|
National Energy Act
The National Energy Act of 1978 (NEA78) was a legislative response by the U.S. Congress to the 1973 energy crisis. It includes the following statutes: * Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act (PURPA) () * Energy Tax Act () * National Energy Conservation Policy Act (NECPA) () * Power Plant and Industrial Fuel Use Act () * Natural Gas Policy Act ({{USPL, 95, 621) The legislative initiative was introduced by President Carter. The package was a major step in the legislation of the energy field, both the supply and the demand side. The package has soon been followed by Energy Security Act, 8 acts signed by president Carter in 1980. This sequel package addressed energy conservation and development of renewable energy sources. The NEA78 and the "security" package established a framework for regulatory and market-based initiatives, energy efficiency programs, tax incentives, tax disincentives, energy conservation programs and alternative fuel programs. Most of the market-based mechani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
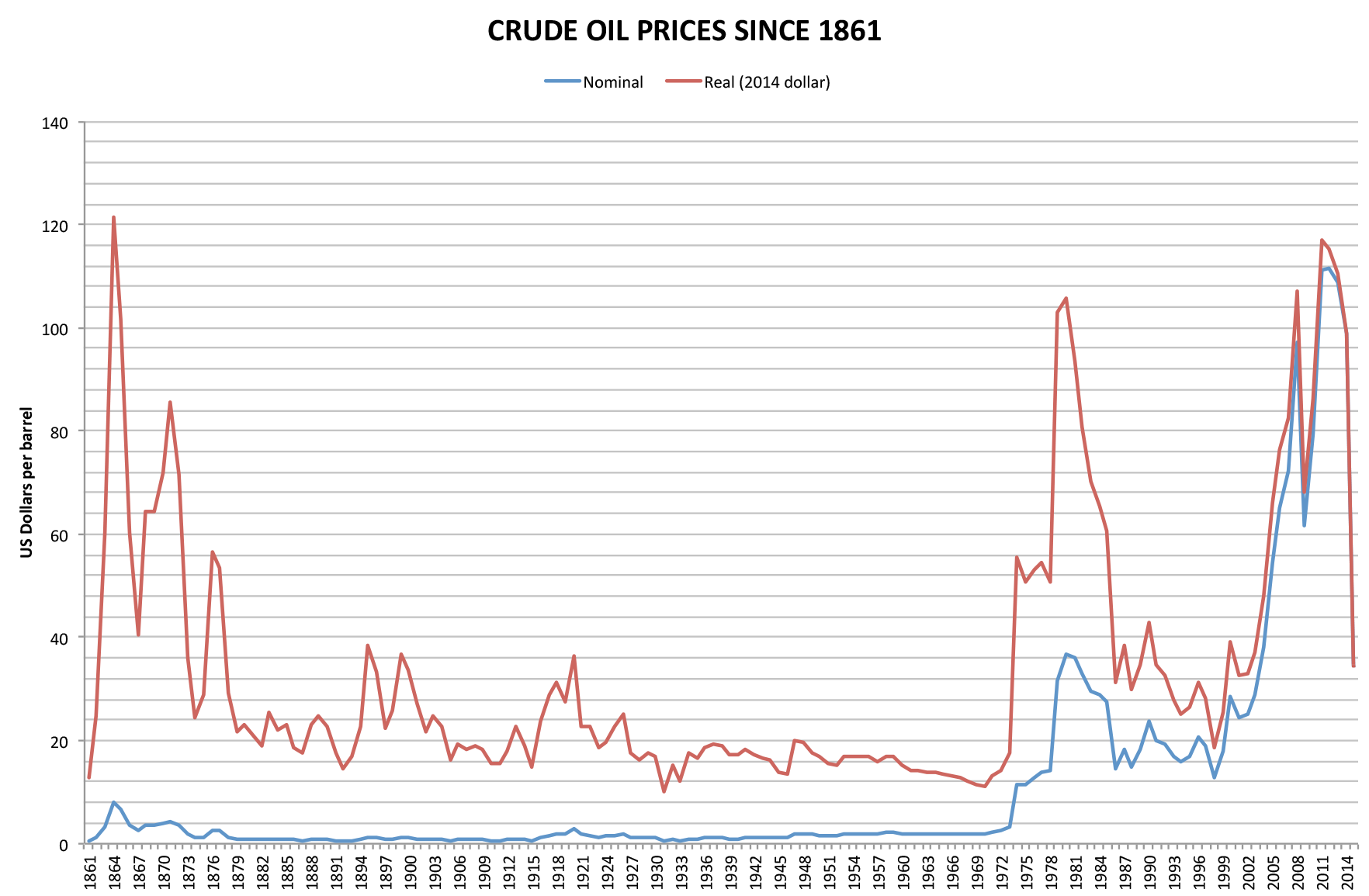
1973 Energy Crisis
The 1973 oil crisis or first oil crisis began in October 1973 when the members of the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC), led by Saudi Arabia, proclaimed an oil embargo. The embargo was targeted at nations that had supported Israel during the Yom Kippur War. The initial nations targeted were Canada, Japan, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom and the United States, though the embargo also later extended to Portugal, Rhodesia and South Africa. By the end of the embargo in March 1974, the price of oil had risen nearly 300%, from US to nearly globally; US prices were significantly higher. The embargo caused an oil crisis, or "shock", with many short- and long-term effects on global politics and the global economy. It was later called the "first oil shock", followed by the 1979 oil crisis, termed the "second oil shock". Background Arab-Israeli conflict Ever since the recreation of the State of Israel in 1948 there has been Arab–Israeli conflict in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulatory
Regulation is the management of complex systems according to a set of rules and trends. In systems theory, these types of rules exist in various fields of biology and society, but the term has slightly different meanings according to context. For example: * in biology, gene regulation and metabolic regulation allow living organisms to adapt to their environment and maintain homeostasis; * in government, typically regulation means stipulations of the delegated legislation which is drafted by subject-matter experts to enforce primary legislation; * in business, industry self-regulation occurs through self-regulatory organizations and trade associations which allow industries to set and enforce rules with less government involvement; and, * in psychology, self-regulation theory is the study of how individuals regulate their thoughts and behaviors to reach goals. Social Regulation in the social, political, psychological, and economic domains can take many forms: legal restrict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Policy Act Of 1992
The Energy Policy Act of 1992, effective October 24, 1992, (102nd Congress H.R.776.ENR, abbreviated as EPACT92) is a United States government act. It was passed by Congress and set goals, created mandates, and amended utility laws to increase clean energy use and improve overall energy efficiency in the United States. The Act consists of twenty-seven titles detailing various measures designed to lessen the nation's dependence on imported energy, provide incentives for clean and renewable energy, and promote energy conservation in buildings. Amendment of prior energy acts It reformed the Public Utility Holding Company Act of 1935 (PUHCA) to help small utility companies stay competitive with larger utilities and amended the Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act (PURPA) of 1978, broadening the range of resource choices for utility companies and outlined new rate-making standards. It also amended parts of the Federal Power Act of 1935 (Title VII). Titles The act addressed: *ener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Command And Control
Command and control (abbr. C2) is a "set of organizational and technical attributes and processes ... hatemploys human, physical, and information resources to solve problems and accomplish missions" to achieve the goals of an organization or enterprise, according to a 2015 definition by military scientists Marius Vassiliou, David S. Alberts, and Jonathan R. Agre. The term often refers to a military system. Versions of the United States Army ''Field Manual 3-0'' circulated circa 1999 define C2 in a military organization as the exercise of authority and direction by a properly designated commanding officer over assigned and attached forces in the accomplishment of a mission. A 1988 NATO definition is that command and control is the exercise of authority and direction by a properly designated individual over assigned resources in the accomplishment of a common goal. An Australian Defence Force definition, similar to that of NATO, emphasises that C2 is the system empowering des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternative Fuel
Alternative fuel, known as non-conventional and advanced fuels, are any materials or substances that can be used as fuels, other than conventional fuels like; ''fossil fuels'' (petroleum (oil), coal, and natural gas), as well as nuclear materials such as uranium and thorium, as well as artificial radioisotope fuels that are made in nuclear reactors. Some well-known alternative fuels include bio-diesel, bio-alcohol (methanol, ethanol, butane), refuse-derived fuel, chemically stored electricity (batteries and fuel cells), hydrogen, non-fossil methane, non-fossil natural gas, vegetable oil, propane and other biomass sources. Background A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as heat energy or to be used for work. The main purpose of fuel is to store energy, which should be in a stable form and can be easily transported to the place of use. Almost all fuels are chemical fuels. The user employs this fuel to generate heat o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Incentives
A tax incentive is an aspect of a government's taxation policy designed to incentivize or encourage a particular economic activity by reducing tax payments. Tax incentives can have both positive and negative impacts on an economy. Among the positive benefits, if implemented and designed properly, tax incentives can attract investment to a country. Other benefits of tax incentives include increased employment, higher number of capital transfers, research and technology development, and also improvement to less developed areas. Though it is difficult to estimate the effects of tax incentives, they can, if done properly, raise the overall economic welfare through increasing economic growth and government tax revenue (after the expiration of the tax holiday/incentive period). However, tax incentive can cause negative effects on a government's financial condition, among other negative effects, if they are not properly designed and implemented. There are four typical costs to tax ince ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efficient Energy Use
Efficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the process of reducing the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a building allows it to use less heating and cooling energy to achieve and maintain a thermal comfort. Installing light-emitting diode bulbs, fluorescent lighting, or natural skylight windows reduces the amount of energy required to attain the same level of illumination compared to using traditional incandescent light bulbs. Improvements in energy efficiency are generally achieved by adopting a more efficient technology or production process or by application of commonly accepted methods to reduce energy losses. There are many motivations to improve energy efficiency. Decreasing energy use reduces energy costs and may result in a financial cost saving to consumers if the energy savings offset any additional costs of implementing an energy-efficient technology. Reducing energy use is also seen as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market-based
A market economy is an economic system in which the decisions regarding investment, production and distribution to the consumers are guided by the price signals created by the forces of supply and demand, where all suppliers and consumers are unimpeded by price controls or restrictions on contract freedom. The major characteristic of a market economy is the existence of factor markets that play a dominant role in the allocation of capital and the factors of production. Market economies range from minimally regulated free-market and ''laissez-faire'' systems where state activity is restricted to providing public goods and services and safeguarding private ownership, to interventionist forms where the government plays an active role in serving special interests and promoting social welfare. State intervention can happen at the production, distribution, trade and consumption areas in the economy. The distribution of basic need services and goods like health care may be enti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy sources are sustainable, some are not. For example, some biomass sources are considered unsustainable at current rates of exploitation. Renewable energy often provides energy for electricity generation to a grid, air and water heating/ cooling, and stand-alone power systems. Renewable energy technology projects are typically large-scale, but they are also suited to rural and remote areas and developing countries, where energy is often crucial in human development. Renewable energy is often deployed together with further electrification, which has several benefits: electricity can move heat or objects efficiently, and is clean at the point of consumption. In addition, electrification with renewable energy is more efficient and therefore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act
The Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act (PURPA, ) is a United States Act passed as part of the National Energy Act. It was meant to promote energy conservation (reduce demand) and promote greater use of domestic energy and renewable energy (increase supply). The law was created in response to the 1973 energy crisis, and one year in advance of a second energy crisis. Upon entering the White House, President Jimmy Carter made energy policy a top priority. The law started the energy industry on the road to restructuring. Law PURPA was originally passed with the intention of conserving electric energy, increasing efficiency in facilities and resources used by utility companies, making retail rates for electric consumers more fair, speeding up the creation of hydroelectric energy production at small dams, and conserving natural gas. The main vehicle that the PURPA law used to try and accomplish these goals was by creating a new class of electric generating facilities called “q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Conservation
Energy conservation is the effort to reduce wasteful energy consumption by using fewer energy services. This can be done by using energy more effectively (using less energy for continuous service) or changing one's behavior to use less service (for example, by driving less). Energy conservation can be achieved through energy efficiency, which has a number of advantages, including a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, a smaller carbon footprint, and cost, water, and energy savings. Energy conservation is an essential factor in building design and construction. It has increased in importance since the 1970s, as 40% of energy use in the U.S. is in buildings. Recently, concern over the effects of climate change and global warming has emphasized the importance of energy conservation. Energy can only be transformed from one form to another, such as when heat energy is converted into vehicle motive power or when water flow's kinetic energy is converted into electricity in hydroelectr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Security Act
The Energy Security Act was signed into law by U.S. President Jimmy Carter on June 30, 1980. Thursday, 19 January 2017 It consisted of six major acts: * U.S. Synthetic Fuels Corporation Act * Biomass Energy and Alcohol Fuels Act * Renewable Energy Resources Act * Solar Energy and Energy Conservation Act * Solar Energy and Energy Conservation Bank Act * Geothermal Energy Act * Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion Act See also *Energy security *Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 The Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007Pub.L. 110-140, originally named the Clean Energy Act of 2007, is an Act of Congress concerning the energy policy of the United States. As part of the Democratic Party's 100-Hour Plan during th ... References DOE Timeline: 1971-1980 Department of EnergyPresident Carter and the Search for Synthetic Fossil Fuels {{Authority control 1980 in law 96th United States Congress United States federal energy legislation Energy security ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)