|
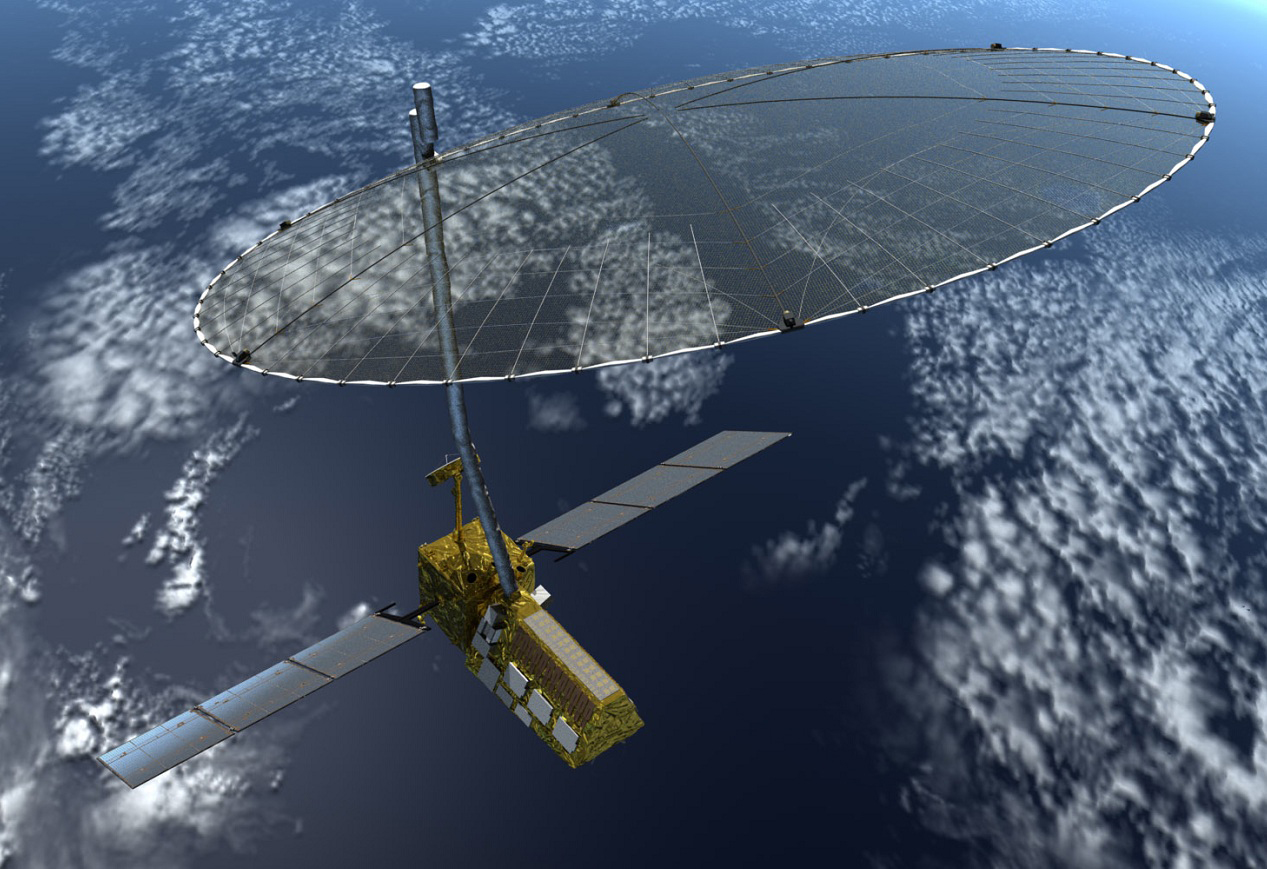
NISAR Artist Concept
The NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) mission is a joint project between NASA and ISRO to co-develop and launch a dual-frequency synthetic aperture radar on an Earth observation satellite. The satellite will be the first radar imaging satellite to use dual frequencies. It will be used for remote sensing, to observe and understand natural processes on Earth. For example, its left-facing instruments will study the Antarctic cryosphere. With a total cost estimated at US$1.5 billion, NISAR is likely to be the world's most expensive Earth-imaging satellite. Overview The NASA-ISRO Synthetic-aperture radar, Synthetic Aperture Radar, or NISAR satellite, will use advanced radar imaging to map the elevation of Earth's land and ice masses 4 to 6 times a month at resolutions of 5 to 10 meters. It is designed to observe and measure some of the planet's most complex natural processes, including ecosystem disturbances, ice-sheet collapse, and natural hazards such as earthquakes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NISAR Artist Concept
The NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) mission is a joint project between NASA and ISRO to co-develop and launch a dual-frequency synthetic aperture radar on an Earth observation satellite. The satellite will be the first radar imaging satellite to use dual frequencies. It will be used for remote sensing, to observe and understand natural processes on Earth. For example, its left-facing instruments will study the Antarctic cryosphere. With a total cost estimated at US$1.5 billion, NISAR is likely to be the world's most expensive Earth-imaging satellite. Overview The NASA-ISRO Synthetic-aperture radar, Synthetic Aperture Radar, or NISAR satellite, will use advanced radar imaging to map the elevation of Earth's land and ice masses 4 to 6 times a month at resolutions of 5 to 10 meters. It is designed to observe and measure some of the planet's most complex natural processes, including ecosystem disturbances, ice-sheet collapse, and natural hazards such as earthquakes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar Imaging
Imaging radar is an application of radar which is used to create two-dimensional images, typically of landscapes. Imaging radar provides its light to illuminate an area on the ground and take a picture at radio wavelengths. It uses an antenna and digital computer storage to record its images. In a radar image, one can see only the energy that was reflected back towards the radar antenna. The radar moves along a flight path and the area illuminated by the radar, or footprint, is moved along the surface in a swath, building the image as it does so. Digital radar images are composed of many dots. Each pixel in the radar image represents the radar backscatter for that area on the ground: brighter areas represent high backscatter, darker areas represents low backscatter. The traditional application of radar is to display the position and motion of typically highly reflective objects (such as aircraft or ships) by sending out a radiowave signal, and then detecting the direction and de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crust (geology)
In geology, the crust is the outermost solid shell of a rocky planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. It is usually distinguished from the underlying mantle by its chemical makeup; however, in the case of icy satellites, it may be distinguished based on its phase (solid crust vs. liquid mantle). The crusts of Earth, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Io, the Moon and other planetary bodies formed via igneous processes and were later modified by erosion, impact cratering, volcanism, and sedimentation. Most terrestrial planets have fairly uniform crusts. Earth, however, has two distinct types: continental crust and oceanic crust. These two types have different chemical compositions and physical properties and were formed by different geological processes. Types of crust Planetary geologists divide crust into three categories based on how and when it formed. Primary crust / primordial crust This is a planet's "original" crust. It forms from solidification of a magma ocean. Towa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Bus
A satellite bus (or spacecraft bus) is the main body and structural component of a satellite or spacecraft, in which the payload and all scientific instruments are held. Bus-derived satellites are opposed to specially produced satellites. Bus-derived satellites are usually customized to customer requirements, for example with specialized sensors or transponders, in order to achieve a specific mission. They are commonly used for geosynchronous satellites, particularly communications satellites, but are also used in spacecraft which occupy lower orbits, occasionally including low Earth orbit missions. Examples Some satellite bus examples include: * Boeing DS&S 702 * Lockheed Martin Space Systems A2100 * Alphabus * INVAP ARSAT-3K * Airbus D&S Eurostar * ISRO's I-1K, I-2K, I-3K, I-4K, I-6K, and Indian Mini Satellite bus * NASA Ames MCSB * SSL 1300 * Orbital ATK GEOStar * Mitsubishi Electric DS2000 * Spacecraft bus of the James Webb Space Telescope * SPUTNIX TabletSat * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Navigation Device
A satellite navigation device (satnav device) is a user equipment that uses one or more of several global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) to calculate the device's geographical position and provide navigational advice. Depending on the software used, the satnav device may display the position on a map, as Geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinates, or may offer routing directions. As of September 2020, there were four operational GNSS systems, the original United States' Global Positioning System (GPS), the European Union's Galileo (satellite navigation), Galileo, Russia's GLONASS, and China's BeiDou Navigation Satellite System. The Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) will follow and Japan's Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS) scheduled for 2023 will augment the accuracy of a number of GNSS. A satellite navigation device can retrieve location and time information from one or more GNSS systems in all weather conditions, anywhere on or near th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landslide
Landslides, also known as landslips, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, deep-seated grade (slope), slope failures, mudflows, and debris flows. Landslides occur in a variety of environments, characterized by either steep or gentle slope gradients, from mountain ranges to coastal cliffs or even underwater, in which case they are called submarine landslides. Gravity is the primary driving force for a landslide to occur, but there are other factors affecting slope stability that produce specific conditions that make a slope prone to failure. In many cases, the landslide is triggered by a specific event (such as a heavy rainfall, an earthquake, a slope cut to build a road, and many others), although this is not always identifiable. Causes Landslides occur when the slope (or a portion of it) undergoes some processes that change its condition from stable to unstable. This is essentially due to a decrease in the She ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcano
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism, of which the Hawaiian hotspot is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
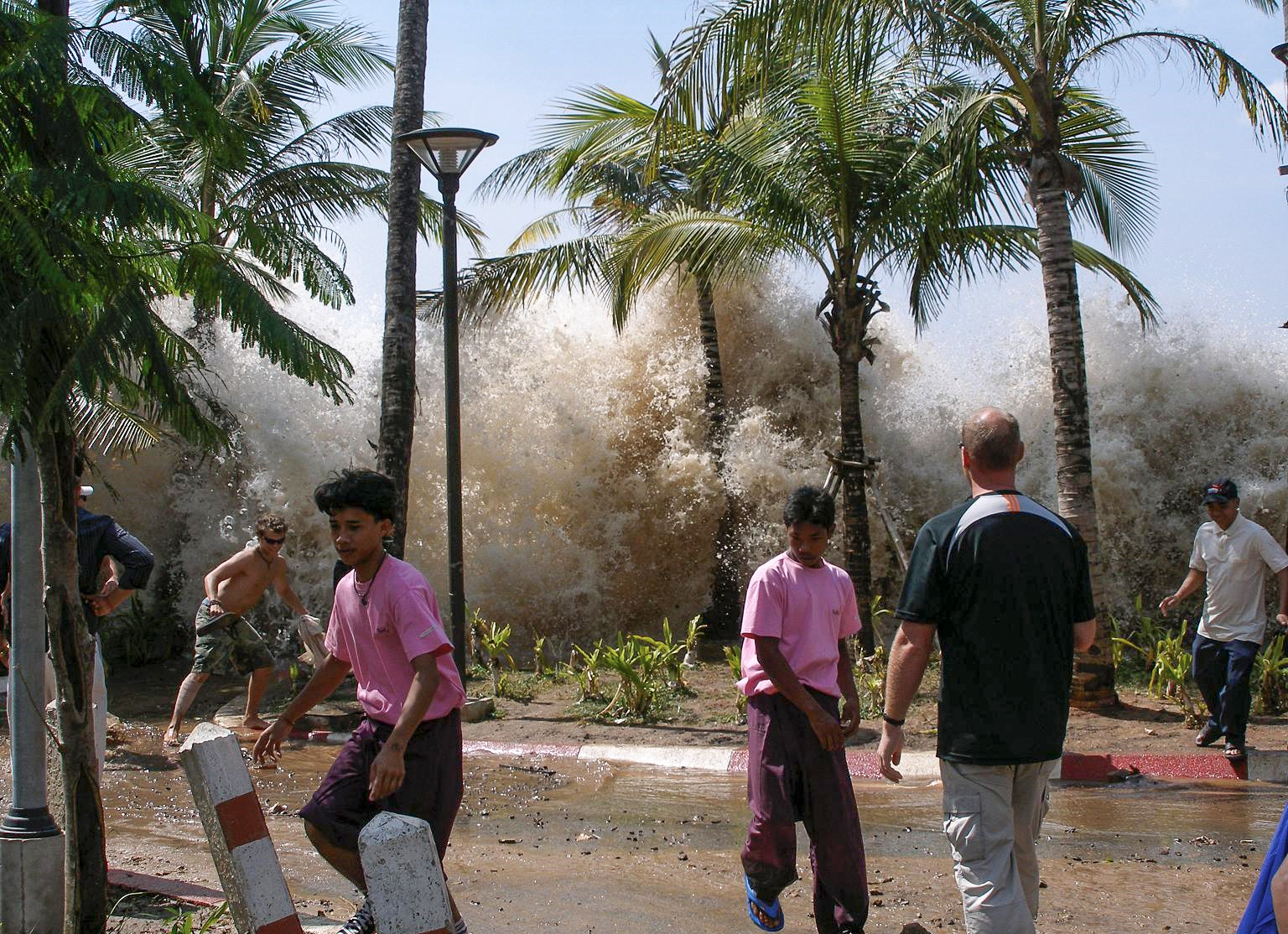
Tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explosions (including detonations, landslides, glacier calvings, meteorite impacts and other disturbances) above or below water all have the potential to generate a tsunami. Unlike normal ocean waves, which are generated by wind, or tides, which are in turn generated by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun, a tsunami is generated by the displacement of water from a large event. Tsunami waves do not resemble normal undersea currents or sea waves because their wavelength is far longer. Rather than appearing as a breaking wave, a tsunami may instead initially resemble a rapidly rising tide. For this reason, it is often referred to as a tidal wave, although this usage is not favoured by the scientific community because it might give ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those that are so weak that they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time period. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. The word ''tremor'' is also used for Episodic tremor and slip, non-earthquake seismic rumbling. At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and displacing or disrupting the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice-sheet Dynamics
Ice sheet dynamics describe the motion within large bodies of ice, such those currently on Greenland and Antarctica. Ice motion is dominated by the movement of glaciers, whose gravity-driven activity is controlled by two main variable factors: the temperature and the strength of their bases. A number of processes alter these two factors, resulting in cyclic surges of activity interspersed with longer periods of inactivity, on both hourly and centennial time scales. Ice-sheet dynamics are of interest in modelling future sea level rise. General Boundary conditions The interface between an ice stream and the ocean is a significant control of the rate of flow. Ice shelves are thick layers of ice floating on the sea – can stabilise the glaciers that feed them. These tend to have accumulation on their tops, may experience melting on their bases, and calve icebergs at their periphery. The catastrophic collapse of the Larsen B ice shelf in the space of three weeks during Feb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disturbance (ecology)
In ecology, a disturbance is a temporary change in environmental conditions that causes a pronounced change in an ecosystem. Disturbances often act quickly and with great effect, to alter the physical structure or arrangement of biotic and abiotic elements. A disturbance can also occur over a long period of time and can impact the biodiversity within an ecosystem. Major ecological disturbances may include fires, flooding, storms, insect outbreaks and trampling. Earthquakes, various types of volcanic eruptions, tsunami, firestorms, impact events, climate change, and the devastating effects of human impact on the environment (anthropogenic disturbances) such as clearcutting, forest clearing and the introduction of invasive species can be considered major disturbances. Not only invasive species can have a profound effect on an ecosystem, but also naturally occurring species can cause disturbance by their behavior. Disturbance forces can have profound immediate effects on ecosystem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryosphere
] The cryosphere (from the Ancient Greek, Greek ''kryos'', "cold", "frost" or "ice" and ''sphaira'', "globe, ball") is an all-encompassing term for those portions of Earth's surface where water is in solid form, including sea ice, lake ice, river ice, snow cover, glaciers, ice caps, ice sheets, and frozen ground (which includes permafrost). Thus, there is a wide overlap with the hydrosphere. The cryosphere is an integral part of the global climate system with important linkages and feedbacks generated through its influence on surface energy and moisture fluxes, clouds, precipitation, hydrology, atmospheric and oceanic circulation. Through these feedback processes, the cryosphere plays a significant role in the global climate and in climate model response to global changes. Approximately 10% of the Earth's surface is covered by ice, but this is rapidly decreasing. The term '' deglaciation'' describes the retreat of cryospheric features. Cryology is the study of cryospheres. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |