|
NNTP
The Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP) is an application protocol used for transporting Usenet news articles (''netnews'') between news servers, and for reading/posting articles by the end user client applications. Brian Kantor of the University of California, San Diego, and Phil Lapsley of the University of California, Berkeley, wrote , the specification for the Network News Transfer Protocol, in March 1986. Other contributors included Stan O. Barber from the Baylor College of Medicine and Erik Fair of Apple Computer. Usenet was originally designed based on the UUCP network, with most article transfers taking place over direct point-to-point telephone links between news servers, which were powerful time-sharing systems. Readers and posters logged into these computers reading the articles directly from the local disk. As local area networks and Internet participation proliferated, it became desirable to allow newsreaders to be run on personal computers connected to lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YProxy
yProxy is a Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP) proxy server for the Windows operating system. yProxy's main function is to convert yEnc-encoded attachments to UUE-encoded attachments on the fly. The main purpose of this is to add functionality to NNTP newsreaders that do not have native support for yEnc. The inventor of yEnc recommends yProxy for use by Windows users whose newsreaders do not support yEnc decoding. yProxy comes in two varieties: # yProxy # yProxy Pro yProxy The latest free version of yProxy is version 1.3. History of yProxy yEnc (8 bit ASCII of 8 bit data) was released in 2001, and almost immediately the most popular utility for decoding yEnc became a software utility named yEnc32. yEnc32 was an early provider of yEnc decoding, but yEnc32, while flexible through its user interface, requires manual steps to decode yEnc attachments. In the spring of 2002, shortly after yEnc gained popularity in binary newsgroups, yProxy was released as freeware. yProxy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usenet
Usenet (), a portmanteau of User's Network, is a worldwide distributed discussion system available on computers. It was developed from the general-purpose UUCP, Unix-to-Unix Copy (UUCP) dial-up network architecture. Tom Truscott and Jim Ellis (computing), Jim Ellis conceived the idea in 1979, and it was established in 1980.''From Usenet to CoWebs: interacting with social information spaces'', Christopher Lueg, Danyel Fisher, Springer (2003), , Users read and post messages (called ''articles'' or ''posts'', and collectively termed ''news'') to one or more topic categories, known as Usenet newsgroup, newsgroups. Usenet resembles a bulletin board system (BBS) in many respects and is the precursor to the Internet forums that have become widely used. Discussions are Threaded discussion, threaded, as with web forums and BBSes, though posts are stored on the server sequentially. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of TCP And UDP Port Numbers
This is a list of TCP and UDP port numbers used by protocols for operation of network applications. The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) only need one Port (computer networking), port for Duplex (telecommunications), bidirectional traffic. TCP usually uses port numbers that match the services of the corresponding UDP implementations, if they exist, and vice versa. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) is responsible for maintaining the official assignments of port numbers for specific uses, However, many unofficial uses of both well-known and registered port numbers occur in practice. Similarly, many of the official assignments refer to protocols that were never or are no longer in common use. This article lists port numbers and their associated protocols that have experienced significant uptake. Table legend Well-known ports The port numbers in the range from 0 to 1023 (0 to 210 − 1) are the ''well-known ports'' or ''system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
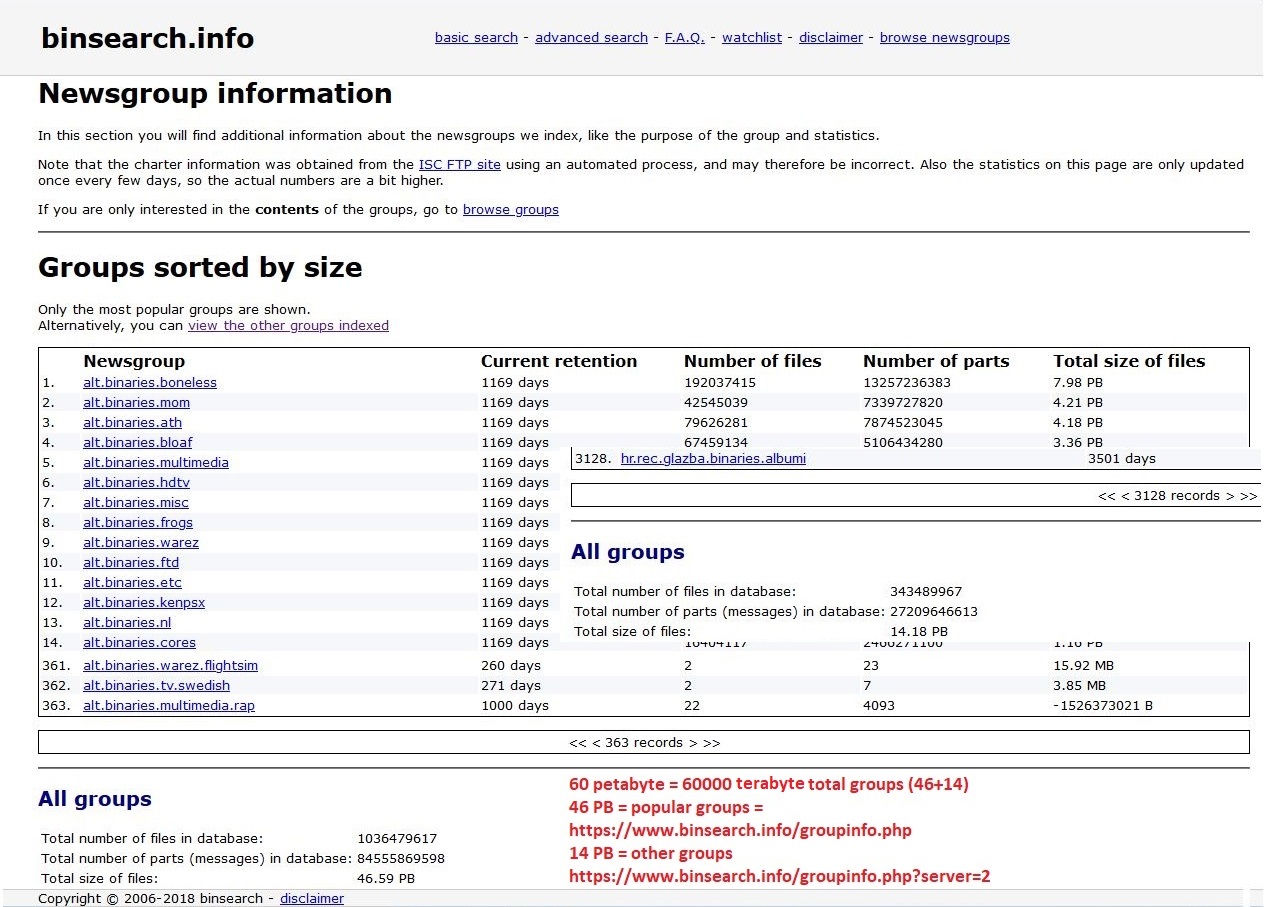
Usenet Newsgroup
A Usenet newsgroup is a repository usually within the Usenet system for messages posted from users in different locations using the Internet. They are not only discussion groups or conversations, but also a repository to publish articles, start developing tasks like creating Linux, sustain mailing lists and file uploading. That’s thank to the protocol that poses no article size limit, but are to the providers to decide. In the late 1980s, Usenet articles were often limited by the providers to 60,000 characters, but in time, Usenet groups have been split into two types: ''text'' for mainly discussions, conversations, articles, limited by most providers to about 32,000 characters, and ''binary'' for file transfer, with providers setting limits ranging from less than 1 MB to about 4 MB. Newsgroups are technically distinct from, but functionally similar to, discussion forums on the World Wide Web. Newsreader software is used to read the content of newsgroups. Before the adoption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
News Server
A news server is a collection of software used to handle Usenet articles. It may also refer to a computer itself which is primarily or solely used for handling Usenet. Access to Usenet is only available through news server providers. Articles and posts End users often use the term "posting" to refer to a single message or file posted to Usenet. For articles containing plain text, this is synonymous with an article. For binary content such as pictures and files, it is often necessary to split the content among multiple articles. Typically through the use of numbered Subject: headers, the multiple-article postings are automatically reassembled into a single unit by the newsreader. Most servers do not distinguish between single and multiple-part postings, dealing only at the level of the individual component articles. Headers and overviews Each news article contains a complete set of header lines, but in common use the term "headers" is also used when referring to the News Over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STARTTLS
Opportunistic TLS (Transport Layer Security) refers to extensions in plain text communication protocols, which offer a way to upgrade a plain text connection to an encrypted ( TLS or SSL) connection instead of using a separate port for encrypted communication. Several protocols use a command named "STARTTLS" or "Explicit TLS" for this purpose. It is a form of opportunistic encryption and is primarily intended as a countermeasure to passive monitoring. The STARTTLS command for IMAP and POP3 is defined in , for SMTP in , for XMPP in and for NNTP in . For IRC, the IRCv3 Working Group defined a STARTTLS extension, though it was later deprecated. FTP uses the command "AUTH TLS" defined in and LDAP defines a protocol extension OID in . HTTP uses an upgrade header. Layering TLS is application-neutral; in the words of : :One advantage of TLS is that it is application protocol independent. Higher-level protocols can layer on top of the TLS protocol transparently. The TLS standa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
InterNetNews
InterNetNews (INN) is a Usenet news server package, originally released by Rich Salz in 1991, and presented at the Summer 1992 USENIX conference in San Antonio, Texas. It was the first news server with integrated Network News Transfer Protocol, NNTP functionality. While previous servers processed articles individually or in batches, ''innd'' is a single continuously running process that receives articles from the network, files them, and records what remote hosts should receive them. Readers can access articles directly from the disk in the same manner as B News and C News, but an included program, called ''nnrpd'', also serves News client, newsreaders that employ NNTP. A later improvement was the Cyclical News Filesystem (CNFS), which sequentially stores articles in large on-disk buffers. This method, implemented by Scott Fritchie, greatly increased performance by eliminating the operating system overhead needed to deal with thousands of individual article files. James Bris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Usenet Newsreaders
Usenet is a worldwide, distributed discussion system that uses the Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP). Programs called newsreaders are used to read and post messages (called ''articles'' or ''posts'', and collectively termed ''news'') to one or more newsgroups. Users must have access to a news server to use a newsreader. This is a list of such newsreaders. Types of clients * Text newsreader – designed primarily for reading/posting text posts; unable to download binary attachments * Traditional newsreader – a newsreader with text support that can also handle binary attachments, though sometimes less efficiently than more specialized clients * Binary grabber/plucker – designed specifically for easy and efficient downloading of multi-part binary post attachments; limited or nonexistent reading/posting ability. These generally offer multi- server and multi-connection support. Most now support NZBs, and several either support or plan to support automatic Par2 processing. Some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phil Lapsley
Philip D. Lapsley (born 1965) is an American electrical engineer, hacker, author and entrepreneur. Early life Lapsley attended the University of California, Berkeley, in the 1980s, graduating with a B.S. and M.S. in electrical engineering and computer science in 1988 and 1991. While there he became involved in the Berkeley UNIX project and co-founded the eXperimental Computing Facility, where he was involved in defending against the Morris worm in 1988. Lapsley received an M.B.A. from the MIT Sloan School of Management. Career Lapsley co-authored RFC 977, Network News Transfer Protocol ( NNTP), an Internet standard for transmission of USENET news articles, and was the primary developer of the NNTP reference implementation, nntpd. After leaving Berkeley he co-founded Berkeley Design Technology, Inc., a digital signal processing technology advisory firm, and is the author of a book on DSP processors. He later co-founded SmartTouch, a biometric financial transaction processing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leafnode
''Leafnode'' is a store-and-forward NNTP (or Usenet) proxy server designed for small sites with just a few active newsgroups, but very easy to set up and maintain, when compared to INN. Originally created by Arnt Gulbrandsen in 1995 while he was working at Trolltech, it is currently maintained by Matthias Andree and Ralf Wildenhues. The term leaf node can also be used to describe a node on a binary tree In computer science, a binary tree is a tree data structure in which each node has at most two children, referred to as the ''left child'' and the ''right child''. That is, it is a ''k''-ary tree with . A recursive definition using set theor ... (or any other sort of tree that has nodes) which has no sub-nodes. References External links Official websiteLeafnode at SourceForge.orgInstalling and Configuring LeafNode Usenet Usenet servers {{compu-network-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Time Protocol
The Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a networking protocol for clock synchronization between computer systems over packet-switched, variable-Network latency, latency data networks. In operation since before 1985, NTP is one of the oldest Internet protocols in current use. NTP was designed by David L. Mills of the University of Delaware. NTP is intended to synchronize participating computers to within a few milliseconds of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). It uses the intersection algorithm, a modified version of Marzullo's algorithm, to select accurate time servers and is designed to mitigate the effects of variable network latency. NTP can usually maintain time to within tens of milliseconds over the public Internet, and can achieve better than one millisecond accuracy in local area networks under ideal conditions. Asymmetric Routing, routes and network congestion can cause errors of 100 ms or more. The protocol is usually described in terms of a client–server model, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport Layer Security
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a cryptographic protocol designed to provide communications security over a computer network, such as the Internet. The protocol is widely used in applications such as email, instant messaging, and voice over IP, but its use in securing HTTPS remains the most publicly visible. The TLS protocol aims primarily to provide security, including privacy (confidentiality), integrity, and authenticity through the use of cryptography, such as the use of certificates, between two or more communicating computer applications. It runs in the presentation layer and is itself composed of two layers: the TLS record and the TLS handshake protocols. The closely related Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) is a communications protocol that provides security to datagram-based applications. In technical writing, references to "(D)TLS" are often seen when it applies to both versions. TLS is a proposed Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standard, fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |