|
Nenglish
Nepalese English ( ne, अङ्ग्रेजी) refers to a variety of the English language principally used in Nepal and is heavily influenced by the Indo-Aryan languages of Nepal. Many Nepalese speak English as a second or foreign language, with English use being most prevalent among city dwellers residing in Kathmandu (the capital of Nepal). Although Nepali is the native language, English is the primary language used for business in Nepal. In Nepal, where modern English education began in the 1850s, there is little or no consensus among teachers and practitioners on whether to follow British, American or Indian variants of English, or allow the development of a Nepal-specific variety of English. Colloquially Nepalese English is known as Nenglish (a term first recorded in 1999), or, less commonly, as ''Nepanglish'' (2000) or ''Neplish'' (2002). See also *Languages of Nepal *Nepali Language *Nepal *Gurung Language *Magar Language *Tamang Language *Limbu Language *Newar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne, सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, bordering the Tibet Autonomous Region of China to the north, and India in the south, east, and west, while it is narrowly separated from Bangladesh by the Siliguri Corridor, and from Bhutan by the Indian state of Sikkim. Nepal has a diverse geography, including fertile plains, subalpine forested hills, and eight of the world's ten tallest mountains, including Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth. Nepal is a multi-ethnic, multi-lingual, multi-religious and multi-cultural state, with Nepali as the official language. Kathmandu is the nation's capital and the largest city. The name "Nepal" is first recorded in texts from the Vedic period of the India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kathmandu
, pushpin_map = Nepal Bagmati Province#Nepal#Asia , coordinates = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , subdivision_type1 = Province , subdivision_name1 = Bagmati Province , subdivision_type2 = District , subdivision_name2 = Kathmandu , established_title = , founder = Manjushri , parts_type = No. of Wards , parts = 32 , seat_type = , seat = , government_footnotes = , government_type = Mayor–council government , governing_body = Kathmandu Metropolitan Government, , leader_title = Mayor , leader_name = Balendra Shah ( Ind.) , leader_title1 = Deputy mayor , leader_name1 = Sunita Dangol (UML) , leader_title2 = Executive Officer , leader_name2 = Basanta Adhikari , unit_pref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Attested From The 1850s
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of methods, including spoken, sign, and written language. Many languages, including the most widely-spoken ones, have writing systems that enable sounds or signs to be recorded for later reactivation. Human language is highly variable between cultures and across time. Human languages have the properties of productivity and displacement, and rely on social convention and learning. Estimates of the number of human languages in the world vary between and . Precise estimates depend on an arbitrary distinction (dichotomy) established between languages and dialects. Natural languages are spoken, signed, or both; however, any language can be encoded into secondary media using auditory, visual, or tactile stimuli – for example, writing, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newar Language
Newar (), or Newari and known officially in Nepal as Nepal Bhasa, is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken by the Newar people, the indigenous inhabitants of Nepal Mandala, which consists of the Kathmandu Valley and surrounding regions in Nepal. "Nepal Bhasa" literally means "Nepalese language", however the language is not the same as Nepali (Devanāgarī: नेपाली), the country's current official language of the central government. The two languages belong to different language families (Sino-Tibetan and Indo-European, respectively), but centuries of contact have resulted in a significant body of shared vocabulary. Newar was Nepal's administrative language from the 14th to the late 18th century. From the early 20th century until democratisation, Newar suffered from official suppression. From 1952 to 1991, the percentage of Newar speakers in the Kathmandu Valley dropped from 75% to 44% and today Newar culture and language are under threat. The language has been listed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
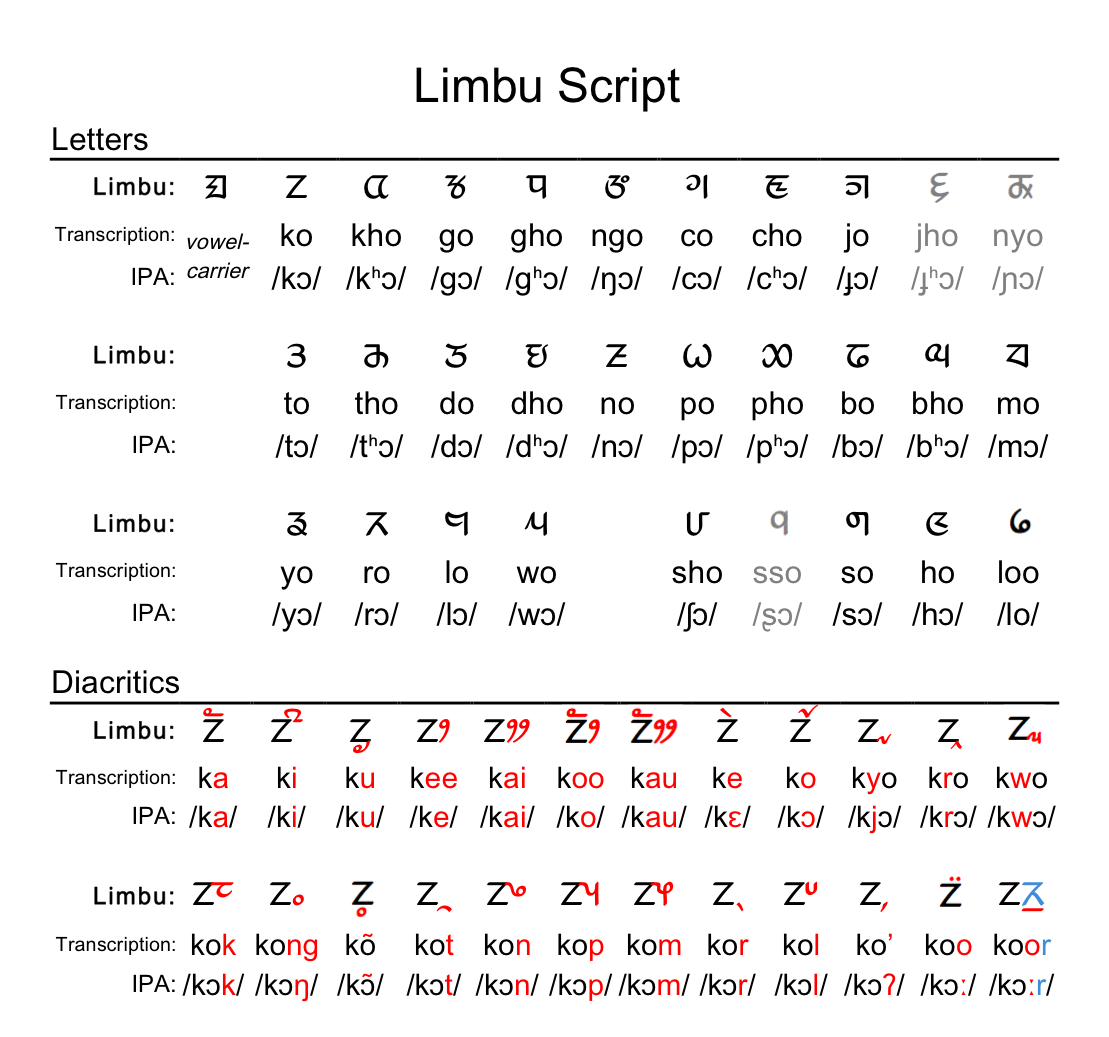
Limbu Language
Limbu (Limbu: , ''yakthuṅ pan'') is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken by the Limbu people of Nepal and Northeastern India (particularly Darjeeling, Kalimpong, Sikkim, Assam and Nagaland) as well as expatriate communities in Bhutan. The Limbu refer to themselves as ''Yakthung'' and their language as ''Yakthungpan.'' Yakthungpan has four main dialects: Phedape, Chhathare, Tambarkhole and Panthare dialects. Among four dialects and/or many dialects, the Phedape dialect is widely spoken and well understood by most Yakthungpan speakers. However, as there are some dominant Panthare scholars who have role to create knowledge and control knowledge in the Limbu communities, Panthare dialect is being popularised as a "standard" Limbu language. As Panthare Yakthungs are much more engaged in central political position and administrative positions, they are trying to introduce Panthare dialect as a Standard Yakthungpan. Yakthungpan (Limbu language) is one of the major languages spoken and wri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamang Language
Tamang (Devanagari: तामाङ; ''tāmāng'') is a term used to collectively refer to a dialect cluster spoken mainly in Nepal, Sikkim, West Bengal (Darjeeling) and North-Eastern India. It comprises Eastern Tamang, Northwestern Tamang, Southwestern Tamang, Eastern Gorkha Tamang, and Western Tamang. Lexical similarity between Eastern Tamang (which is regarded as the most prominent) and other Tamang languages varies between 81% to 63%. For comparison, lexical similarity between Spanish and Portuguese, is estimated at 89%. Ethnologue report for Spanish Dialects ''Ethnologue'' divides Tamang into the following varieties due to mutual unintelligibility. *Eastern Tamang: 759,000 in Nepal (2000 WCD). Population total all countries: 773,000. Sub-dialects are as follows. **Outer-Eastern Tamang (Sailung Tamang) **Central-Eastern Tamang (Temal Tamang) **Southwestern Tamang (Kath-Bhotiya, Lama Bhote, Murmi, Rongba, Sain, Tamang Gyoi, Tamang Gyot, Tamang Lengmo, Tamang Tam) *Western T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magar Language
Magar Dhut ( ne, मगर ढुट, ) is a Sino-Tibetan Language spoken mainly in Nepal, Southern Bhutan, and in Darjeeling and Sikkim, India, by the Magar people. It is divided into two groups (Eastern and Western) and further dialect divisions give distinct tribal identity. In Nepal 788,530 people speak the language. While the government of Nepal developed Magar language curricula, as provisioned by the constitution, the teaching materials have never successfully reached Magar schools, where most school instruction is in the Nepali language. It is not unusual for groups with their own language to feel that the "mother-tongue" is an essential part of identity. The Dhut Magar language is sometimes lumped with the Magar Kham language spoken further west in Bheri, Dhaulagiri, and Rapti zones. Although the two languages share many common words, they have major structural differences and are not mutually intelligible. Geographical distribution Western Magar Western Magar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gurung Language
Gurung (Devanagari: ), also known as Tamu Kyi (, ; Tibetan: ) or Tamu Bhaasaa (, ), is a language spoken by the Gurung people of Nepal. The total number of all Gurung speakers in Nepal was 227,918 in 1991 and 325,622 in 2011. The official language of Nepal, Nepali, is an Indo-European language, whereas Gurung is a Sino-Tibetan language. Gurung is one of the major languages of Nepal, and is also spoken in India, Bhutan, and by diaspora communities in countries such as Singapore and Hong Kong. Geographical distribution Gurung is spoken in the following districts of Nepal and India (''Ethnologue''): *Gandaki Province: Kaski District, Syangja District, Lamjung District, Tanahu District, Gorkha District, Manang District and Mustang *Dhawalagiri Zone: Parbat district *Sikkim: South Sikkim, West Sikkim, East Sikkim Classification At higher levels, Gurung is a member of the Tibeto-Burman (or Trans-Himalayan) family. Robert Shafer classified Gurung within the Bodic division, sub-gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
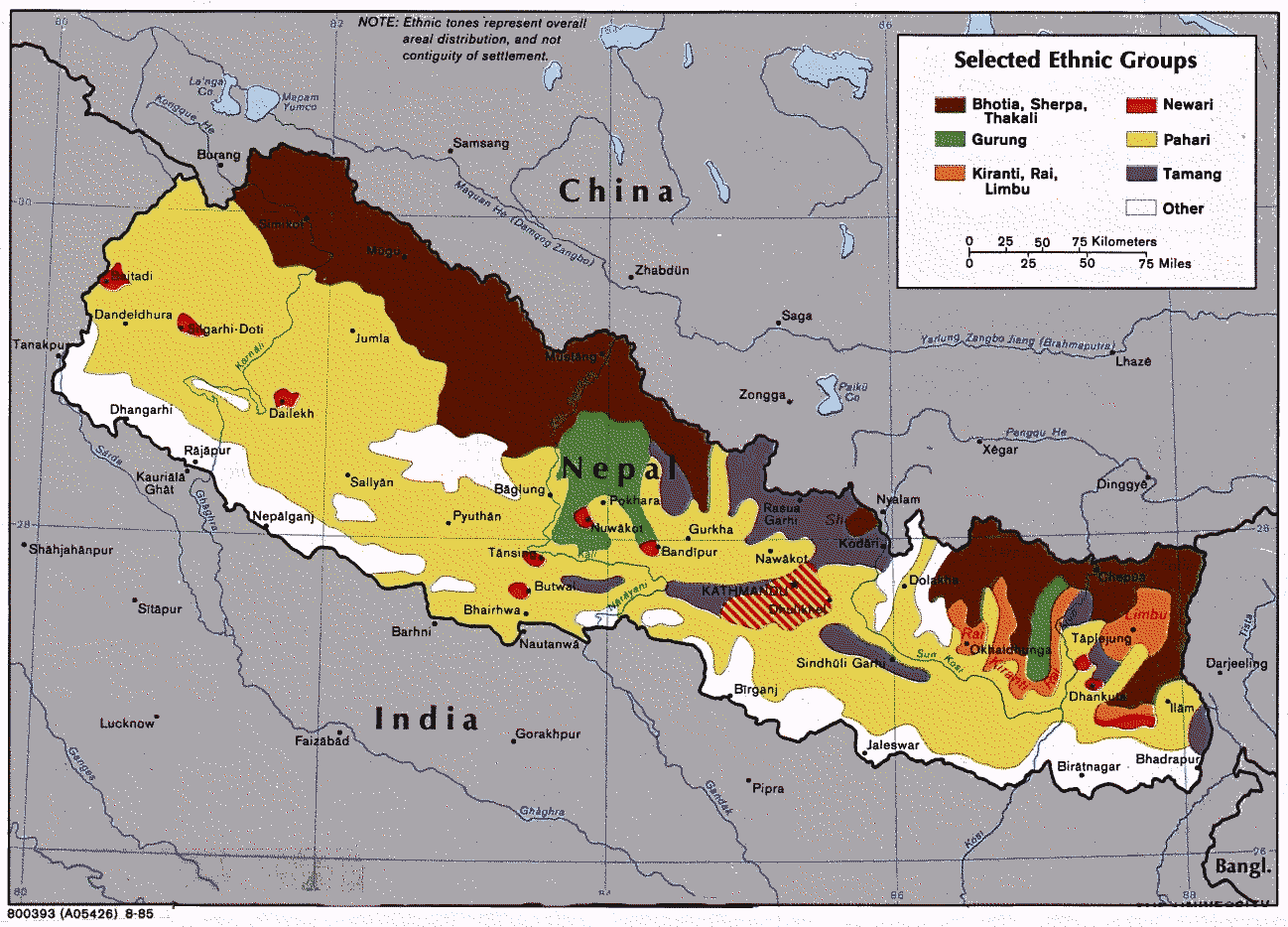
Languages Of Nepal
Languages of Nepal constitutionally called Nepalese languages are the languages having at least an ancient history or origin inside the sovereign territory of Nepal spoken by Nepalis. The 2011 National census lists 123 languages spoken as a mother tongue (first language) in Nepal. Most belong to the Indo-Aryan and Sino-Tibetan language families. The official working language at federal level is Nepali, but the constitution provisions each province to choose one or more additional official working languages. The Language Commission of Nepal on 6 Sept 2021 recommended 14 official languages for different provinces of Nepal. The mother languages of Nepal, or languages of Nepali origin are sometimes referred to as ''Nepali languages''. National languages According to the constitution of Nepal, "all languages spoken as the mother tongues in Nepal are the languages of the nation". Many of the languages also have various dialects. For example, the Rai community has about 30 languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian English
Indian English (IE) is a group of English dialects spoken in the republic of India and among the Indian diaspora. English is used by the Indian government for communication, along with Hindi, as enshrined in the Constitution of India. English is also an official language in seven states and seven union territories of India, and the additional official language in seven other states and one union territory. Furthermore, English is the sole official language of the Indian Judiciary, unless the state governor or legislature mandates the use of a regional language, or if the President of India has given approval for the use of regional languages in courts. Status After gaining independence from the British Raj in 1947, English remained an official language of the new Dominion of India and later the Republic of India. Only a few hundred thousand Indians, or less than 0.1% of the total population, speak English as their first language, and around 30% of the Indian populatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of variety (linguistics), varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the Languages of the United States, most widely spoken language in the United States and in most circumstances is the de facto common language used in government, education and commerce. Since the 20th century, American English has become the most influential form of English worldwide. American English varieties include many patterns of pronunciation, vocabulary, grammar and particularly spelling that are unified nationwide but distinct from other English dialects around the world. Any North American English, American or Canadian accent (sociolinguistics), accent perceived as lacking noticeably local, ethnic or cultural markedness, markers is popularly called General American, "General" or "Standard" American, a fairly uniform dialect continuum, accent continuum native to certain regions of the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Lexico, Oxford Dictionaries, "English language, English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in England, or, more broadly, to the collective dialects of English throughout the British Isles taken as a single umbrella variety, for instance additionally incorporating Scottish English, Welsh English, and Ulster English, Northern Irish English. Tom McArthur (linguist), Tom McArthur in the ''Oxford Guide to World English'' acknowledges that British English shares "all the ambiguities and tensions [with] the word 'British people, British' and as a result can be used and interpreted in two ways, more broadly or more narrowly, within a range of blurring and ambiguity". Variations exist in formal (both written and spoken) English in the United Kingdom. For example, the adjective ''wee'' is almost exclusively used in parts of Scotland, North E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |