|
Nanaya
Nanaya (Sumerian language, Sumerian , Dingir, DNA.NA.A; also transcribed as "Nanāy", "Nanaja", "Nanāja", '"Nanāya", or "Nanai"; antiquated transcription: "Nanâ"; in Greek language, Greek: ''Ναναια'' or ''Νανα''; Aramaic: ''ננױננאױ;'' Syriac language, Syriac: ܢܢܝ) was a Mesopotamian goddess of love, closely associated with Inanna. While she is well attested in Mesopotamian textual sources from many periods, from the times of the Third Dynasty of Ur to the conquest of Babylonia by the Achaemenids and beyond, and was among the most commonly worshiped goddesses through much of Mesopotamian history, both her origin and the meaning of her name are unknown. It has been proposed that she originated either as a minor Akkadian Empire, Akkadian goddess or as a hypostasis of Sumer, Sumerian Inanna, but the evidence is inconclusive. Her primary role was that of a goddess of love, and she was associated with eroticism and sensuality, though she was also a patron of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanisurra
Kanisurra (also Gansurra, Ganisurra) was a Mesopotamian goddess who belonged to the entourage of Nanaya. Much about her character remains poorly understood, though it is known she was associated with love. Her name might be derived from the word ''ganzer'', referring to the underworld or to its entrance. In addition to Nanaya, she could be associated with deities such as Gazbaba, Ishara and Uṣur-amāssu. She is first attested in sources from Uruk from the Ur III period, and continued to be worshiped in this city as late as in the Seleucid period. Name and character The character and functions of Kanisurra are unclear. Her best attested characteristic is her association with Nanaya. Both of them belonged to a group of female deities invoked in love and potency incantations, which also included Ishtar, Ishara and Gazbaba. Some of these texts use formulas such as "at the command of Kanisurra and Ishara, patron goddess of love" or "at the command of Kanisurra and Ishara, patroness o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inanna
Inanna, also sux, 𒀭𒊩𒌆𒀭𒈾, nin-an-na, label=none is an List of Mesopotamian deities, ancient Mesopotamian goddess of love, war, and fertility. She is also associated with beauty, sex, Divine law, divine justice, and political power. She was originally worshiped in Sumer under the name "Inanna", and later by the Akkadian Empire, Akkadians, Babylonian religion, Babylonians, and Assyrians under the name Ishtar, (occasionally represented by the logogram ). She was known as the "Queen of heaven (antiquity), Queen of Heaven" and was the patron goddess of the Eanna temple at the city of Uruk, which was her main Cult (religious practice), cult center. She was associated with the planet Venus and her most prominent symbols included the Lion of Babylon, lion and the Star of Ishtar, eight-pointed star. Her husband was the god Dumuzid (later known as Tammuz) and her , or personal attendant, was the goddess Ninshubur (who later became conflated with the male deities Ilabrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gazbaba
Gazbaba, also known as Kazbaba or Kazba, was a Mesopotamian goddess closely associated with Inanna, Nanaya and Kanisurra. Like them, she was connected with love and eroticism. Name and character Gazbaba's name is most likely derived from the Akkadian word ''kazbu'', which can be translated as "sexual attraction." A form ending in the hypocoristic suffix ''-īya/-āya/-ūya'', ''dKa-az-ba-a-a'', is also attested, possibly representing an attempt at making the name more similar to Nanaya's, or resulting from confusion with a similar personal name. Little is known about Gazbaba's character, but she was associated with love and sex. Šurpu describes her as ''ṣayyaḫatu'', "the smiling one," which is likely a reference to the frequent mention of smiles in Akkadian erotic literature. She belonged to a group of deities invoked in love incantations, which also included Inanna/Ishtar, Nanaya, Kanisurra and Ishara. For example, one such text contains the formula "Ishtar, Nanaya, Gazbab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uṣur-amāssu
Uṣur-amāssu (also spelled Uṣur-awāssu or Uṣur-amāssa) was a Mesopotamian deity. While originally viewed as male, she later came to be regarded as a goddess. Regardless of gender, Uṣur-amāssu was considered as a child of Adad and Shala and like other members of their entourage was considered a deity of justice. The earliest attestations of veneration of Uṣur-amāssu are theophoric names from cities such as Kish, but the female version of this deity is best attested in sources from Uruk from the Neo-Babylonian period. She belonged to the pentad of goddesses who stood on top of the local pantheon, which also included Ishtar, Nanaya, Bēltu-ša-Rēš and Urkayītu. She is still attested in texts from the Seleucid period, and continued to be celebrated during an '' akitu'' festival. Name and gender Uṣur-amāssu's name was derived from an ordinary masculine given name known from Old Babylonian and Old Assyrian sources, Uṣur-awāssu, whose historically notable bearer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
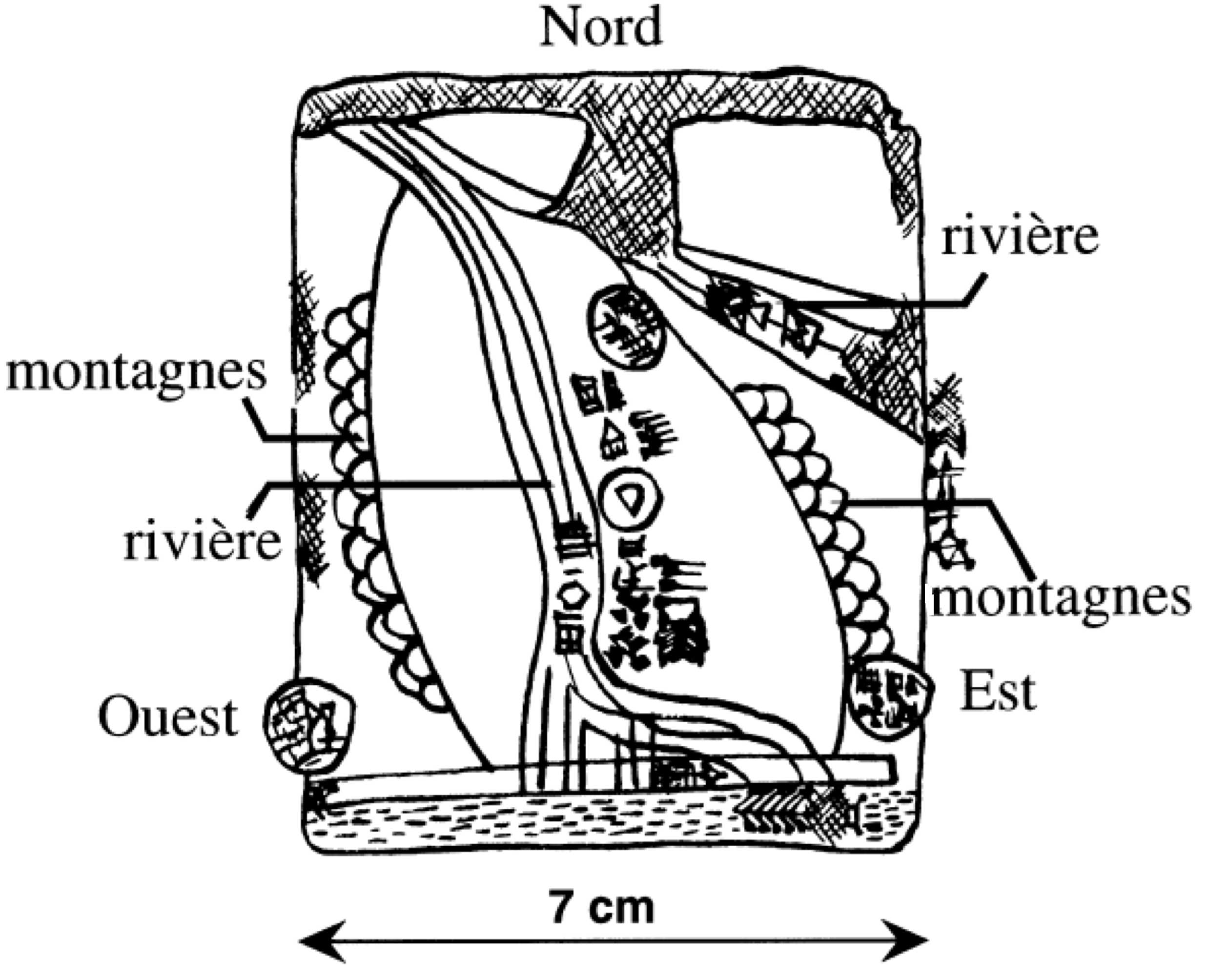
Land Grant To Ḫunnubat-Nanaya Kudurru
The Land grant to Ḫunnubat-Nanaya kudurru is an ancient Mesopotamian entitlement ''narû'' recording the gift of forty GUR (around a thousand acres) of uncultivated land and control over three settlements by Kassite king Meli-Šipak to his daughter and the provision of exemptions from service and taxation to villages in the region guaranteed with a sealed tablet given to her, presumably to make the land transfer more palatable to the local population. It was excavated by a French archaeological team under the auspices of Jacques de Morgan at the turn of the twentieth century at Susa where it (excavation reference Sb 23) was found with a duplicate (reference Sb 24). It had been taken as booty by Elamite king Šutruk-Naḫḫunte after his 1158 BC campaign that brought about the demise of the regime of Babylonian king Zababa-šuma-iddina, the penultimate monarch of the Kassite dynasty. It is significant in that it shows the king making a second bequest with land ''he purchased' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urash (god)
Urash (Uraš) was a Mesopotamian god who was the tutelary deity of Dilbat. He was an agricultural god, and in that capacity he was frequently associated with Ninurta. His wife was the goddess Ninegal, while his children were the underworld deity Lagamal, who like him was associated with Dilbat, and the love goddess Nanaya. Urash occasionally appears in myths, though they only survive in small, late fragments. Functions Urash was the tutelary god of Dilbat, modern Tell al-Deylam in Iraq's Babil Governorate. His character was regarded as Ninurta-like, with an emphasis on the role of a farming deity, as evidenced by explanatory texts referring to him as "Ninurta of the hoe," "of the calendar" or "of the tenant farmer." In a late commentary (KAR 142), he is a member of a group labeled as "seven Ninurtas." Another late text describes him as "Marduk of planting." Associations with other deities The god Urash worshiped in Dilbat was not the same as Urash, the spouse of Anu. Eviden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sin (mythology)
Nanna, Sīn or Suen ( akk, ), and in Aramaic ''syn'', ''syn’'', or even ''shr'' 'moon', or Nannar ( sux, ) was the god of the moon in the Mesopotamian religions of Sumer, Akkad, Assyria, Babylonia and Aram. He was also associated with cattle, perhaps due to the perceived similarity between bull horns and the crescent moon. He was always described as a major deity, though only a few sources, mostly these from the reign of Nabonidus, consider him to be the head of the Mesopotamian pantheon. The two chief seats of his worship were Ur in the south of Mesopotamia and Harran in the north, though he was also worshiped in numerous other cities, especially in the proximity of Ur and in the Diyala area. In Ur, he was connected to royal power, and many Mesopotamian kings visited his temple in this city. According to Mesopotamian mythology, his parents were Enlil and Ninlil, while his wife was Ningal, worshiped with him in his major cult centers. Their children included major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ishara
Ishara (Išḫara) was the tutelary goddess of the ancient Syrian city of Ebla. The origin of her name is unknown. Both Hurrian and West Semitic etymologies have been proposed, but they found no broad support and today it is often assumed that her name belongs to an unknown linguistic substrate. Her cult had a wide reach across the ancient Near East. In addition to Ebla, she was also worshiped in cities such as Mari, Emar, Alalakh and Ugarit. From these Syrian cities the worship of Ishara spread to Mesopotamia. The Hurrians also adopted her into their pantheon after arriving in Syria, from which she found her way to the Hittite pantheon. In various time periods and areas different functions were assigned to her. In Ebla she was the tutelary deity of the ruling family, but also a love goddess. In Mesopotamia the latter function lead to an association with Ishtar, and later Nanaya, Kanisurra and Gazbaba as well. In Hurrian religion she acquired the role of a goddess associate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meli-Shipak II
Meli-Šipak II, or alternatively ''Melišiḫu''''Me-li-''dŠI-ḪU or m''Me-li-''ŠI-ḪU, where the reading of ḪU is uncertain, -ḫu or -pak. in contemporary inscriptions, was the 33rd king of the Kassite or 3rd Dynasty of Babylon ca. 1186–1172 BC (short chronology) and he ruled for 15 years.''Kinglist A'', BM 33332, ii 12. Tablets with two of his year names, 4 and 10, were found at Ur. His reign marks the critical synchronization point in the chronology of the Ancient Near East. His provenance He is recorded as the son of Adad-šuma-uṣur, his predecessor, on a kudurru.''Estate of Takil-ana-ilīšu kudurru'', BM 90827, published as BBSt 3, column 4, line 31, but note King’s 1912 edition uses the alternative reading of the cuneiform –MU-ŠEŠ to give ''Adad-nadin-aḫi''. Elsewhere he seemed reluctant to name him in his royal inscriptions, despite Adad-šuma-uṣur’s apparent renown as restorer of Kassite independence, which has been the subject of much speculation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kassites
The Kassites () were people of the ancient Near East, who controlled Babylonia after the fall of the Old Babylonian Empire c. 1531 BC and until c. 1155 BC (short chronology). They gained control of Babylonia after the Hittite sack of Babylon in 1531 BC, and established a dynasty generally assumed to have been based first in that city, after a hiatus. Later rule shifted to the new city of Dur-Kurigalzu. By the time of Babylon's fall, the Kassites had already been part of the region for a century and a half, acting sometimes with the Babylon's interests and sometimes against. There are records of Kassite and Babylonian interactions, in the context of military employment, during the reigns of Babylonian kings Samsu-iluna (1686 to 1648 BC), Abī-ešuh, and Ammī-ditāna. The origin and classification of the Kassite language, like the Sumerian language and Hurrian language, is uncertain, and, also like the two latter languages, has generated a wide array of speculation over the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dingir
''Dingir'' (, usually transliterated DIĜIR, ) is a Sumerian word for "god" or "goddess". Its cuneiform sign is most commonly employed as the determinative for religious names and related concepts, in which case it is not pronounced and is conventionally transliterated as a superscript "d" as in e.g. dInanna. The cuneiform sign by itself was originally an ideogram for the Sumerian word ''an'' ("sky" or "heaven");Hayes, 2000 its use was then extended to a logogram for the word ''diĝir'' ("god" or "goddess")Edzard, 2003 and the supreme deity of the Sumerian pantheon ''An'', and a phonogram for the syllable . Akkadian took over all these uses and added to them a logographic reading for the native '' ilum'' and from that a syllabic reading of . In Hittite orthography, the syllabic value of the sign was again only ''an''. The concept of "divinity" in Sumerian is closely associated with the heavens, as is evident from the fact that the cuneiform sign doubles as the ideogram f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gasur
Nuzi (or Nuzu; Akkadian Gasur; modern Yorghan Tepe, Iraq) was an ancient Mesopotamian city southwest of the city of Arrapha (modern Kirkuk), located near the Tigris river. The site consists of one medium-sized multiperiod tell and two small single period mounds. History The site showed occupation as far back as the late Uruk period. The city, then named Gasur, was founded in the third millennium during the time of the Akkadian Empire. In the middle of the second millennium the Hurrians gained control of the town and renamed it Nuzi. The history of the site during the intervening period is unclear, though the presence of a few cuneiform tablets from the Old Assyrian Empire indicates that trade with nearby Assur was taking place. After the fall of the Hurrian kingdom of Mitanni to Ashur-uballit I of the Middle Assyrian Empire, Nuzi went into gradual decline. Note that while the Hurrian period is well known from full excavation of those strata, the earlier history is not as rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |