|
Nabarzanes
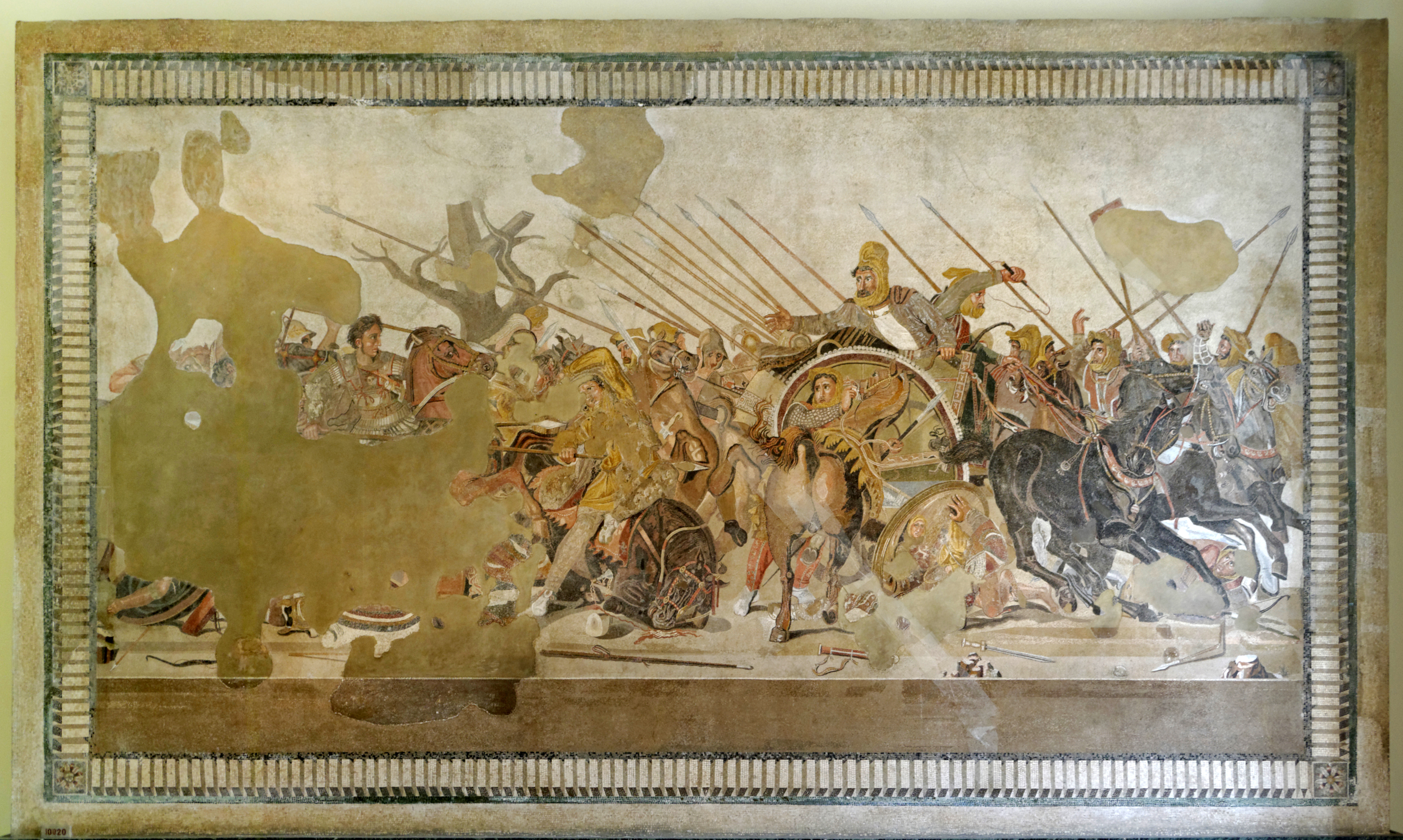
Nabarzanes (died ) was a high-ranking Persian commander, who served as the chiliarch of the royal cavalry of the Achaemenid King of Kings Darius III (). Following the Persian defeat against the Macedonian king Alexander the Great () at the Battle of Gaugamela in 331 BC, Nabarzanes conspired against Darius III with other Persian grandees, such as Bessus, the satrap of Bactria, and Barsaentes, the satrap of Arachosia-Drangiana. Together they arrested Darius III in mid-330 BC, with Bessus being chosen as the leader of the Achaemenid forces, probably due to his Achaemenid descent. The arrest of Darius III gave Alexander the pretext of avenging him. Fleeing from the pursuing Macedonian forces, Bessus and the rebels carried Darius III in a covered wagon, reportedly in golden chains. In order to buy some time for their escape, Bessus and his co-conspirators killed Darius III and left his body by the road. Bessus then appointed Nabarzanes the satrap of Hyrcania and Parthia, which were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bessus
Bessus or Bessos ( peo, *Bayaçā; grc-gre, Βήσσος), also known by his throne name Artaxerxes V ( peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης; died summer 329 BC), was a Persian satrap of the eastern Achaemenid satrapy of Bactria, as well as the self-proclaimed King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 330 to 329 BC. A member of the ruling Achaemenid dynasty, Bessus came to power shortly after killing the legitimate Achaemenid ruler Darius III (), and subsequently attempted to hold the eastern part of the empire against the Macedonian king Alexander the Great (). His realm quickly started to fall apart, including Bactria, which was the main center. Fleeing into Sogdia, he was arrested by his own officers, who handed him over to Alexander, who had him executed at Ecbatana. Bessus appears in the 11th-century Persian epic ''Shahnameh'' under the name of Janusipar/Janushyar. Name "Bessus" (Βήσσος) is the Greek transliteration of the Old ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darius III
Darius III ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; c. 380 – 330 BC) was the last Achaemenid King of Kings of Persia, reigning from 336 BC to his death in 330 BC. Contrary to his predecessor Artaxerxes IV Arses, Darius was a distant member of the Achaemenid dynasty. During his early career, he was reportedly an obscure figure among his peers and first rose to prominence during the Cadusian expedition of Artaxerxes III in the 350s BC. As a reward for his bravery, he was given the Satrapy of Armenia. Around 340 BC, he was placed in charge of the royal "postal service," a high-ranking position. In 338 BC, Artaxerxes III met an abrupt end after being poisoned by the court eunuch and chiliarch (''hazahrapatish'') Bagoas, who installed his youngest son Arses on the throne. He only reigned for a few years, until Bagoas had him poisoned as well. Darius was subsequently installed on the throne and soon forced Bagoas to drink his poison after discovering th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagoas (courtier)
Bagoas (Old Persian: ''Bagāvahyā'', grc, Βαγώας ''Bagōas'') was the name of two eunuchs in the court of the Persian Empire in the 4th century BC. Bagoas the Younger was a courtier of Darius and later of Alexander the Great. Bagoas' kiss According to Plutarch, Bagoas won a dancing contest after the Macedonian crossing of the Gedrosian Desert. The Macedonian troops, with whom Bagoas was very popular, demanded that king Alexander should kiss Bagoas, and he did so. Fictionalized versions * Bagoas is the narrator and title character of ''The Persian Boy'', the historical novel by Mary Renault, which portrays him sympathetically. He reappears in a smaller but still significant role in the sequel ''Funeral Games''. *The Serpent's Oath' (2021) by A.R. Valeson portrays a historical fiction romance between King Henry VIII's Master Secretary, Thomas Cromwell and the eunuch, Arthamaeus, inspired by the courtier Bagoas. * He makes an even briefer appearance in ''Les Conquêtes d'A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyrcania
Hyrcania () ( el, ''Hyrkania'', Old Persian: 𐎺𐎼𐎣𐎠𐎴 ''Varkâna'',Lendering (1996) Middle Persian: 𐭢𐭥𐭫𐭢𐭠𐭭 ''Gurgān'', Akkadian: ''Urqananu'') is a historical region composed of the land south-east of the Caspian Sea in modern-day Iran and Turkmenistan, bound in the south by the Alborz mountain range and the Kopet Dag in the east. The region served as a satrapy (province) of the Median Empire, a sub-province of the Achaemenid Empire, and a province within its successors, the Seleucid, Arsacid and Sasanian empires. Hyrcania bordered Parthia to the east (later known as Abarshahr), Dihistan to the north, Media to the south and Mardia to the west. Etymology ''Hyrcania'' () is the Greek name for the region, a borrowing from the Old Persian ''Verkâna'' as recorded in Darius the Great's Behistun Inscription (522 BC), as well as in other Old Persian cuneiform inscriptions. ''Verkā'' means "wolf" in Old Iranian, cf. Avestan ''vəhrkō'', Gila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dara II
Dara II or Darab II was the last king of the mythological Kayanian dynasty, ruling between 14 and 16 years. He is generally identified with Darius III (), the last king of the Achaemenid Empire. In Middle Persian literature and Islamic chronicles, he is generally known as "Dara", while he is known as "Darab" in the New Persian proses '' Darab-nama'' and ''Iskandar-nama''. He was the son and successor of Dara I. According to early traditions, Dara II's mother was Mahnahid, daughter of Hazarmard, while later traditions refer her to as Thamrusia, a Greek woman who was the daughter of Fastabiqun and former wife of the king of Oman. Dara II was the half-brother of Iskandar (Alexander the Great), who, after refusing to pay tribute, rebelled. During the rebellion, Dara II was assassinated by his ministers Mahyar and Janushyar (Bessus and Nabarzanes). He had three sons, Ashk, Ardashir, and a third, who name is uncertain. The Sasanian monarchs of Iran (224–651) invented a descent that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barsaentes
Barsaentes ( el, Βαρσαέντης, translit=Barsaéntēs) was a Persian nobleman, who served as the satrap of Arachosia and Drangiana under the Achaemenid King of Kings Darius III (). Barsaentes took part in the Battle of Gaugamela against the Macedonian king Alexander the Great () in 331 BC, where he led his regional troops, as well as the supposed "Mountain" Indians. Following the Persian defeat, Barsaentes accompanied Darius III in his flight to the Upper Satrapies. There he conspired against Darius III with other Persian grandees, such as the chiliarch Nabarzanes, and Bessus, the satrap of Bactria. Together they arrested Darius III in mid-330 BC, with Bessus being chosen as the leader of the Achaemenid forces, probably due to his Achaemenid descent. The arrest of Darius III gave Alexander the pretext A pretext (adj: pretextual) is an excuse to do something or say something that is not accurate. Pretexts may be based on a half-truth or developed in the context of a misle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian. The ancient Persians were originally an ancient Iranian people who had migrated to the region of Persis (corresponding to the modern-day Iranian province of Fars) by the 9th century BCE. Together with their compatriot allies, they established and ruled some of the world's most powerful empires that are well-recognized for their massive cultural, political, and social influence, which covered much of the territory and population of the ancient world.. Throughout history, the Persian people have contributed greatly to art and science. Persian literature is one of the world's most prominent literary traditions. In contemporary terminology, people from Afghanistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan who natively speak the Persian language are kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satraps Of The Achaemenid Empire
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires. The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with considerable autonomy. The word came to suggest tyranny or ostentatious splendour, and in modern usage refers to any subordinate or local ruler, usually with unfavourable connotations of corruption. A satrapy is the territory governed by a satrap. Etymology The word is derived via Latin from Greek ''satrápes'' (), itself borrowed from an Old Iranian ''*khshathra-pa''. In Old Persian, which was the native language of the Achaemenids, it is recorded as ''khshathapavan'' (, literally "protector of the province"). The Median form is reconstructed as ''*khshathrapavan-''. It is cognate with Sanskrit ''kshetrapal'' (). The Biblical Hebrew form is ''aḥashdarpan'' , as found in . In the Parthian (language of the Arsacid Empire) and Middle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Leaders Of The Achaemenid Empire
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th-century BC Iranian People
The 4th century (per the Julian calendar and Anno Domini/Common era) was the time period which lasted from 301 ( CCCI) through 400 ( CD). In the West, the early part of the century was shaped by Constantine the Great, who became the first Roman emperor to adopt Christianity. Gaining sole reign of the empire, he is also noted for re-establishing a single imperial capital, choosing the site of ancient Byzantium in 330 (over the current capitals, which had effectively been changed by Diocletian's reforms to Milan in the West, and Nicomedeia in the East) to build the city soon called Nova Roma (New Rome); it was later renamed Constantinople in his honor. The last emperor to control both the eastern and western halves of the empire was Theodosius I. As the century progressed after his death, it became increasingly apparent that the empire had changed in many ways since the time of Augustus. The two emperor system originally established by Diocletian in the previous century fel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shahnameh
The ''Shahnameh'' or ''Shahnama'' ( fa, شاهنامه, Šāhnāme, lit=The Book of Kings, ) is a long epic poem written by the Persian poet Ferdowsi between c. 977 and 1010 CE and is the national epic of Greater Iran. Consisting of some 50,000 "distichs" or couplets (two-line verses), the ''Shahnameh'' is one of the world's longest epic poems. It tells mainly the mythical and to some extent the historical past of the Persian Empire from the creation of the world until the Muslim conquest in the seventh century. Iran, Azerbaijan, Afghanistan, Tajikistan and the greater region influenced by Persian culture such as Armenia, Dagestan, Georgia, Turkey, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan celebrate this national epic. The work is of central importance in Persian culture and Persian language, regarded as a literary masterpiece, and definitive of the ethno-national cultural identity of Iran. It is also important to the contemporary adherents of Zoroastrianism, in that it traces th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
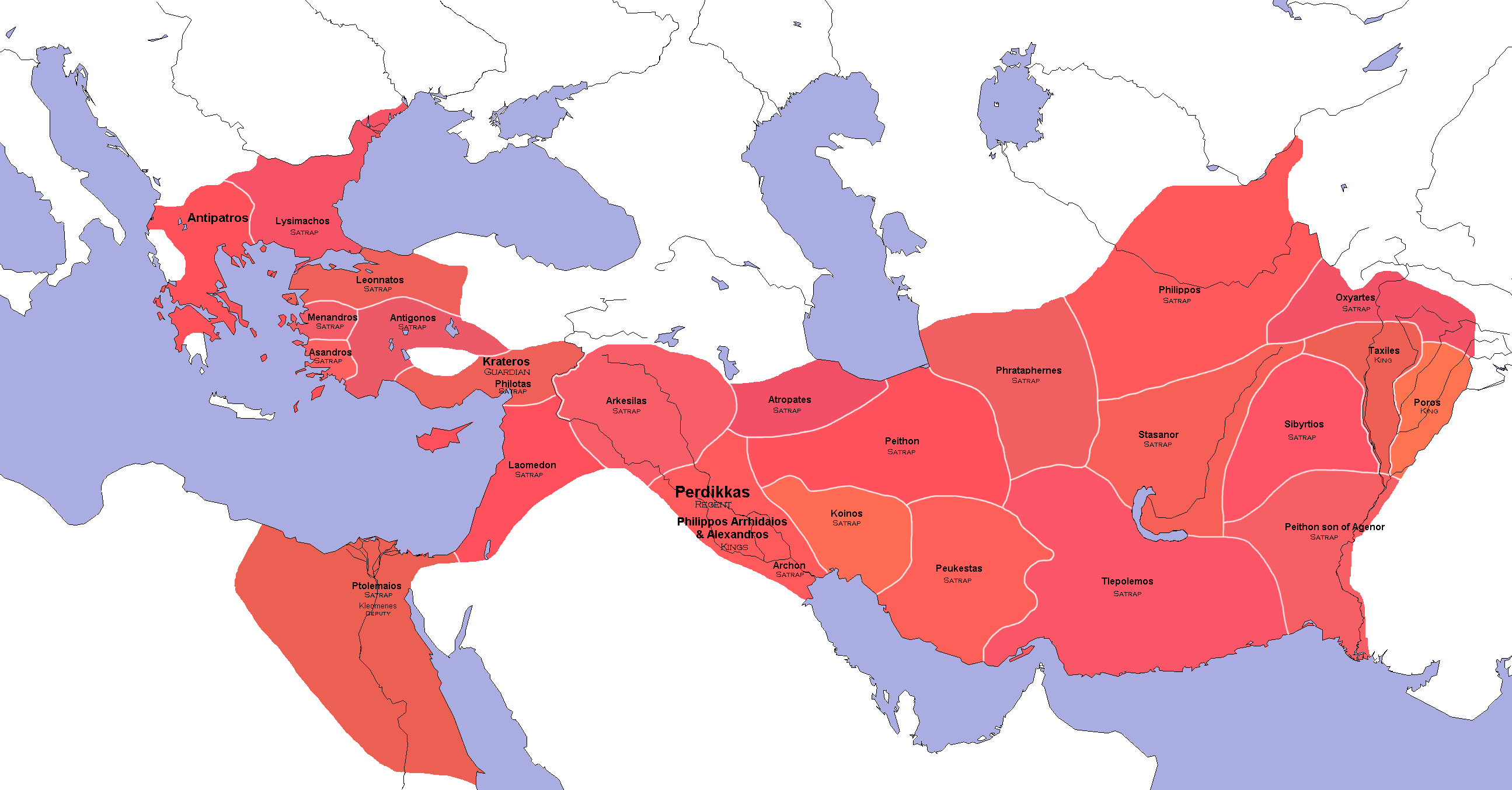
Phrataphernes
Phrataphernes (Median: ''Fratafarnah'', grc, Φραταφέρνης; lived 4th century BC) was a Persian who held the government of Parthia and Hyrcania, under the king Darius III Codomannus, and joined that monarch with the contingents from the provinces subject to his rule, shortly before the battle of Gaugamela in 331 BC. He afterwards accompanied the king on his flight into Hyrcania. Service with Alexander the Great After the death of Darius, Phrataphernes surrendered voluntarily to Alexander the Great, by whom he was kindly received, and appears to have been shortly after reinstated in his satrapy. At least he is termed by Arrian satrap of Parthia, during the advance of Alexander against Bessus, when he was detached by the king, together with Erigyius and Caranus to crush the revolt of Satibarzanes, in Aria (329 BC). He rejoined the king at Zariaspa in 328 BC. The next winter (328–327 BC), during the stay of Alexander at Nautaca, Phrataphernes was again despatched to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)