|
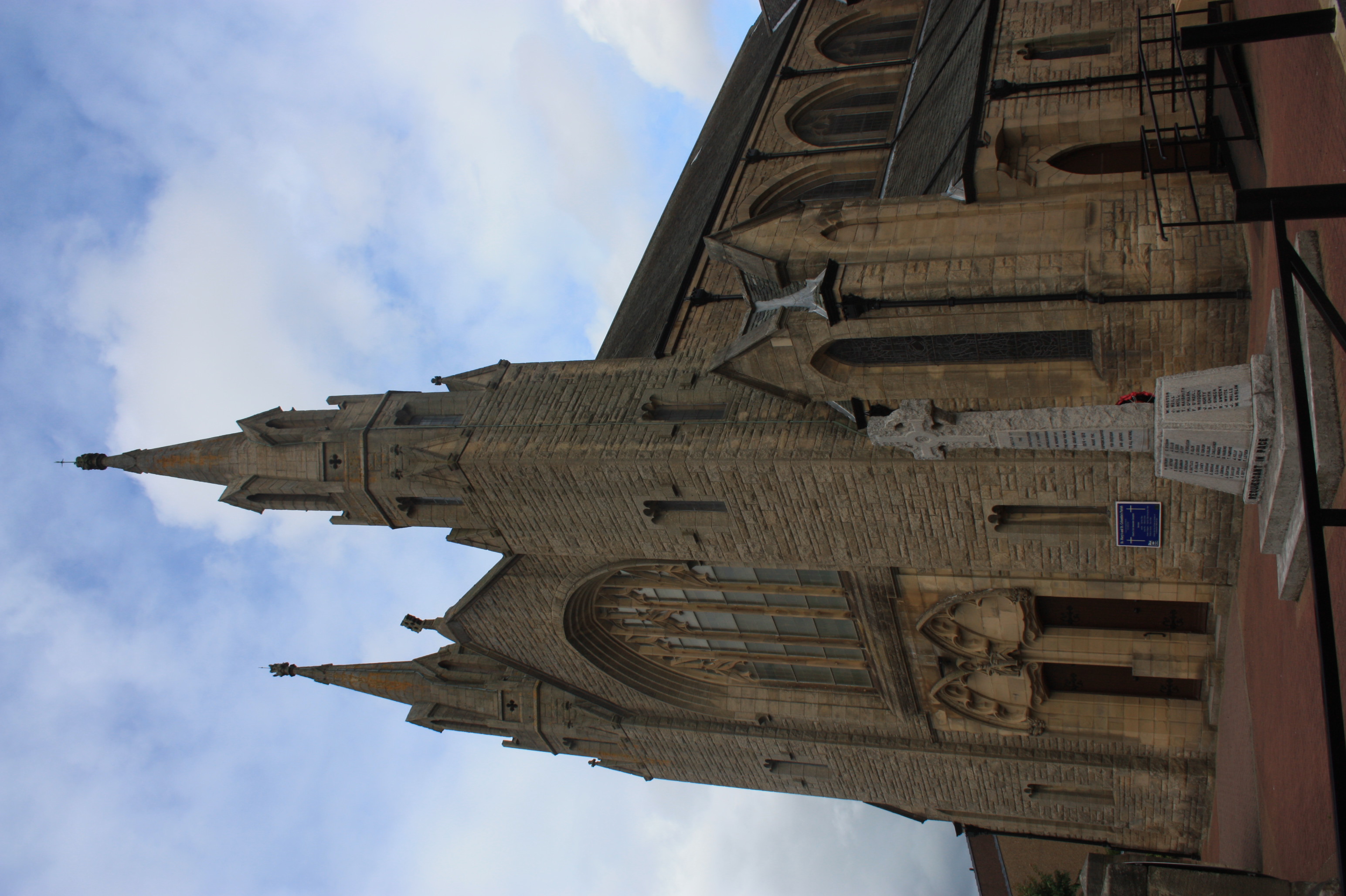
Namur Cathedral
St Aubin's Cathedral, Namur, Wallonia, the only cathedral in Belgium in academic Late Baroque style. It was the only church built in the Low Countries as a cathedral after 1559, when most of the dioceses of the Netherlands were reorganized. It is classified as part of ''Wallonia's Major Heritage'' by the Walloon Region. History The cathedral was founded as a collegiate church in 1047 by Albert II of Namur. The first dean, Frederick of Lorraine, brother-in-law of Albert II, about 1050 secured from Mainz Cathedral a portion of the head of Saint Albanus, to whose patronage the collegiate church was dedicated. In 1057 Frederick became pope under the name of Stephen IX. In 1209, Pope Innocent III formally took the church of St Aubin under his protection. The church became a cathedral by virtue of the papal bull of 12 May 1559 establishing the new bishoprics in the Low Countries, with the Diocese of Namur created as a suffragan see of the Archdiocese of Cambrai. In the cathedral a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namur Ca1JPG
Namur (; ; nl, Namen ; wa, Nameur) is a city and municipality in Wallonia, Belgium. It is both the capital of the province of Namur and of Wallonia, hosting the Parliament of Wallonia, the Government of Wallonia and its administration. Namur stands at the confluence of the rivers Sambre and Meuse and straddles three different regions – Hesbaye to the north, Condroz to the south-east, and Entre-Sambre-et-Meuse to the south-west. The city of Charleroi is located to the west. The language spoken is French. The municipality consists of the following districts: Beez, Belgrade, Boninne, Bouge, Champion, Cognelée, Daussoulx, Dave, Erpent, Flawinne, Gelbressée, Jambes, Lives-sur-Meuse, Loyers, Malonne, Marche-les-Dames, Naninne, Saint-Servais, Saint-Marc, Suarlée, Temploux, Vedrin, Wépion, and Wierde. History Early history The town began as an important trading settlement in Celtic times, straddling east–west and north–south trade routes across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
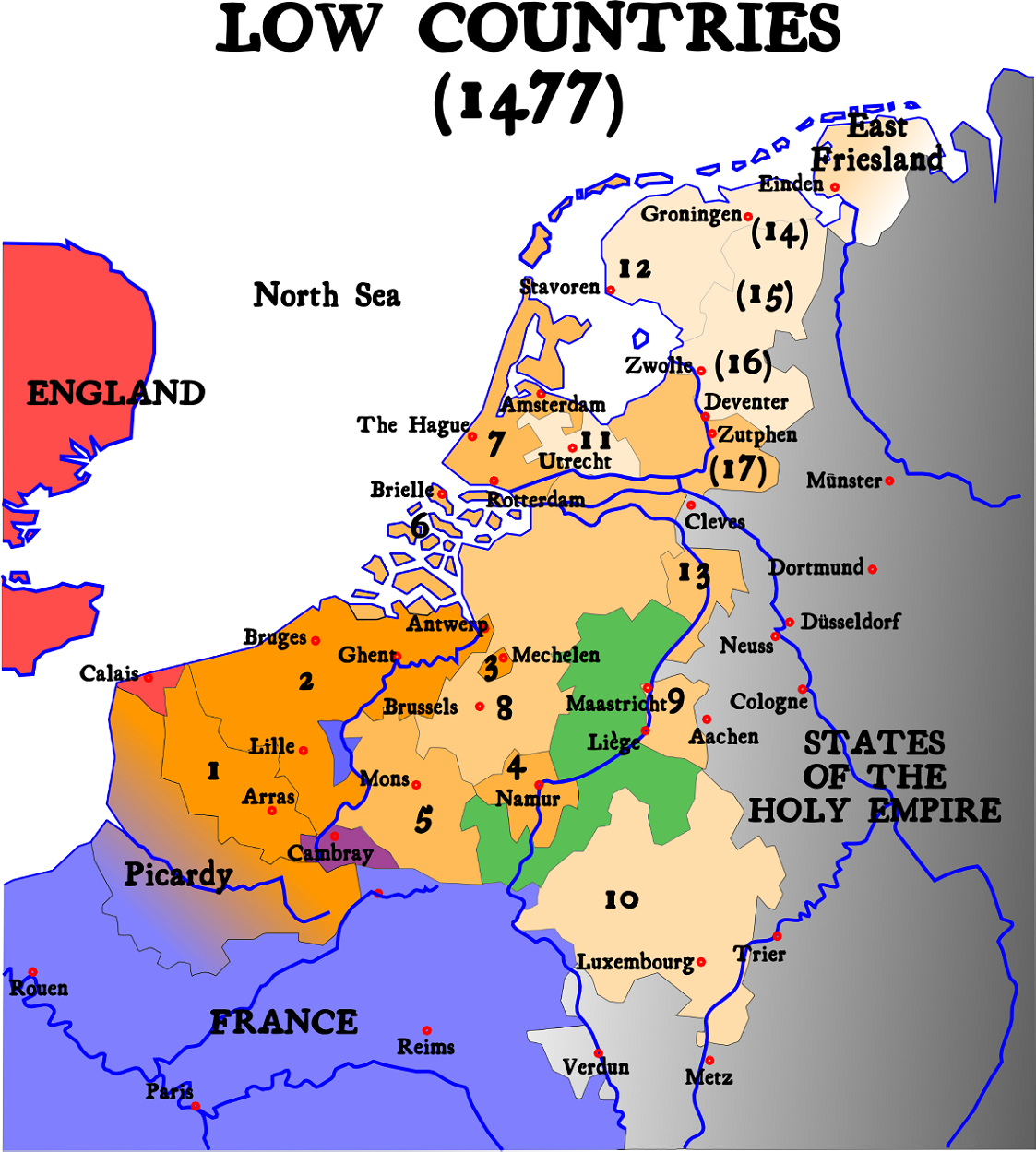
Habsburg Netherlands
Habsburg Netherlands was the Renaissance period fiefs in the Low Countries held by the Holy Roman Empire's House of Habsburg. The rule began in 1482, when the last House of Valois-Burgundy, Valois-Burgundy ruler of the Netherlands, Mary of Burgundy, Mary, wife of Maximilian I of Austria, died. Their grandson, Emperor Charles V, was born in the Habsburg Netherlands and made Brussels one of his capitals. Becoming known as the Seventeen Provinces in 1549, they were held by the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs from 1556, known as the Spanish Netherlands from that time on. In 1581, in the midst of the Dutch Revolt, the Seven United Provinces seceded from the rest of this territory to form the Dutch Republic. The remaining Spanish Southern Netherlands became the Austrian Netherlands in 1714, after Austrian acquisition under the Treaty of Rastatt. De facto Habsburg rule ended with the annexation by the revolutionary French First Republic in 1795. Austria, however, did not relinquish its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society Of Jesus
, image = Ihs-logo.svg , image_size = 175px , caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits , abbreviation = SJ , nickname = Jesuits , formation = , founders = , founding_location = , type = Order of clerics regular of pontifical right (for men) , headquarters = Generalate:Borgo S. Spirito 4, 00195 Roma-Prati, Italy , coords = , region_served = Worldwide , num_members = 14,839 members (includes 10,721 priests) as of 2020 , leader_title = Motto , leader_name = la, Ad Majorem Dei GloriamEnglish: ''For the Greater Glory of God'' , leader_title2 = Superior General , leader_name2 = Fr. Arturo Sosa, SJ , leader_title3 = Patron saints , leader_name3 = , leader_title4 = Ministry , leader_name4 = Missionary, educational, literary works , main_organ = La Civiltà Cattoli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Nicolaï
Ancient and noble French family names, Jacques, Jacq, or James are believed to originate from the Middle Ages in the historic northwest Brittany region in France, and have since spread around the world over the centuries. To date, there are over one hundred identified noble families related to the surname by the Nobility & Gentry of Great Britain & Ireland. Origins The origin of this surname ultimately originates from the Latin, Jacobus which belongs to an unknown progenitor. Jacobus comes from the Hebrew name, Yaakov, which translates as "one who follows" or "to follow after". Ancient history A French knight returning from the Crusades in the Holy Lands probably adopted the surname from "Saint Jacques" (or "James the Greater"). James the Greater was one of Jesus' Twelve Apostles, and is believed to be the first martyred apostle. Being endowed with this surname was an honor at the time and it is likely that the Church allowed it because of acts during the Crusades. Indeed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacob Jordaens
Jacob (Jacques) Jordaens (19 May 1593 – 18 October 1678) was a Flemish painter, draughtsman and tapestry designer known for his history paintings, genre scenes and portraits. After Peter Paul Rubens and Anthony van Dyck, he was the leading Flemish Baroque painter of his day. Unlike those contemporaries he never travelled abroad to study Italian painting, and his career is marked by an indifference to their intellectual and courtly aspirations.d'Hulst, pp. 23 In fact, except for a few short trips to locations elsewhere in the Low Countries, he remained in Antwerp his entire life. As well as being a successful painter, he was a prominent designer of tapestries.d'Hulst, pp. 24–25. Like Rubens, Jordaens painted altarpieces, mythological, and allegorical scenes, and after 1640—the year Rubens died—he was the most important painter in Antwerp for large-scale commissions and the status of his patrons increased in general.d'Hulst, p. 26–27. However, he is best known today for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthony Van Dyck
Sir Anthony van Dyck (, many variant spellings; 22 March 1599 – 9 December 1641) was a Brabantian Flemish Baroque artist who became the leading court painter in England after success in the Southern Netherlands and Italy. The seventh child of Frans van Dyck, a wealthy Antwerp silk merchant, Anthony painted from an early age. He was successful as an independent painter in his late teens, and became a master in the Antwerp guild in 1618. By this time he was working in the studio of the leading northern painter of the day, Peter Paul Rubens, who became a major influence on his work. Van Dyck worked in London for some months in 1621, then returned to Flanders for a brief time, before travelling to Italy, where he stayed until 1627, mostly in Genoa. In the late 1620s he completed his greatly admired ''Iconography'' series of portrait etchings, mostly of other artists. He spent five years in Flanders after his return from Italy, and from 1630 was court painter for the arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pendentive
In architecture, a pendentive is a constructional device permitting the placing of a circular dome over a square room or of an elliptical dome over a rectangular room. The pendentives, which are triangular segments of a sphere, taper to points at the bottom and spread at the top to establish the continuous circular or elliptical base needed for a dome. In masonry the pendentives thus receive the weight of the dome, concentrating it at the four corners where it can be received by the piers beneath. Prior to the pendentive's development, builders used the device of corbelling or squinches in the corners of a room. Pendentives commonly occurred in Orthodox, Renaissance, and Baroque churches, with a drum with windows often inserted between the pendentives and the dome. The first experimentation with pendentives began with Roman dome construction in the 2nd–3rd century AD, while full development of the form came in the 6th-century Eastern Roman Hagia Sophia at Constantinople. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bas-relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term ''relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that the sculpted material has been raised above the background plane. When a relief is carved into a flat surface of stone (relief sculpture) or wood (relief carving), the field is actually lowered, leaving the unsculpted areas seeming higher. The approach requires a lot of chiselling away of the background, which takes a long time. On the other hand, a relief saves forming the rear of a subject, and is less fragile and more securely fixed than a sculpture in the round, especially one of a standing figure where the ankles are a potential weak point, particularly in stone. In other materials such as metal, clay, plaster stucco, ceramics or papier-mâché the form can be simply added to or raised up from the background. Monumental bronze reliefs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corinthian Order
The Corinthian order (Greek: Κορινθιακός ρυθμός, Latin: ''Ordo Corinthius'') is the last developed of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric order which was the earliest, followed by the Ionic order. In Ancient Greek architecture, the Corinthian order follows the Ionic in almost all respects other than the capitals of the columns. When classical architecture was revived during the Renaissance, two more orders were added to the canon: the Tuscan order and the Composite order. The Corinthian, with its offshoot the Composite, is the most ornate of the orders. This architectural style is characterized by slender fluted columns and elaborate capitals decorated with acanthus leaves and scrolls. There are many variations. The name ''Corinthian'' is derived from the ancient Greek city of Corinth, although the style had its own model in Roman practice, following precedents set by the Tem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 635,640. Straddling the border between historic Lanarkshire and Renfrewshire, the city now forms the Glasgow City Council area, one of the 32 council areas of Scotland, and is governed by Glasgow City Council. It is situated on the River Clyde in the country's West Central Lowlands. Glasgow has the largest economy in Scotland and the third-highest GDP per capita of any city in the UK. Glasgow's major cultural institutions – the Burrell Collection, Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum, the Royal Conservatoire of Scotland, the Royal Scottish National Orchestra, Scottish Ballet and Scottish Opera – enjoy international reputations. The city was the European Capital of Culture in 1990 and is notable for its architecture, cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
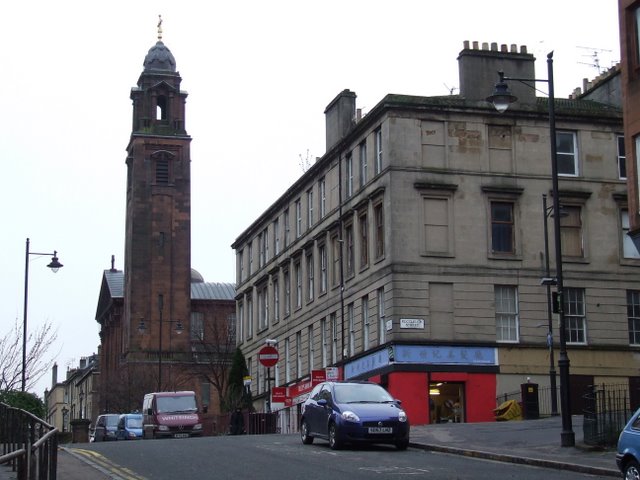
St Aloysius Church, Glasgow
St Aloysius Church is a Roman Catholic Parish church in the Garnethill area of Glasgow in Scotland. It is the only church in Glasgow to be run by the Society of Jesus. It is situated on the corner of Hill Street and Rose Street and is next door to St Aloysius' College, Glasgow, having a close relationship with the school. When it was built, it was the only Catholic church in Glasgow to have a tower. It is modelled on Namur Cathedral in Belgium and is a Category A listed building. History Founding The Jesuits arrived in Glasgow in 1859 by taking over the parish of St Joseph's Church, North Woodside Road. In the early 1860s they purchased land in the Garnethill district, which, at that time, was on the western outskirts of the city and a residential area recently favoured by the wealthier classes. In 1868, Fr William Kay SJ arrived at Garnethill with instructions to found a mission at St Aloysius which would be distinct from St Joseph’s. He quickly set about constructing a lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Ménart
Charles Jean Ménart (1876 – 7 April 1956) was a Belgian architect who worked in Scotland in the early 20th century and specialised in designing Roman Catholic churches in the Baroque Revival style. Early life He was born in Leuze-en-Hainaut, Belgium, to Émile-Jean Ménart, who was from France, and Agnes Joseph Meurisse. around 1876 and went on to study at the Glasgow School of Art from 1893 to 1898. He became a British citizen in 1897. He later settled in Perth.C. J. Ménart from GlasgowSculpture.com, accessed 29 March 2013 However, in 1903, he moved to and went into partnership with John Stirling Jarvie from |




.jpg)

