|
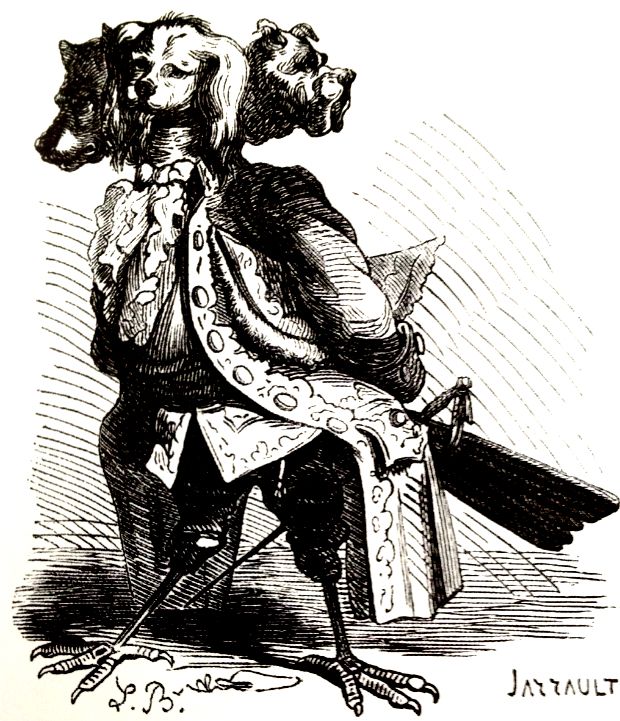
Naberius
The demon Naberius was first mentioned by Johann Weyer in 1583. He is supposedly the most valiant Marquess of Hell, and has nineteen legions of demons under his command. He makes men cunning in all arts (and sciences, according to most authors), but especially in rhetoric, speaking with a hoarse voice. He also restores lost dignities and honors, although to Johann Weyer, he procures the loss of them. Description Naberius appears as a three-headed dog or a raven. He has a raucous voice, but presents himself as eloquent and amiable. He teaches the art of gracious living. He has also been depicted as a crow or a black crane. Concerning his name, it is unclear if there is an association with the Greek Cerberus. It is said that in 1583, Johann Weyer considers both of them to be the same demon. He claimed: Naberius aberus alias Cerberus, is a valiant marquesse, showing himself in the form of a crow, when he speaks with a hoarse voice: he makes a man amiable and cunning in all arts, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naberius Cerbere
The demon Naberius was first mentioned by Johann Weyer in 1583. He is supposedly the most valiant Marquess of Hell, and has nineteen legions of demons under his command. He makes men cunning in all arts (and sciences, according to most authors), but especially in rhetoric, speaking with a hoarse voice. He also restores lost dignities and honors, although to Johann Weyer, he procures the loss of them. Description Naberius appears as a three-headed dog or a raven. He has a raucous voice, but presents himself as eloquent and amiable. He teaches the art of gracious living. He has also been depicted as a Corvus (genus), crow or a black crane (bird), crane. Concerning his name, it is unclear if there is an association with the Greek mythology, Greek Cerberus. It is said that in 1583, Johann Weyer considers both of them to be the same demon. He claimed: Naberius [Naberus], alias Cerberus, is a valiant marquesse, showing himself in the form of a crow, when he speaks with a hoarse voice: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
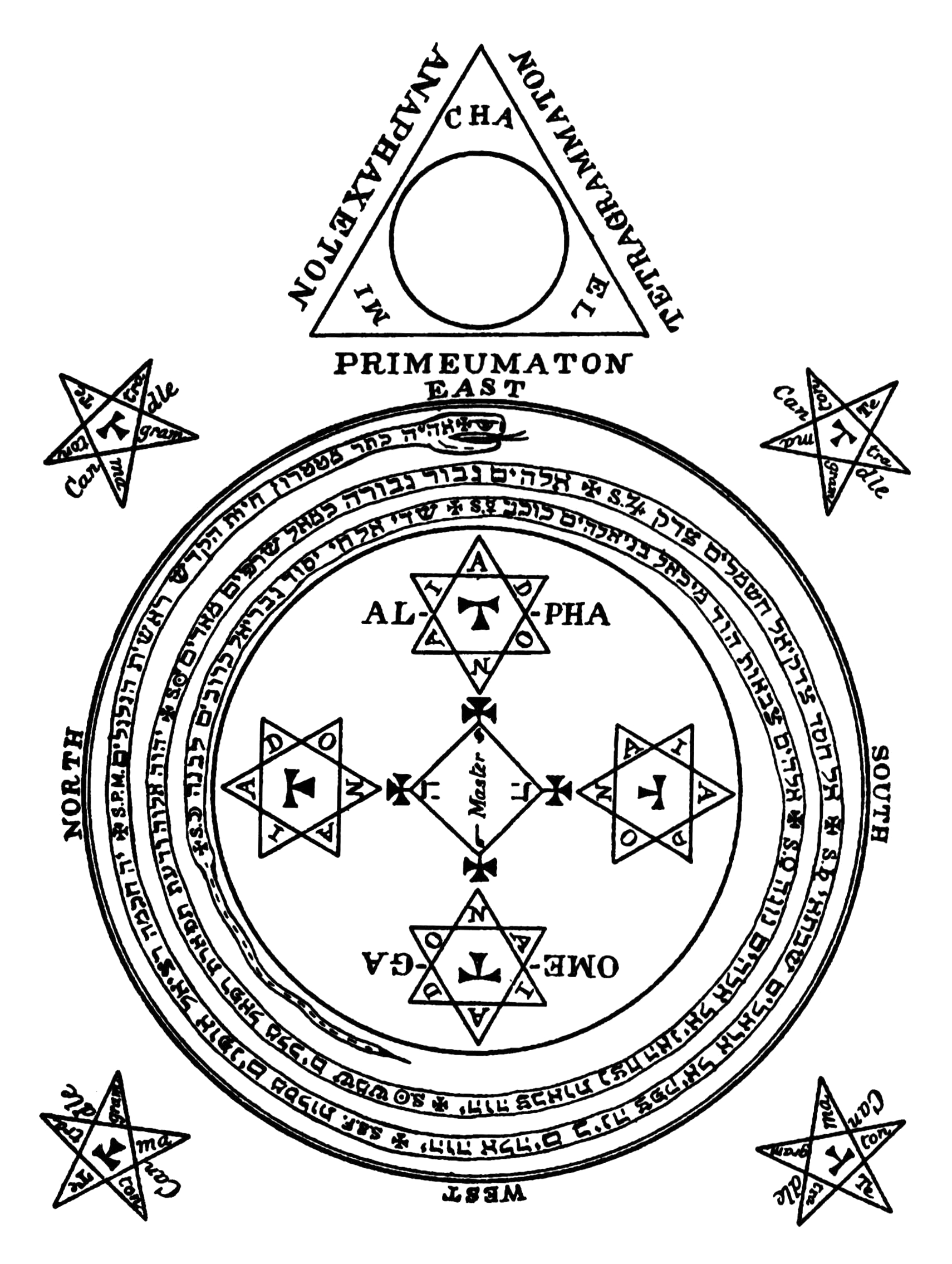
The Lesser Key Of Solomon
''The Lesser Key of Solomon'', also known as ''Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis'' or simply ''Lemegeton'', is an anonymous grimoire on demonology. It was compiled in the mid-17th century, mostly from materials a couple of centuries older.''Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis: The Lesser Key of Solomon, Detailing the Ceremonial Art of Commanding Spirits Both Good and Evil''; ed. Joseph H. Peterson; Weiser Books Maine; 2001. pp. xi–xvii.''The Goetia of Dr Rudd''; Thomas Rudd, Eds. Stephen Skinner & David Rankine; 2007, Golden Hoard Press. p. 399. It is divided into five books—the ''Ars Goetia'', ''Ars Theurgia-Goetia'', ''Ars Paulina'', ''Ars Almadel'', and ''Ars Notoria''. ''Ars Goetia'' Etymology The text is more properly called "Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis, or, The little Key of Solomon". The title most commonly used, "The Lesser Key of Solomon," does not in fact occur in the manuscripts. A.E. Waite, in his 1898 ''Book of Black Magic and of Pacts'' does use the ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demon
A demon is a malevolent supernatural entity. Historically, belief in demons, or stories about demons, occurs in religion, occultism, literature, fiction, mythology, and folklore; as well as in media such as comics, video games, movies, anime, and television series. Belief in demons probably goes back to the Paleolithic age, stemming from humanity's fear of the unknown, the strange and the horrific. ''A Dictionary of Comparative Religion'' edited by S.G.F. Brandon 1970 In ancient Near Eastern religions and in the Abrahamic religions, including early Judaism and ancient-medieval Christian demonology, a demon is considered a harmful spiritual entity which may cause demonic possession, calling for an exorcism. Large portions of Jewish demonology, a key influence on Christianity and Islam, originated from a later form of Zoroastrianism, and was transferred to Judaism during the Persian era. Demons may or may not also be considered to be devils: minions of the Devil. In ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Weyer
Johann Weyer or Johannes Wier ( la, Ioannes Wierus or '; 1515 – 24 February 1588) was a Dutch physician, occultist and demonologist, disciple and follower of Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa. He was among the first to publish against the persecution of witches. His most influential work is ('On the Illusions of the Demons and on Spells and Poisons'; 1563). Biography Weyer was born in Grave, a small town in the Duchy of Brabant in the Habsburg Netherlands. He attended the Latin schools in 's-Hertogenbosch and Leuven and when he was about 14 years of age, he became a live-in student of Agrippa, in Antwerp. Agrippa had to leave Antwerp in 1532 and he and Weyer settled in Bonn, under the protection of prince-bishop Hermann von Wied. (Agrippa completed a work on demons in 1533 and perished two years later while on a trip to France). From 1534, Weyer studied medicine in Paris and later in Orléans, but it appears unlikely that he obtained the title of Doctor through these s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marquess
A marquess (; french: marquis ), es, marqués, pt, marquês. is a nobleman of high hereditary rank in various European peerages and in those of some of their former colonies. The German language equivalent is Markgraf (margrave). A woman with the rank of a marquess or the wife (or widow) of a marquess is a marchioness or marquise. These titles are also used to translate equivalent Asian styles, as in Imperial China and Imperial Japan. Etymology The word ''marquess'' entered the English language from the Old French ("ruler of a border area") in the late 13th or early 14th century. The French word was derived from ("frontier"), itself descended from the Middle Latin ("frontier"), from which the modern English word ''march'' also descends. The distinction between governors of frontier territories and interior territories was made as early as the founding of the Roman Empire when some provinces were set aside for administration by the senate and more unpacified or vulnerab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hell
In religion and folklore, hell is a location in the afterlife in which evil souls are subjected to punitive suffering, most often through torture, as eternal punishment after death. Religions with a linear divine history often depict hells as eternal destinations, the biggest examples of which are Christianity and Islam, whereas religions with reincarnation usually depict a hell as an intermediary period between incarnations, as is the case in the dharmic religions. Religions typically locate hell in another dimension or under Earth's surface. Other afterlife destinations include heaven, paradise, purgatory, limbo, and the underworld. Other religions, which do not conceive of the afterlife as a place of punishment or reward, merely describe an abode of the dead, the grave, a neutral place that is located under the surface of Earth (for example, see Kur, Hades, and Sheol). Such places are sometimes equated with the English word ''hell'', though a more correct translatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhetoric
Rhetoric () is the art of persuasion, which along with grammar and logic (or dialectic), is one of the three ancient arts of discourse. Rhetoric aims to study the techniques writers or speakers utilize to inform, persuade, or motivate particular audiences in specific situations. Aristotle defines rhetoric as "the faculty of observing in any given case the available means of persuasion" and since mastery of the art was necessary for victory in a case at law, for passage of proposals in the assembly, or for fame as a speaker in civic ceremonies, he calls it "a combination of the science of logic and of the ethical branch of politics". Rhetoric typically provides heuristics for understanding, discovering, and developing arguments for particular situations, such as Aristotle's three persuasive audience appeals: logos, pathos, and ethos. The five canons of rhetoric or phases of developing a persuasive speech were first codified in classical Rome: invention, arrangement, style ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raven
A raven is any of several larger-bodied bird species of the genus ''Corvus''. These species do not form a single taxonomic group within the genus. There is no consistent distinction between "crows" and "ravens", common names which are assigned to different species chiefly on the basis of their size. The largest raven species are the common raven and the thick-billed raven. Etymology The term "raven" originally referred to the common raven (''Corvus corax''), the type species of the genus ''Corvus'', which has a larger distribution than any other species of ''Corvus'', ranging over much of the Northern Hemisphere. The modern English word ''raven'' has cognates in all other Germanic languages, including Old Norse (and subsequently modern Icelandic) and Old High German , all of which descend from Proto-Germanic . Collective nouns for a group of ravens (or at least the common raven) include "rave", "treachery", "unkindness" and "conspiracy". In practice, most people use the more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corvus (genus)
''Corvus'' is a widely distributed genus of medium-sized to large birds in the family Corvidae. It includes species commonly known as crows, ravens and rooks. The species commonly encountered in Europe are the carrion crow, the hooded crow, the common raven and the rook; those discovered later were named "crow" or "raven" chiefly on the basis of their size, crows generally being smaller. The genus name is Latin for "crow". The 45 or so members of this genus occur on all temperate continents except South America, and several islands. The ''Corvus'' genus makes up a third of the species in the family Corvidae. The members appear to have evolved in Asia from the corvid stock, which had evolved in Australia. The collective name for a group of crows is a "flock" or a "murder". Recent research has found some crow species capable of not only tool use, but also tool construction. Crows are now considered to be among the world's most intelligent animals with an encephalization quotie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crane (bird)
Cranes are a family, the Gruidae, of large, long-legged, and long-necked birds in the group Gruiformes. The 15 species of cranes are placed in three genera, ''Antigone'', ''Balearica'', and '' Grus''. Unlike the similar-looking but unrelated herons, cranes fly with necks outstretched, not pulled back. Cranes live on most continents, with the exception of Antarctica and South America. They are opportunistic feeders that change their diets according to the season and their own nutrient requirements. They eat a range of items from small rodents, eggs of birds, fish, amphibians, and insects to grain and berries. Cranes construct platform nests in shallow water, and typically lay two eggs at a time. Both parents help to rear the young, which remain with them until the next breeding season. Some species and populations of cranes migrate over long distances; others do not migrate at all. Cranes are solitary during the breeding season, occurring in pairs, but during the nonbreeding se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical cosmology, nature of the world, the lives and activities of List of Greek mythological figures, deities, Greek hero cult, heroes, and List of Greek mythological creatures, mythological creatures, and the origins and significance of the ancient Greeks' own cult (religious practice), cult and ritual practices. Modern scholars study the myths to shed light on the religious and political institutions of ancient Greece, and to better understand the nature of myth-making itself. The Greek myths were initially propagated in an oral tradition, oral-poetic tradition most likely by Minoan civilization, Minoan and Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaean singers starting in the 18th century BC; eventually the myths of the heroes of the Trojan War and its after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
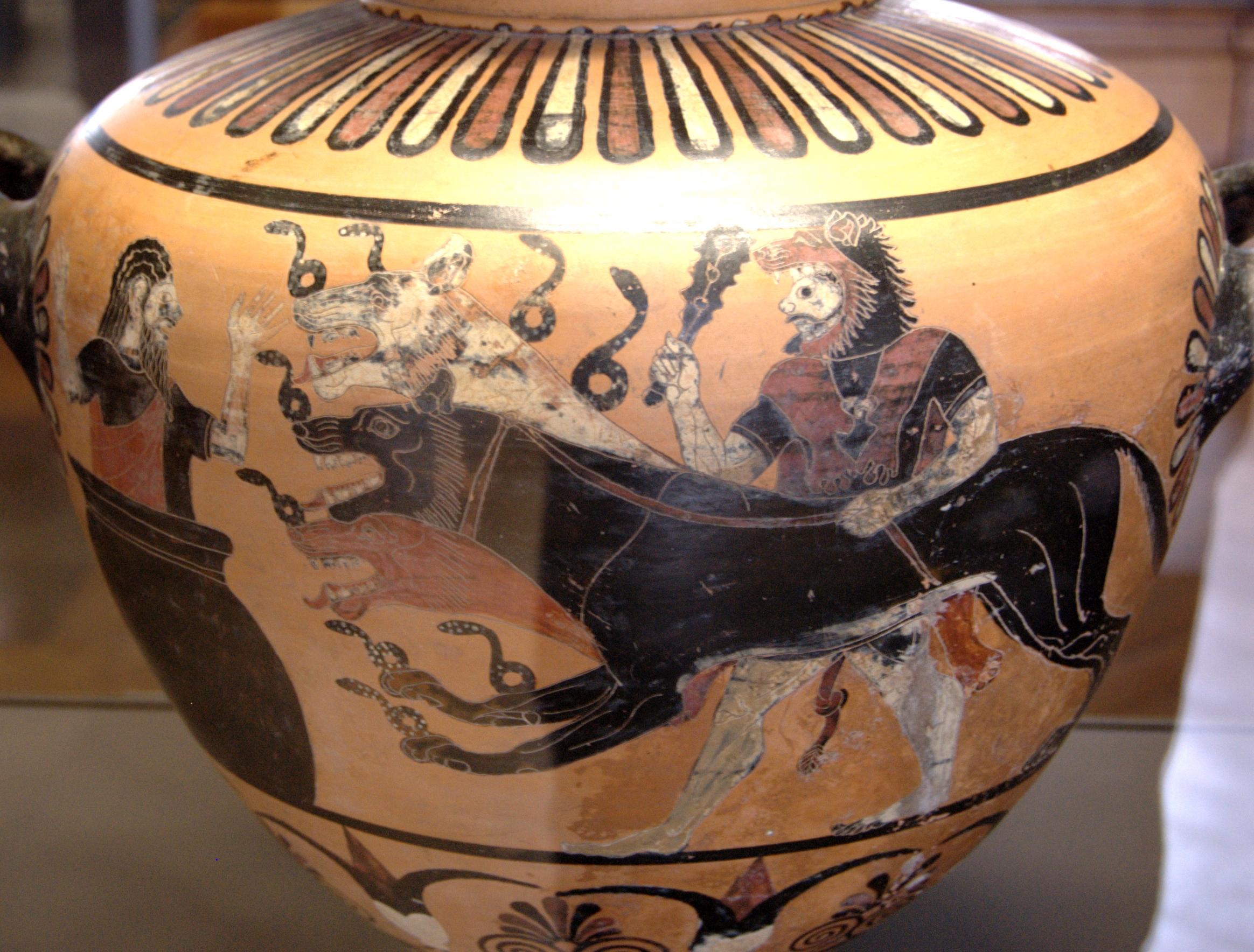
Cerberus
In Greek mythology, Cerberus (; grc-gre, Κέρβερος ''Kérberos'' ), often referred to as the hound of Hades, is a multi-headed dog that guards the gates of the Underworld to prevent the dead from leaving. He was the offspring of the monsters Echidna and Typhon, and was usually described as having three heads, a serpent for a tail, and snakes protruding from multiple parts of his body. Cerberus is primarily known for his capture by Heracles, the last of Heracles' twelve labours. Descriptions Descriptions of Cerberus vary, including the number of his heads. Cerberus was usually three-headed, though not always. Cerberus had several multi-headed relatives. His father was the multi snake-headed Typhon, and Cerberus was the brother of three other multi-headed monsters, the multi-snake-headed Lernaean Hydra; Orthrus, the two-headed dog who guarded the Cattle of Geryon; and the Chimera, who had three heads: that of a lion, a goat, and a snake. And, like these close relatives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

.jpg)




