|
NFE2L1
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 1 (Nrf1) also known as nuclear factor erythroid-2-like 1 (NFE2L1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NFE2L1'' gene. Since NFE2L1 is referred to as Nrf1, it is often confused with nuclear respiratory factor 1 (Nrf1). NFE2L1 is a cap ‘n’ collar, basic-leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor. Several isoforms of NFE2L1 have been described for both human and mouse genes. NFE2L1 was first cloned in yeast using a genetic screening method. NFE2L1 is ubiquitously expressed, and high levels of transcript are detected in the heart, kidney, skeletal muscle, fat, and brain. Four separate regions — an asparagine/serine/threonine, acidic domains near the N-terminus, and a serine-rich domain located near the CNC motif — are required for full transactivation function of NFE2L1. NFE2L1 is a key regulator of cellular functions including oxidative stress response, differentiation, inflammatory response, metabolism, cholesterol hand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-jun
Transcription factor Jun is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''JUN'' gene. c-Jun, in combination with protein c-Fos, forms the AP-1 early response transcription factor. It was first identified as the Fos-binding protein p39 and only later rediscovered as the product of the JUN gene. c-jun was the first oncogenic transcription factor discovered. The proto-oncogene c-Jun is the cellular homolog of the viral oncoprotein v-jun (). The viral homolog v-jun was discovered in avian sarcoma virus 17 and was named for ''ju-nana'', the Japanese word for 17. The human JUN encodes a protein that is highly similar to the viral protein, which interacts directly with specific target DNA sequences to regulate gene expression. This gene is intronless and is mapped to 1p32-p31, a chromosomal region involved in both translocations and deletions in human malignancies. Function Regulation Both Jun and its dimerization partners in AP-1 formation are subject to regulation by diverse extr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
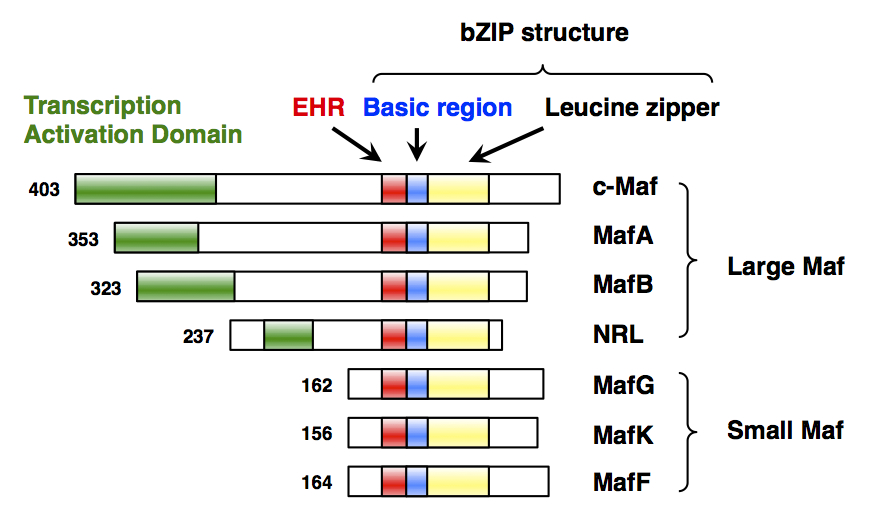
MAFG
Transcription factor MafG is a bZip Maf transcription factor protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MAFG'' gene. MafG is one of the small Maf proteins, which are basic region and leucine zipper (bZIP)-type transcription factors. The HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee-approved gene name of ''MAFG'' is “v-maf avian musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog G”. Discovery MafG was first cloned and identified in chicken in 1995 as a new member of the small Maf (sMaf) genes. MAFG has been identified in many vertebrates, including humans. There are three functionally redundant sMaf proteins in vertebrates, MafF, MafG, and MafK. Structure MafG has a bZIP structure that consists of a basic region for DNA binding and a leucine zipper structure for dimer formation. Similar to other sMafs, MafG lacks any canonical transcriptional activation domains. Expression ''MAFG'' is broadly but differentially expressed in various tissues. ''MAFG'' expression was detected in all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAFF (gene)
Transcription factor MafF is a bZip Maf transcription factor protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MAFF'' gene. MafF is one of the small Maf proteins, which are basic region and leucine zipper (bZIP)-type transcription factors. The HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee-approved gene name of ''MAFF'' is “v-maf avian musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog F”. Discovery MafF was first cloned and identified in chicken in 1993 as a member of the small Maf (sMaf) genes. MAFF has been identified in many vertebrates, including humans. There are three functionally redundant sMaf proteins in vertebrates, MafF, MafG, and MafK. Structure MafF has a bZIP structure that consists of a basic region for DNA binding and a leucine zipper structure for dimer formation. Similar to other sMafs, MafF lacks any canonical transcriptional activation domains. Expression ''MAFF'' is broadly but differentially expressed in various tissues. ''MAFF'' expression was detected in all 16 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldolase B
Aldolase B also known as fructose-bisphosphate aldolase B or liver-type aldolase is one of three isoenzymes (A, B, and C) of the class I fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase enzyme (EC 4.1.2.13), and plays a key role in both glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. The generic fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase enzyme catalyzes the reversible cleavage of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (FBP) into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) as well as the reversible cleavage of fructose 1-phosphate (F1P) into glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone phosphate. In mammals, aldolase B is preferentially expressed in the liver, while aldolase A is expressed in muscle and erythrocytes and aldolase C is expressed in the brain. Slight differences in isozyme structure result in different activities for the two substrate molecules: FBP and fructose 1-phosphate. Aldolase B exhibits no preference and thus catalyzes both reactions, while aldolases A and C prefer FBP. In humans, aldolase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ubiquitin
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 1980s. Four genes in the human genome code for ubiquitin: UBB, UBC, UBA52 and RPS27A. The addition of ubiquitin to a substrate protein is called ubiquitylation (or, alternatively, ubiquitination or ubiquitinylation). Ubiquitylation affects proteins in many ways: it can mark them for degradation via the proteasome, alter their cellular location, affect their activity, and promote or prevent protein interactions. Ubiquitylation involves three main steps: activation, conjugation, and ligation, performed by ubiquitin-activating enzymes (E1s), ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s), and ubiquitin ligases (E3s), respectively. The result of this sequential cascade is to bind ubiquitin to lysine residues on the protein substrate via an isopeptide bond, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteasome
Proteasomes are protein complexes which degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases. Proteasomes are part of a major mechanism by which cells regulate the concentration of particular proteins and degrade misfolded proteins. Proteins are tagged for degradation with a small protein called ubiquitin. The tagging reaction is catalyzed by enzymes called ubiquitin ligases. Once a protein is tagged with a single ubiquitin molecule, this is a signal to other ligases to attach additional ubiquitin molecules. The result is a ''polyubiquitin chain'' that is bound by the proteasome, allowing it to degrade the tagged protein. The degradation process yields peptides of about seven to eight amino acids long, which can then be further degraded into shorter amino acid sequences and used in synthesizing new proteins. Proteasomes are found inside all eukaryotes and archaea, and in so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PSMB6
Proteasome subunit beta type-6 also known as 20S proteasome subunit beta-1 (based on systematic nomenclature) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PSMB6'' gene. This protein is one of the 17 essential subunits (alpha subunits 1-7, constitutive beta subunits 1-7, and inducible subunits including beta1i, beta2i, beta5i) that contributes to the complete assembly of 20S proteasome complex. In particular, proteasome subunit beta type-6, along with other beta subunits, assemble into two heptameric rings and subsequently a proteolytic chamber for substrate degradation. This protein contains "Caspase-like" activity and is capable of cleaving after acidic residues of peptide. The eukaryotic proteasome recognized degradable proteins, including damaged proteins for protein quality control purpose or key regulatory protein components for dynamic biological processes. An essential function of a modified proteasome, the immunoproteasome, is the processing of class I MHC peptides. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
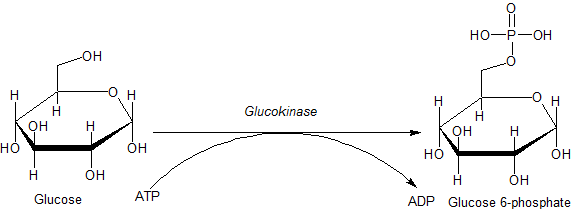
Glucokinase
Glucokinase () is an enzyme that facilitates phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate. Glucokinase occurs in cells in the liver and pancreas of humans and most other vertebrates. In each of these organs it plays an important role in the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism by acting as a glucose sensor, triggering shifts in metabolism or cell function in response to rising or falling levels of glucose, such as occur after a meal or when fasting. Mutations of the gene for this enzyme can cause unusual forms of diabetes or hypoglycemia. Glucokinase (GK) is a hexokinase isozyme, related homologously to at least three other hexokinases. All of the hexokinases can mediate phosphorylation of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate (G6P), which is the first step of both glycogen synthesis and glycolysis. However, glucokinase is coded by a separate gene and its distinctive kinetic properties allow it to serve a different set of functions. Glucokinase has a lower affinity for glucos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PGK1
Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PGK1'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b .... Interactive pathway map References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links PDBe-KB provides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Human Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 {{gene-X-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMOX1
''HMOX1'' (heme oxygenase 1 gene) is a human gene that encodes for the enzyme heme oxygenase 1 (). Heme oxygenase (abbreviated HMOX or HO) mediates the first step of heme catabolism, it cleaves heme to form biliverdin. The ''HMOX'' gene is located on the long (q) arm of chromosome 22 at position 12.3, from base pair 34,101,636 to base pair 34,114,748. Related conditions * Heme oxygenase-1 deficiency Heme oxygenase Heme oxygenase, an essential enzyme in heme catabolism, cleaves heme to form biliverdin, carbon monoxide, and ferrous iron. The biliverdin is subsequently converted to bilirubin by biliverdin reductase. Heme oxygenase activity is induced by its substrate heme and by various nonheme substances. Heme oxygenase occurs as 2 isozymes, an inducible heme oxygenase-1 and a constitutive heme oxygenase-2. HMOX1 and HMOX2 belong to the heme oxygenase family. See also * HMOX2 * Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is a histopatholog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PKLR
Pyruvate kinase PKLR is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PKLR'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a pyruvate kinase Pyruvate kinase is the enzyme involved in the last step of glycolysis. It catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to adenosine diphosphate (ADP), yielding one molecule of pyruvate and one molecule of ATP. P ... that catalyzes the production of pyruvate and ATP from phosphoenolpyruvate. Defects in this enzyme, due to gene mutations or genetic variations, are the common cause of chronic hereditary nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia (CNSHA or HNSHA). Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been described. Interactive pathway map References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-1-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |