narrow and reach a length of 150mm. It is most readily identified by the powerful odour of peppermint emitted when the leaves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
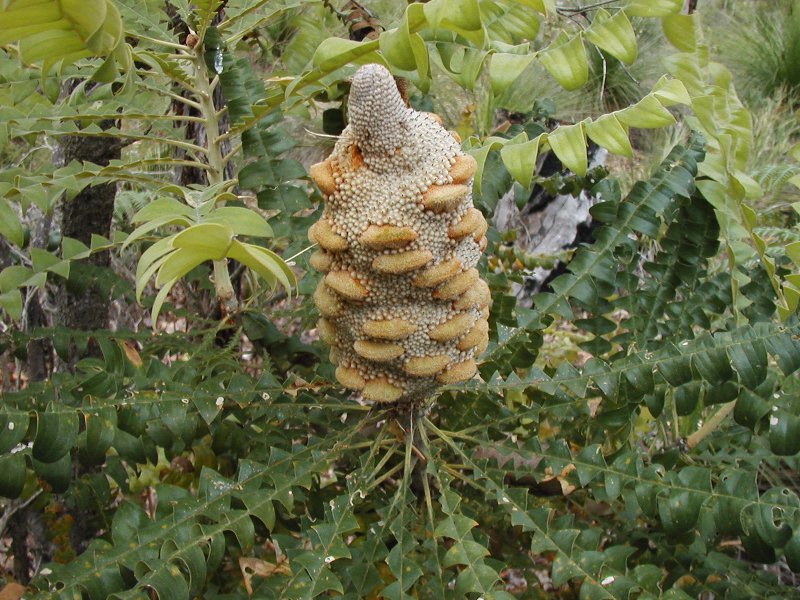
Banksia Grandis
''Banksia grandis'', commonly known as bull banksia or giant banksia, is a species of common and distinctive tree in the south-west of Western Australia. The Noongar peoples know the tree as beera, biara, boongura, gwangia, pira or peera. It has a fire-resistant main stem with thick bark, pinnatisect leaves with triangular side-lobes, pale yellow flowers and elliptical follicles in a large cone. Description ''Banksia grandis'' is usually a tree that typically grows to a height of high, sometimes to . It is also found in the form of a stunted, spreading shrub near the south coast, and whenever it occurs among granite rocks. Its trunks are short, stout and often crooked, with the rough grey bark characteristic of ''Banksia''. The leaves are pinnatisect long and wide on a petiole long, with between eight an twelve large triangular lobes on each side of the leaf. The leaves are shiny dark green on the upper surface and softy-hairy underneath. The flowers are borne in a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eucalyptus Marginata
''Eucalyptus marginata'', commonly known as jarrah, djarraly in Noongar language and historically as Swan River mahogany, is a plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a tree with rough, fibrous bark, leaves with a distinct midvein, white flowers and relatively large, more or less spherical fruit. Its hard, dense timber is insect resistant although the tree is susceptible to dieback. The timber has been utilised for cabinet-making, flooring and railway sleepers. Description Jarrah is a tree which sometimes grows to a height of up to with a diameter at breast height (DBH) of , but more usually with a DBH of up to . Less commonly it can be a small mallee to 3 m. Older specimens have a lignotuber and roots that extend down as far as . It is a stringybark with rough, greyish-brown, vertically grooved, fibrous bark which sheds in long flat strips. The leaves are arranged alternately along the branches, narrow lance-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santalum Acuminatum
''Santalum acuminatum'', the desert quandong, is a hemiparasitic plant in the sandalwood family, Santalaceae, (Native to Australia) which is widely dispersed throughout the central deserts and southern areas of Australia. The species, especially its edible fruit, is also commonly referred to as quandong or native peach. The use of the fruit as an exotic flavouring, one of the best known bush tucker (bush food), has led to the attempted domestication of the species. Desert quandong is an evergreen tree, its fruit can be stewed to make pie filling for quandong pies or made into a fruit juice drink. The seed (kernel) inside the tough shell can be extracted to be crushed into a paste then be used on sore gums or an oral gum boil to ease the pain. In far-west New South Wales being one of the few drought-tolerant fruit trees around, many Aboriginal communities and local Australians that know about this fruit like to grow it. Description ''Santalum acuminatum'' grows as a tall shrub, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corymbia Calophylla
''Corymbia calophylla'', commonly known as marri, is a species of flowering plant in the family Myrtaceae and is endemic to the southwest of Western Australia. It is a tree or mallee with rough bark on part or all of the trunk, lance-shaped adult leaves, branched clusters of cup-shaped or pear-shaped flower buds, each branch with three or seven buds, white to pink flowers, and relatively large oval to urn-shaped fruit, colloquially known as ''honky nuts''. Marri wood has had many uses, both for Aboriginal people, and in the construction industry. Description ''Corymbia calophylla'' is a large tree, or a mallee in poor soil, and that typically grows to a height of , but can reach over . The largest known individual ''C. calophylla'' is tall, has a girth and a wood volume of . The trunk of the tree may become up to wide, the branches becoming large, thick and rambling. It has rough, tessellated, grey-brown to red-brown bark that extends over the length of the trunk and branc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |