|
Name Of Australia
The name '' Australia'' (pronounced in Australian English) is derived from the Latin ''australis'', meaning "southern", and specifically from the hypothetical ''Terra Australis'' postulated in pre-modern geography. The name was popularised by the explorer Matthew Flinders from 1804, and it has been in official use since 1817, replacing " New Holland," an English translation of the Dutch name, first given by Abel Tasman in 1643 as the name for the continent. History The name ''Australia'' has been applied to two continents. Originally, it was applied to the south polar continent, or sixth continent, now known as Antarctica. The name is a shortened form of ''Terra Australis'' which was one of the names given to the imagined (but undiscovered) land mass that was thought to surround the south pole. The earliest known use of the name ''Australia'' in Latin was in 1545, when the word appears in a woodcut illustration of the globe titled "Sphere of the Winds" contained in an as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
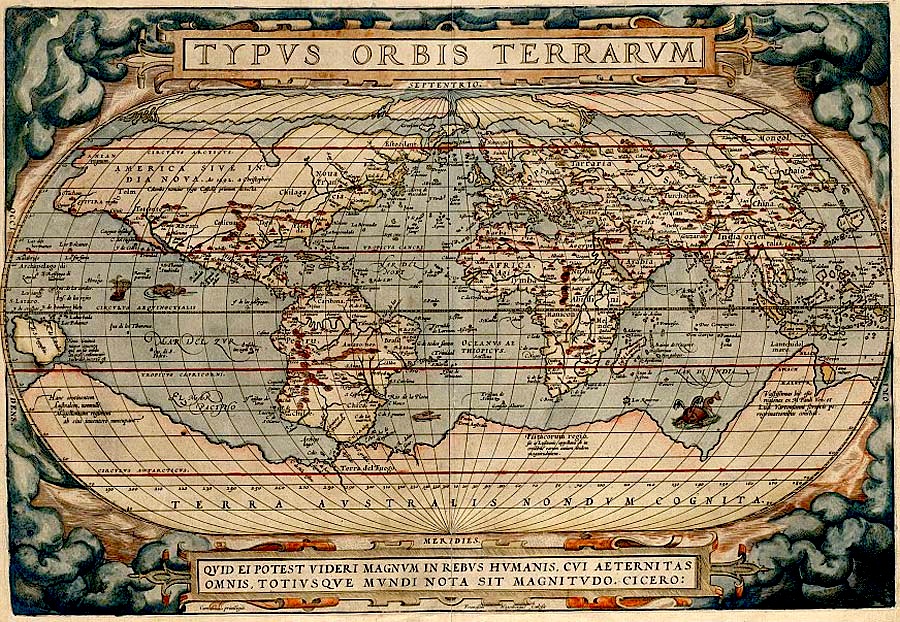
Typus Orbis Terrarum Drawn By Abraham Ortelius
In biology, a type is a particular specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the defining features of that particular taxon. In older usage (pre-1900 in botany), a type was a taxon rather than a specimen. A taxon is a scientifically named grouping of organisms with other like organisms, a set that includes some organisms and excludes others, based on a detailed published description (for example a species description) and on the provision of type material, which is usually available to scientists for examination in a major museum research collection, or similar institution. Type specimen According to a precise set of rules laid down in the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) and the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN), the scientific name of every taxon is almost al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Purchas
Samuel Purchas ( – 1626) was an English Anglican cleric who published several volumes of reports by travellers to foreign countries. Career Purchas was born at Thaxted, Essex son of an English yeoman. He graduated from St John's College, Cambridge, in 1600. In 1604 James I presented him to the vicarage of St. Laurence and All Saints, in Eastwood, Essex. Eastwood is two miles from Leigh-on-Sea, which was then a prosperous shipping centre and a congregational place of seafaring men. Purchas himself never travelled "200 miles from Thaxted in Essex where I was borne." Instead, he recorded personal narratives shared with him by the sailors, who returned to England from their voyages. He added these accounts to a vast compilation of unsorted manuscripts, which were left to him by Richard Hakluyt and were later published as Purchas's third – and final – book. In 1614, Purchas became chaplain to Archbishop George Abbot and rector of St Martin, Ludgate, London. He held a Bach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Voyage To Terra Australis
''A Voyage to Terra Australis: Undertaken for the Purpose of Completing the Discovery of that Vast Country, and Prosecuted in the Years 1801, 1802, and 1803, in His Majesty's Ship the Investigator'' was a sea voyage journal written by English mariner and explorer Matthew Flinders. It describes his circumnavigation of the Australian continent in the early years of the 19th century, and his imprisonment by the French on the island of Mauritius from 1804–1810. Circumnavigation The book told in great detail of his explorations and included maps and drawings of the profiles of unknown coastline areas of what Flinders called " Terra Australis Incognita". By this, he was referring to the great unknown Southern continent that had been sighted and partly mapped by prominent earlier mariners such as Captain James Cook. The ship Flinders commanded, , was a 334-ton sloop. Up until this time the circumnavigation of Australia which was necessary to prove it was a single continent land mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Wilson (navigator)
James Wilson may refer to: Politicians and government officials Canada *James Wilson (Upper Canada politician) (1770–1847), English-born farmer and political figure in Upper Canada *James Crocket Wilson (1841–1899), Canadian MP from Quebec *James Robert Wilson (1866–1941), mayor of Saskatoon and member of the Parliament of Canada *James Wilson (Ontario MPP) (1810–1891), Canadian politician Oceania * James Wilson (New South Wales politician, born 1862) (1862–1925), English-born Australian politician *James Wilson (New South Wales politician, born 1865) (1865–1927), New Zealand-born Australian politician *Sir James Wilson (New Zealand politician, born 1849) (1849–1929), New Zealand politician and farmer *James Wilson (New Zealand politician, born 1814) (1814–1898) *Sir James Milne Wilson (1812–1880), Australian politician in Tasmania *James Phillips Wilson (c. 1852–1925), South Australian Labor politician United Kingdom * James Wilson (MP for York) betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Edward Smith (botanist)
__NOTOC__ Sir James Edward Smith (2 December 1759 – 17 March 1828) was an English botanist and founder of the Linnean Society. Early life and education Smith was born in Norwich in 1759, the son of a wealthy wool merchant. He displayed a precocious interest in the natural world. During the early 1780s he enrolled in the medical course at the University of Edinburgh where he studied chemistry under Joseph Black and natural history under John Walker. He then moved to London in 1783 to continue his studies. Smith was a friend of Sir Joseph Banks, who was offered the entire collection of books, manuscripts and specimens of the Swedish natural historian and botanist Carl Linnaeus following the death of his son Carolus Linnaeus the Younger. Banks declined the purchase, but Smith bought the collection for the bargain price of £1,000. The collection arrived in London in 1784, and in 1785 Smith was elected Fellow of the Royal Society. Academic career Between 1786 and 1788 Sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Shaw (biologist)
George Kearsley Shaw (10 December 1751 – 22 July 1813) was an English botanist and zoologist. Life Shaw was born at Bierton, Buckinghamshire, and was educated at Magdalen Hall, Oxford, receiving his M.A. in 1772. He took up the profession of medical practitioner. In 1786 he became the assistant lecturer in botany at the University of Oxford. He was a co-founder of the Linnean Society in 1788, and became a fellow of the Royal Society in 1789. In 1791 Shaw became assistant keeper of the natural history department at the British Museum, succeeding Edward Whitaker Gray as keeper in 1806. He found that most of the items donated to the museum by Hans Sloane were in very bad condition. Medical and anatomical material was sent to the museum at the Royal College of Surgeons, but many of the stuffed animals and birds had deteriorated and had to be burnt. He was succeeded after his death by his assistant Charles Konig. Works Shaw published one of the first English descrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Dalrymple
Alexander Dalrymple FRS (24 July 1737 – 19 June 1808) was a Scottish geographer and the first Hydrographer of the British Admiralty. He was the main proponent of the theory that there existed a vast undiscovered continent in the South Pacific, Terra Australis Incognita. He produced thousands of nautical charts, mapping a remarkable number of seas and oceans for the first time, and contributing significantly to the safety of shipping. His theories prompted a number of expeditions in search of this mythical land, until James Cook's second journey (1772–1775) led to the conclusion that, if it did exist, it was further south than the 65° line of latitude South. Life Dalrymple was born at Newhailes, near Edinburgh, the eleventh of fifteen children of Sir James Dalrymple and his wife, Lady Christian Hamilton, the daughter of the Earl of Haddington. He went to London in 1752 and was appointed a writer in the British East India Company, being first posted to Madras. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabriel De Foigny
Gabriel de Foigny (ca. 1630-1692) is the author of an important utopia, '' La Terre Australe connue'', 1676. Life All we know about Foigny, including his identity (the book was printed without his name), is based exclusively on the second edition of Pierre Bayle's '' Dictionnaire historique et critique'' (1701, under "Sadeur"). He was born in Lorraine and became a Franciscan, but left the order. He moved near Geneva, now as a Protestant, and made a living as a tutor. The ''Terre australe connue'' was printed at Geneva, as if from Vannes.Geoffroy Atkinson, The Extraordinary Voyage in French Literature Before 1700', 1920 p. 36 In English *Gabriel de Foigny. ''The Southern Land, Known'' (La Terre Australe connue, 1676). Trans. and ed. David Fausett. Syracuse UP, 1993 References *Everett F. Bleiler Everett Franklin Bleiler (April 30, 1920 – June 13, 2010) was an American editor, bibliographer, and scholar of science fiction, detective fiction, and fantasy literature. In the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jakarta
Jakarta (; , bew, Jakarte), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta ( id, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta) is the capital and largest city of Indonesia. Lying on the northwest coast of Java, the world's most populous island, Jakarta is the largest city in Southeast Asia and serves as the diplomatic capital of ASEAN. The city is the economic, cultural, and political centre of Indonesia. It possesses a province-level status and has a population of 10,609,681 as of mid 2021.Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2022. Although Jakarta extends over only , and thus has the smallest area of any Indonesian province, its metropolitan area covers , which includes the satellite cities Bogor, Depok, Tangerang, South Tangerang, and Bekasi, and has an estimated population of 35 million , making it the largest urban area in Indonesia and the second-largest in the world (after Tokyo). Jakarta ranks first among the Indonesian provinces in human development index. Jakar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Jakarta
Jakarta is Indonesia's capital and largest city. Located on an estuary of the Ciliwung River, on the northwestern part of Java, the area has long sustained human settlement. Historical evidence from Jakarta dates back to the 4th century CE, when it was a Hindu settlement and port. The city has been sequentially claimed by the Indianized kingdom of Tarumanegara, the Hindu Kingdom of Sunda, the Muslim Sultanate of Banten, and by Dutch, Japanese and Indonesian administrations. The Dutch East Indies built up the area before it was taken during World War II by the Empire of Japan and finally became independent as part of Indonesia. Jakarta has been known by several names. It was called Sunda Kelapa during the Kingdom of Sunda period and Jayakarta, Djajakarta or Jacatra during the short period of the Banten Sultanate. Thereafter, Jakarta evolved in three stages. The "old city", close to the sea in the north, developed between 1619 and 1799 during the era of the VOC. The "new cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habsburg Dynasty
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Habsburg, french: Maison des Habsbourg and also known as the House of Austriagerman: link=no, Haus Österreich, ; es, link=no, Casa de Austria; nl, Huis van Oostenrijk, pl, dom Austrii, la, Domus Austriæ, french: Maison d'Autriche; hu, Ausztria Háza; it, Casa d'Austria; pt, Casa da Áustria is one of the most prominent and important dynasties in European history. The house takes its name from Habsburg Castle, a fortress built in the 1020s in present-day Switzerland by Radbot of Klettgau, who named his fortress Habsburg. His grandson Otto II was the first to take the fortress name as his own, adding "Count of Habsburg" to his title. In 1273, Count Radbot's seventh-generation descendant Rudolph of Habsburg was elected King of the R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous city and state. A landlocked country, Austria is bordered by Germany to the northwest, the Czech Republic to the north, Slovakia to the northeast, Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west. The country occupies an area of and has a population of 9 million. Austria emerged from the remnants of the Eastern and Hungarian March at the end of the first millennium. Originally a margraviate of Bavaria, it developed into a duchy of the Holy Roman Empire in 1156 and was later made an archduchy in 1453. In the 16th century, Vienna began serving as the empire's administrative capital and Austria thus became the heartland of the Habsburg monarchy. After the dissolution of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

_by_Matthew_Flinders.jpg)


