|
Napier Lioness
The Napier Lion is a 12-cylinder, petrol-fueled 'broad arrow' W12 configuration aircraft engine built by D. Napier & Son from 1917 until the 1930s. A number of advanced features made it the most powerful engine of its day and kept it in production long after other contemporary designs had been superseded. It is particularly well known for its use in a number of racing designs, for aircraft, boats and cars. Design and development Early in the First World War, Napier were contracted to build aero engines to designs from other companies, initially a Royal Aircraft Factory model and then Sunbeams. Both engines proved to be unreliable and in 1916 Napier decided to design an engine with high power, light weight and low frontal area. Napier's engineers laid out the engine with its 12 cylinders in what they called a "broad arrow"—three banks of four cylinders sharing a common crankcase. This suggested the design's first name, the Triple-Four. The configuration is also known as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Rowledge
Arthur John Rowledge, (30 July 1876 – 11 December 1957) was an English engineer who designed the Napier Lion aero engine and was a key figure in the development of the Rolls-Royce Merlin. Career Rowledge was born in Peterborough, Northamptonshire in 1876, the son of John and Ann Rowledge. His father was described as a bricklayer in 1881. 1881 Census of Peterborough, RG11/1594, Folio 20, Page 34, Arthur J Rowledge, 47 Gladstone Street, Peterborough. At the time of the 1891 census, Rowledge was described as an ''Apprentice to Engineers Draughtsman'' 1891 Census of Peterborough, RG12/1228, Folio 78, Page 33, Arthur John Rowledge, 118 Gladstone Street, Peterborough. and in 1901 he was in Erith, Kent boarding at Rose Hill Villas, Bexley Road and described as a ''Mechanical Draughtsman''. 1901 Census of Dartford, RG13/699, Folio 108, Page 46, Arthur Rowledge, Rose Heath Villas, Bexley Road, Erith, Kent. Arthur Rowledge joined D.Napier & Son in 1913 as Chief Designer. After design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolls-Royce R
The Rolls-Royce R is a British aero engine that was designed and built specifically for air racing purposes by Rolls-Royce Limited. Nineteen R engines were assembled in a limited production run between 1929 and 1931. Developed from the Rolls-Royce Buzzard, it was a 37-litre (2,240 cu in) capacity, supercharged V-12 capable of producing just under 2,800 horsepower (2,090 kW), and weighed 1,640 pounds (770 kg). Intensive factory testing revealed mechanical failures which were remedied by redesigning the components, greatly improving reliability. The R was used with great success in the Schneider Trophy seaplane competitions held in England in 1929 and 1931. Shortly after the 1931 competition, an R engine using a special fuel blend powered the winning Supermarine S.6B aircraft to a new airspeed record of over 400 miles per hour (640 km/h). Continuing through the 1930s, both new and used R engines were used to achieve various land and water sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supermarine
Supermarine was a British aircraft manufacturer that is most famous for producing the Supermarine Spitfire, Spitfire fighter plane during World War II as well as a range of seaplanes and flying boats, and a series of Jet engine, jet-powered fighter aircraft after World War II. The company had successes in the Schneider Trophy for seaplanes, with three wins in a row of 1927, 1929 and 1931. The company was founded in 1913 as Pemberton-Billing Ltd on the River Itchen, Hampshire, River Itchen close to Woolston, Southampton, on ground previously purchased by Noel Pemberton Billing to construct motor launches. It produced a couple of prototypes using quadruplane designs to shoot down zeppelins, the Supermarine P.B.29 and the Supermarine Nighthawk. The aircraft were fitted with the recoilless rifle, recoilless Davis gun and the Nighthawk had a separate powerplant to power a searchlight.The World's Worst Aircraft James Gilbert Upon election as a Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schneider Trophy
The Coupe d'Aviation Maritime Jacques Schneider, also known as the Schneider Trophy, Schneider Prize or (incorrectly) the Schneider Cup is a trophy that was awarded annually (and later, biennially) to the winner of a race for seaplanes and flying boats. The Schneider Trophy is now held at the Science Museum, South Kensington, London. Announced in 1912 by Jacques Schneider, a French financier, balloonist and aircraft enthusiast, the competition offered a prize of approximately £1,000. The race was held twelve times between 1913 and 1931. It was intended to encourage technical advances in civil aviation but became a contest for pure speed with laps over a (usually) triangular course, initially and later extended to . The contests were staged as time trials, with aircraft setting off individually at set intervals, usually 15 minutes apart. The contests were very popular and some attracted crowds of over 200,000 spectators. The race was significant in advancing aeroplane design, pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
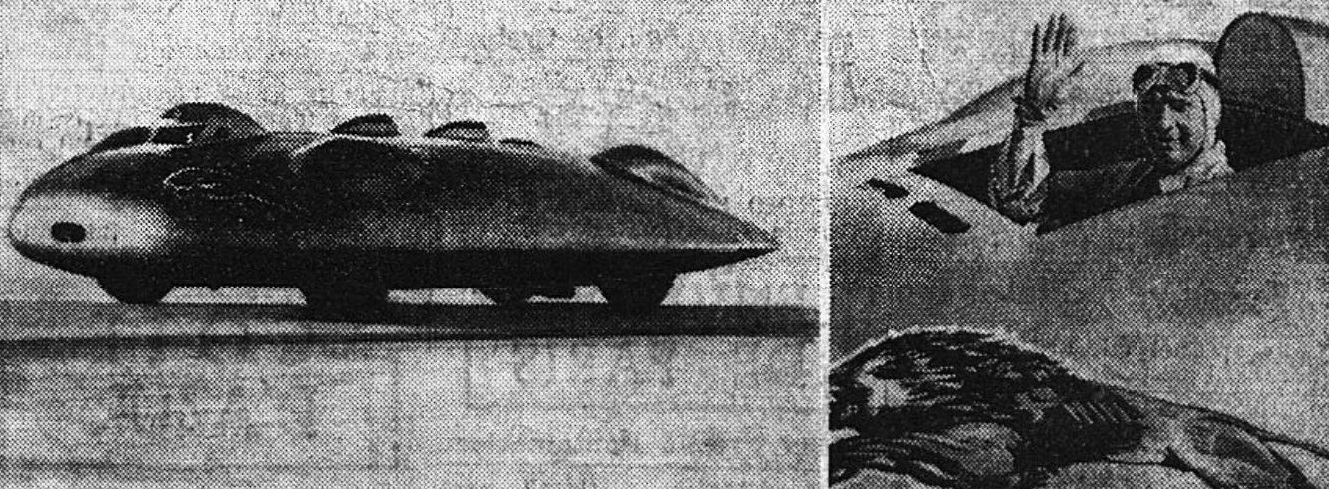
Railton Mobil Special , London, England
{{disambiguation, geo ...
Railton may refer to: * Railton (surname) * Railton (car), a former marque of British automobiles * Railton, Kentucky, a place in the US; see List of tornadoes in the Super Outbreak * Railton, Tasmania, a town in Tasmania, Australia See also * Campbell-Railton, Sir Malcolm Campbell's final land speed record car * Napier-Railton, an aero-engined race car built in 1933 * ''Railton Special'', a motor vehicle designed by Reid Railton built for John Cobb's land speed record in 1938 * Railton Road Railton Road runs between Brixton and Herne Hill in the London Borough of Lambeth. The road is designated the B223. At the northern end of Railton Road it becomes Atlantic Road, linking to Brixton Road at a junction where the Brixton tube stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Cobb (motorist)
John Rhodes Cobb (2 December 1899 – 29 September 1952) was an early to mid 20th century English racing motorist. He was three times holder of the World Land Speed Record, in 1938, 1939 and 1947, set at Bonneville Speedway in Utah, US. He was awarded the Segrave Trophy in 1947. He was killed in 1952 whilst piloting a jet powered speedboat attempting to break the World Water Speed Record on Loch Ness water in Scotland. Early life Cobb was born in Esher, Surrey, on 2 December 1899, near the Brooklands motor racing track which he frequented as a boy. He was the son of Florence and Rhodes Cobb, a wealthy furs broker in the City of London. He received his formal education at Eton College and Trinity Hall, Cambridge, before joining his father's firm and pursuing a successful career as the managing director of a number of companies in the trade, the personal financial resources from which he used to fund a passion for large capacity motor high speed racing. In 1924 he acquired a Royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Malcolm Campbell
Major Sir Malcolm Campbell (11 March 1885 – 31 December 1948) was a British racing motorist and motoring journalist. He gained the world speed record on land and on water at various times, using vehicles called ''Blue Bird'', including a 1921 Grand Prix Sunbeam. His son, Donald Campbell, carried on the family tradition by holding both land speed and water speed records. Early life and family Campbell was born on 11 March 1885 in Chislehurst, Kent, the only son of William Campbell, a Hatton Garden diamond seller. He attended the independent Uppingham School. In Germany, learning the diamond trade, he gained an interest in motorbikes and races. Returning to Britain, he worked for two years at Lloyd's of London for no pay, then for another year at £1 a week. Between 1906 and 1908, he won all three London to Land's End Trials motorcycle races. In 1910, he began racing cars at Brooklands. He christened his car ''Blue Bird'', painting it blue, after seeing the play '' The Blue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine Tuning
Engine tuning is the adjustment or modification of the internal combustion engine or Engine Control Unit (ECU) to yield optimal performance and increase the engine's power output, economy, or durability. These goals may be mutually exclusive; an engine may be de-tuned with respect to output power in exchange for better economy or longer engine life due to lessened stress on engine components. Tuning can include a wide variety of adjustments and modifications, such as the routine adjustment of the carburetor and ignition system to significant engine overhauls. Performance tuning of an engine can involve revising some of the design decisions taken during the development of the engine. Setting the idle speed, air-fuel ratio, carburetor balance, spark plug and distributor point gaps, and ignition timing were regular maintenance tasks for older engines and are the final but essential steps in setting up a racing engine. On modern engines equipped with electronic ignition and fuel i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napier-Railton Engine Bay
The Napier-Railton is an aero-engined racing car built in 1933, designed by Reid Railton to a commission by John Cobb, and built by Thomson & Taylor. It was driven by Cobb, mainly at the Brooklands race track where it holds the all-time lap record () which was set in 1935. The circuit was appropriated for military purposes during the Second World War, and never reopened in that form for racing. It has a W12 engine with 3 different exhaust systems. History Between 1933 and 1937, the Napier-Railton broke 47 world speed records at Brooklands, Autodrome de Linas-Montlhéry and Bonneville Salt Flats in Utah. (photo of the Napier-Railton at Bonneville) The car is powered by the high compression version (6.1:1) (RAF specification) of the naturally aspirated Napier Lion, a W12 of capacity, producing at 2585 revolutions per minute (recorded at 5,000ft - performance at ground level may be different), and of torque. The 12 cylinders are in three banks of four (broad-arrow configurat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement. The current categorisation is that a turbocharger is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gasses, whereas a supercharger is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft). However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. History Prior to the invention of the turbocharger, |