|
NFAT5
Nuclear factor of activated T-cells 5, also known as NFAT5 and sometimes TonEBP, is a human gene that encodes a transcription factor that regulates the expression of genes involved in the osmotic stress. The product of this gene is a member of the nuclear factors of activated T cells (NFAT) family of transcription factors. Proteins belonging to this family play a central role in inducible gene transcription during the immune response. This protein regulates gene expression induced by osmotic stress in mammalian cells. Unlike monomeric members of this protein family, this protein exists as a homodimer and forms stable dimers with DNA elements. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Osmotic stress Tissues that comprise the kidneys, skin, and eyes are often subjected to osmotic stresses. When the extracellular environment is hypertonic, cells lose water and consequently, shrink. To counteract this, cells increase their sodium uptake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NFAT5 Osmotic Response Activation Pathway3
Nuclear factor of activated T-cells 5, also known as NFAT5 and sometimes TonEBP, is a human gene that encodes a transcription factor that regulates the expression of genes involved in the osmotic stress. The product of this gene is a member of the nuclear factors of activated T cells (NFAT) family of transcription factors. Proteins belonging to this family play a central role in inducible gene transcription during the immune response. This protein regulates gene expression induced by osmotic stress in mammalian cells. Unlike monomeric members of this protein family, this protein exists as a homodimer and forms stable dimers with DNA elements. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Osmotic stress Tissues that comprise the kidneys, skin, and eyes are often subjected to osmotic stresses. When the extracellular environment is hypertonic, cells lose water and consequently, shrink. To counteract this, cells increase their sodium uptake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NFAT
Nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) is a family of transcription factors shown to be important in immune response. One or more members of the NFAT family is expressed in most cells of the immune system. NFAT is also involved in the development of cardiac, skeletal muscle, and nervous systems. NFAT was first discovered as an activator for the transcription of IL-2 in T cells (as a regulator of T cell immune response) but has since been found to play an important role in regulating many more body systems. NFAT transcription factors are involved in many normal body processes as well as in development of several diseases, such as inflammatory bowel diseases and several types of cancer. NFAT is also being investigated as a drug target for several different disorders. Family members The NFAT transcription factor family consists of five members NFATc1, NFATc2, NFATc3, NFATc4, and NFAT5. NFATc1 through NFATc4 are regulated by calcium signalling, and are known as the classical mem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SLC6A12
Sodium- and chloride-dependent betaine transporter, also known as Na(+)/Cl(-) betaine/GABA transporter (BGT-1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC6A12'' gene. BGT-1 is predominantly expressed in the liver (hepatocytes). It is also expressed in the kidney where it is regulated by NFAT5 during a response to osmotic stress. Further, BGT1 is also present in the leptomeninges In anatomy, the meninges (, ''singular:'' meninx ( or ), ) are the three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. In mammals, the meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. Cerebrospinal fluid is located in th ... surrounding the brain. Deletion of the BGT1 gene in mice did not appear to have any impact on the tendency to develop epilepsy. This is to be expected considering that BGT1 is expressed at far lower levels than GAT1 and also has lower affinity for GABA. This implies that it is not likely to contribute significantly to the inactivation of the inhibi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuropathy Target Esterase
Neuropathy target esterase, also known as patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 6 (PNPLA6), is an esterase enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PNPLA6'' gene. Neuropathy target esterase is a phospholipase that deacetylates intracellular phosphatidylcholine to produce glycerophosphocholine. It is thought to function in neurite outgrowth and process elongation during neuronal differentiation. The protein is anchored to the cytoplasmic face of the endoplasmic reticulum in both neurons and non-neuronal cells. Function Neuropathy target esterase is an enzyme with phospholipase B activity: it sequentially hydrolyses both fatty acids from the major membrane lipid phosphatidylcholine, generating water-soluble glycerophosphocholine. In eukaryotic cells, NTE is anchored to the cytoplasmic face of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. In mammals, it is particularly abundant in neurons, the placenta, and the kidney. Loss of NTE activity results in abnormally-elevated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SLC5A3
Sodium/myo-inositol cotransporter is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC5A3'' gene. Expression of the myo-inositol transport protein is regulated by osmotic stress Osmotic shock or osmotic stress is physiologic dysfunction caused by a sudden change in the solute concentration around a cell, which causes a rapid change in the movement of water across its cell membrane. Under hypertonic conditions - conditions .... See also * Solute carrier family References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * Solute carrier family {{membrane-protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rel Homology Domain
The Rel homology domain (RHD) is a protein domain found in a family of eukaryotic transcription factors, including both NF-κB and NFAT, among others. Some of these transcription factors appear to form multi-protein DNA-bound complexes. Phosphorylation of the RHD appears to play a role in the regulation of some of these transcription factors, acting to modulate the expression of their target genes. The RHD is composed of two immunoglobulin-like beta barrel subdomains that grip the DNA in the major groove. The N-terminal specificity domain resembles the core domain of the p53 transcription factor, and contains a recognition loop that interacts with DNA bases. In the case of NF-κB, the C-terminal dimerization subdomain determines dimerization propensity with other proteins in the NF-κB Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) is a protein complex that controls transcription of DNA, cytokine production and cell survival. NF-κB is found in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
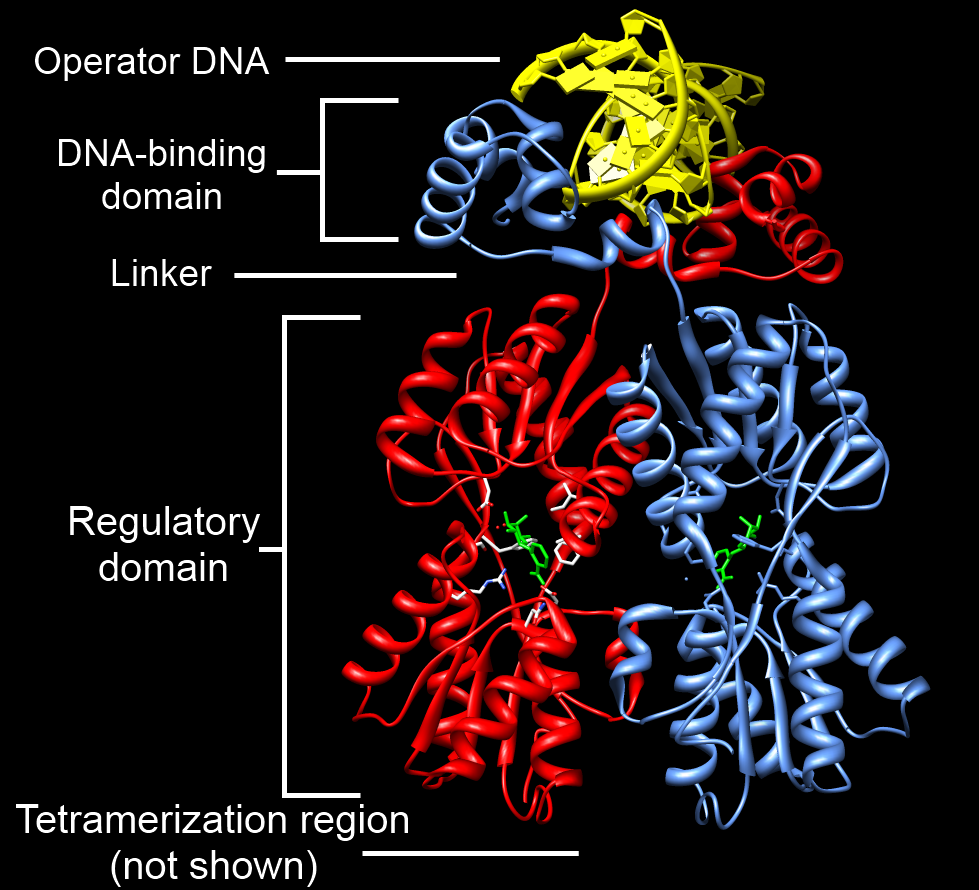
DNA-binding Domain
A DNA-binding domain (DBD) is an independently folded protein domain that contains at least one structural motif that recognizes double- or single-stranded DNA. A DBD can recognize a specific DNA sequence (a recognition sequence) or have a general affinity to DNA. Some DNA-binding domains may also include nucleic acids in their folded structure. Function One or more DNA-binding domains are often part of a larger protein consisting of further protein domains with differing function. The extra domains often regulate the activity of the DNA-binding domain. The function of DNA binding is either structural or involves transcription regulation, with the two roles sometimes overlapping. DNA-binding domains with functions involving DNA structure have biological roles in DNA replication, repair, storage, and modification, such as methylation. Many proteins involved in the regulation of gene expression contain DNA-binding domains. For example, proteins that regulate transcription by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinases
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases are a class of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) that are responsive to stress stimuli, such as cytokines, ultraviolet irradiation, heat shock, and osmotic shock, and are involved in cell differentiation, apoptosis and autophagy. Persistent activation of the p38 MAPK pathway in muscle satellite cells (muscle stem cells) due to ageing, impairs muscle regeneration. p38 MAP Kinase (MAPK), also called RK or CSBP (Cytokinin Specific Binding Protein), is the mammalian orthologue of the yeast Hog1p MAP kinase, which participates in a signaling cascade controlling cellular responses to cytokines and stress. Four p38 MAP kinases, p38-α (MAPK14), -β (MAPK11), -γ ( MAPK12 / ERK6), and -δ ( MAPK13 / SAPK4), have been identified. Similar to the SAPK/JNK pathway, p38 MAP kinase is activated by a variety of cellular stresses including osmotic shock, inflammatory cytokines, lipopolysaccharides (LPS), ultraviolet light, and growth facto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AKAP13
A-kinase anchor protein 13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AKAP13'' gene. This protein is also called AKAP-Lbc because it encodes the lymphocyte blast crisis (Lbc) oncogene, and ARHGEF13/RhoGEF13 because it contains a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) domain for the RhoA small GTP-binding protein. Function A-kinase anchor protein 13/Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 13 is guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for the RhoA small GTPase protein. Rho is a small GTPase protein that is inactive when bound to the guanine nucleotide GDP. But when acted on by Rho GEF proteins such as AKAP13, this GDP is released and replaced by GTP, leading to the active state of Rho. In this active, GTP-bound conformation, Rho can bind to and activate specific effector proteins and enzymes to regulate cellular functions. In particular, active Rho is a major regulator of the cell actin cytoskeleton. AKAP13 is a member of a group of four RhoGEF proteins known to be activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NF-κB
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) is a protein complex that controls transcription of DNA, cytokine production and cell survival. NF-κB is found in almost all animal cell types and is involved in cellular responses to stimuli such as stress, cytokines, free radicals, heavy metals, ultraviolet irradiation, oxidized LDL, and bacterial or viral antigens. NF-κB plays a key role in regulating the immune response to infection. Incorrect regulation of NF-κB has been linked to cancer, inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, septic shock, viral infection, and improper immune development. NF-κB has also been implicated in processes of synaptic plasticity and memory. Discovery NF-κB was discovered by Ranjan Sen in the lab of Nobel laureate David Baltimore via its interaction with an 11-base pair sequence in the immunoglobulin light-chain enhancer in B cells. Later work by Alexander Poltorak and Bruno Lemaitre in mice and ''Drosophila'' frui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor
Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) are proteins or protein domains that activate monomeric GTPases by stimulating the release of guanosine diphosphate (GDP) to allow binding of guanosine triphosphate (GTP). A variety of unrelated structural domains have been shown to exhibit guanine nucleotide exchange activity. Some GEFs can activate multiple GTPases while others are specific to a single GTPase. Function Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) are proteins or protein domains involved in the activation of small GTPases. Small GTPases act as molecular switches in intracellular signaling pathways and have many downstream targets. The most well-known GTPases comprise the Ras superfamily and are involved in essential cell processes such as cell differentiation and proliferation, cytoskeletal organization, vesicle trafficking, and nuclear transport. GTPases are active when bound to GTP and inactive when bound to GDP, allowing their activity to be regulated by GEFs and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |