|
Nancy Marcus
Nancy Helen Marcus (May 17, 1950 – February 12, 2018) was an American biologist and oceanographer. During her graduate studies, Marcus became known as an expert on copepod ecology and evolutionary biology. She began her career as a postdoctoral fellow at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution where she studied copepod dormancy and its implications for marine aquaculture. She continued her field research as a professor of oceanography and later as the director of the Florida State University Marine Laboratory (FSU). During this time Marcus was elected as a Fellow of the Association for Women in Science and the American Association for the Advancement of Science and served as the president of the Association for the Sciences of Limnology and Oceanography. As the president, she led efforts in increase education activities and to increase the endowment fund. In 2005, Marcus transitioned from the sciences to college administration when she was appointed Dean of the FSU Gradua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florida State University
Florida State University (FSU) is a public research university in Tallahassee, Florida. It is a senior member of the State University System of Florida. Founded in 1851, it is located on the oldest continuous site of higher education in the state of Florida. Florida State University comprises 16 separate colleges and more than 110 centers, facilities, labs and institutes that offer more than 360 programs of study, including professional school programs. In 2021, the university enrolled 45,493 students from all 50 states and 130 countries. Florida State is home to Florida's only national laboratory, the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, and is the birthplace of the commercially viable anti-cancer drug Taxol. Florida State University also operates the John & Mable Ringling Museum of Art, the State Art Museum of Florida and one of the largest museum/university complexes in the nation. The university is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools (SACS). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uveal Melanoma
Uveal melanoma is a type of eye cancer in the uvea of the eye. It is traditionally classed as originating in the Iris (anatomy), iris, choroid, and ciliary body, but can also be divided into class I (low metastatic risk) and class II (high metastatic risk). Symptoms include blurred vision, loss of vision or photopsia, but there may be no symptoms. Tumors arise from the pigment cells (melanocytes) that reside within the uvea and give color to the eye. These melanocytes are distinct from the retinal pigment epithelium cells underlying the retina that do not form melanomas. When eye melanoma is spread to distant parts of the body, the five-year survival rate is about 15%.Eye Cancer Survival Rates American Cancer Society, Last Medical Review: December 9, 2014 Last Revised: February 5, 2016 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Grice
George may refer to: People * George (given name) * George (surname) * George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George * George Washington, First President of the United States * George W. Bush, 43rd President of the United States * George H. W. Bush, 41st President of the United States * George V, King of Great Britain, Ireland, the British Dominions and Emperor of India from 1910-1936 * George VI, King of Great Britain, Ireland, the British Dominions and Emperor of India from 1936-1952 * Prince George of Wales * George Papagheorghe also known as Jorge / GEØRGE * George, stage name of Giorgio Moroder * George Harrison, an English musician and singer-songwriter Places South Africa * George, Western Cape ** George Airport United States * George, Iowa * George, Missouri * George, Washington * George County, Mississippi * George Air Force Base, a former U.S. Air Force base located in California Characters * George (Peppa Pig), a 2-y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. lotus). Aquaculture involves cultivating freshwater, brackish water and saltwater populations under controlled or semi-natural conditions, and can be contrasted with commercial fishing, which is the harvesting of wild fish. Mariculture, commonly known as marine farming, refers specifically to aquaculture practiced in seawater habitats and lagoons, opposed to in freshwater aquaculture. Pisciculture is a type of aquaculture that consists of fish farming to obtain fish products as food. Aquaculture can also be defined as the breeding, growing, and harvesting of fish and other aquatic plants, also known as farming in water. It is an environmental source of food and commercial product which help to improve healthier habitats and used to recon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NICHD
The ''Eunice Kennedy Shriver'' National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) is one of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in the United States Department of Health and Human Services. It supports and conducts research aimed at improving the health of children, adults, families, and communities, including: *Reducing infant deaths *Promoting healthy pregnancy and childbirth *Investigating growth and human development *Examining problems of birth defects and intellectual and developmental disabilities *Understanding reproductive health *Enhancing function across the lifespan through rehabilitation research History The impetus for NICHD came from the Task Force on the Health and Well-Being of Children, convened in 1961 and led by Dr. Robert E. Cooke, a senior medical advisor to President John F. Kennedy. Eunice Kennedy Shriver also served on the task force, which reported that more research was needed on the physical, emotional, and intellectual growth of chil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigma Xi
Sigma Xi, The Scientific Research Honor Society () is a highly prestigious, non-profit honor society for scientists and engineers. Sigma Xi was founded at Cornell University by a junior faculty member and a small group of graduate students in 1886, making it one of the oldest honor societies. Membership in Sigma Xi is by invitation only, where members nominate others on the basis of their research achievements or potential. Sigma Xi goals aim to honor excellence in scientific investigation and encourage cooperation among researchers in all fields of science and engineering. Information about Sigma Xi has nearly 100,000 members who were elected to membership based on their research achievements and potential. It has more than 500 chapters in North America and around the world. In addition to publishing ''American Scientist'' magazine, Sigma Xi provides grants annually to promising young researchers and sponsors a variety of programs supporting ethics in research, science and engineer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bermuda Biological Station For Research
The Bermuda Institute of Ocean Sciences (known as BIOS) is an independent, non-profit marine science and education institute located in Ferry Reach, St. George's, Bermuda. The institute, founded in 1903 as the Bermuda Biological Station, hosts a full-time faculty of oceanographers, biologists, and environmental scientists, graduate and undergraduate students, K-12 groups, and Road Scholar (formerly Elderhostel) groups. BIOS's strategic mid-Atlantic Ocean location has at its doorstep a diverse marine environment, with close proximity to deep ocean as well as coral reef and near shore habitats. Prior to 5 September 2006, BIOS was known as the Bermuda Biological Station for Research (BBSR). History Founded in 1903 and incorporated in New York as a US not-for-profit institution in 1926, in its initial years BIOS was a seasonal field station for visiting zoologists and biologists to take advantage of Bermuda's diverse marine environment. After the Second World War, BIOS became a ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke University
Duke University is a private research university in Durham, North Carolina. Founded by Methodists and Quakers in the present-day city of Trinity in 1838, the school moved to Durham in 1892. In 1924, tobacco and electric power industrialist James Buchanan Duke established The Duke Endowment and the institution changed its name to honor his deceased father, Washington Duke. The campus spans over on three contiguous sub-campuses in Durham, and a marine lab in Beaufort. The West Campus—designed largely by architect Julian Abele, an African American architect who graduated first in his class at the University of Pennsylvania School of Design—incorporates Gothic architecture with the Duke Chapel at the campus' center and highest point of elevation, is adjacent to the Medical Center. East Campus, away, home to all first-years, contains Georgian-style architecture. The university administers two concurrent schools in Asia, Duke-NUS Medical School in Singapore (established in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
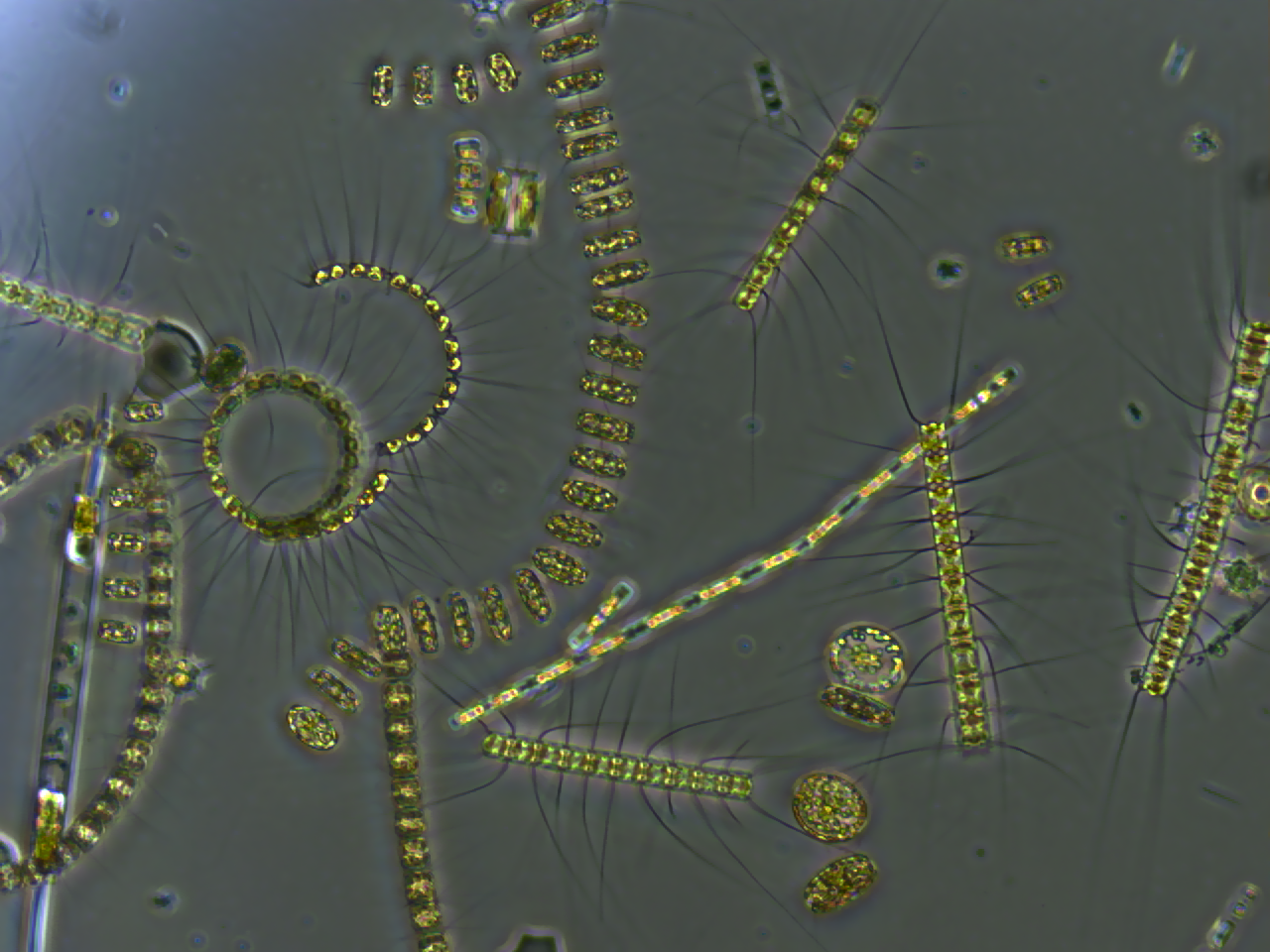
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'. Phytoplankton obtain their energy through photosynthesis, as do trees and other plants on land. This means phytoplankton must have light from the sun, so they live in the well-lit surface layers (euphotic zone) of oceans and lakes. In comparison with terrestrial plants, phytoplankton are distributed over a larger surface area, are exposed to less seasonal variation and have markedly faster turnover rates than trees (days versus decades). As a result, phytoplankton respond rapidly on a global scale to climate variations. Phytoplankton form the base of marine and freshwater food webs and are key players in the global carbon cycle. They account for about half of global photosynthetic activity and at least half of the oxygen production, despite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National Institutes of Health. With an annual budget of about $8.3 billion (fiscal year 2020), the NSF funds approximately 25% of all federally supported basic research conducted by the United States' colleges and universities. In some fields, such as mathematics, computer science, economics, and the social sciences, the NSF is the major source of federal backing. The NSF's director and deputy director are appointed by the President of the United States and confirmed by the United States Senate, whereas the 24 president-appointed members of the National Science Board (NSB) do not require Senate confirmation. The director and deputy director are responsible for administration, planning, budgeting and day-to-day operations of the foundation, while t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Roland (Maryland)
Lake Roland is a defunct reservoir in Baltimore County, Maryland. It was named for Roland Run, a nearby stream that feeds the lake and eventually flows into Jones Falls. It runs southeast through the city center to the Northwest Branch of the Patapsco River and the Baltimore Harbor. It is located just north of the Baltimore city limits. The lake is contained within the bounds of Lake Roland Park, which was established in the 1920s and supervised by the newly organized Baltimore City Department of Parks and Recreation.Bryan MacKay, ''Hiking, Cycling, and Canoeing in Maryland: A Family Guide'', Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 1995, pp. 82–89. The lake is an artificial impoundment created by a dam on Jones Falls and two smaller streams: Towson Run and Roland Run. The lake supports wildlife including Canada geese, largemouth bass, and common carp. The lake is part of the Lake Roland Historic District. History The lake was once called Lake Swann to honor Mayor Thomas S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Towson University
Towson University (TU or Towson) is a public university in Towson, Maryland. Founded in 1866 as Maryland's first training school for teachers, Towson University is a part of the University System of Maryland. Since its founding, the university has evolved into eight subsidiary colleges with over 20,000 students. Its 329-acre campus is situated in Baltimore County, Maryland eight miles north of downtown Baltimore. Towson is one of the largest public universities in Maryland and still produces the most teachers of any university in the state. History Maryland State Normal School The General Assembly of Maryland established what would eventually become Towson University in 1865, with the allocation of funds directed toward Maryland's first teacher-training school, or then called "normal school" (term used from a new French tradition). On January 15, 1866, this institution, known then as the "Maryland State Normal School" (M.S.N.S.), officially opened its doors as part of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |