|
NFAT5 Osmotic Response Activation Pathway3
Nuclear factor of activated T-cells 5, also known as NFAT5 and sometimes TonEBP, is a human gene that encodes a transcription factor that regulates the expression of genes involved in the osmotic stress. The product of this gene is a member of the nuclear factors of activated T cells (NFAT) family of transcription factors. Proteins belonging to this family play a central role in inducible gene transcription during the immune response. This protein regulates gene expression induced by osmotic stress in mammalian cells. Unlike monomeric members of this protein family, this protein exists as a homodimer and forms stable dimers with DNA elements. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Osmotic stress Tissues that comprise the kidneys, skin, and eyes are often subjected to osmotic stresses. When the extracellular environment is hypertonic, cells lose water and consequently, shrink. To counteract this, cells increase their sodium uptake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NFAT1
Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NFATC2'' gene. Function This gene is a member of the nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) family. The product of this gene is a DNA-binding protein with a REL-homology region (RHR) and an NFAT-homology region (NHR). This protein is present in the cytosol and only translocates to the nucleus upon T cell receptor (TCR) stimulation, where it becomes a member of the nuclear factors of activated T cells transcription complex. This complex plays a central role in inducing gene transcription during the immune response. Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. Clinical significance Translocation forming an in frame fusions product between EWSR1 gene and the NFATc2 gene has been described in bone tumor with a Ewing sarcoma-like clinical appearance. The translocation breakpoint led to the loss of the controlling elements of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAP2K3
Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAP2K3'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a dual specificity protein kinase that belongs to the MAP kinase kinase family. This kinase is activated by mitogenic and environmental stress, and participates in the MAP kinase-mediated signaling cascade. It phosphorylates and thus activates MAPK14/p38-MAPK. This kinase can be activated by insulin, and is necessary for the expression of glucose transporter. Expression of RAS oncogene is found to result in the accumulation of the active form of this kinase, which thus leads to the constitutive activation of MAPK14, and confers oncogenic transformation of primary cells. The inhibition of this kinase is involved in the pathogenesis of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode distinct isoforms have been reported for this gene. Interactions MAP2K3 has been shown to interact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanosine Triphosphate
Guanosine-5'-triphosphate (GTP) is a purine nucleoside triphosphate. It is one of the building blocks needed for the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process. Its structure is similar to that of the guanosine nucleoside, the only difference being that nucleotides like GTP have phosphates on their ribose sugar. GTP has the guanine nucleobase attached to the 1' carbon of the ribose and it has the triphosphate moiety attached to ribose's 5' carbon. It also has the role of a source of energy or an activator of substrates in metabolic reactions, like that of ATP, but more specific. It is used as a source of energy for protein synthesis and gluconeogenesis. GTP is essential to signal transduction, in particular with G-proteins, in second-messenger mechanisms where it is converted to guanosine diphosphate (GDP) through the action of GTPases. Uses Energy transfer GTP is involved in energy transfer within the cell. For instance, a GTP molecule is generated by one of the enz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanosine Diphosphate
Guanosine diphosphate, abbreviated GDP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside guanosine. GDP consists of a pyrophosphate group, a pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase guanine. GDP is the product of GTP dephosphorylation by GTPases, e.g., the G-proteins that are involved in signal transduction. GDP is converted into GTP with the help of pyruvate kinase and phosphoenolpyruvate. See also * DNA *Guanosine triphosphate *Nucleoside *Nucleotide *Oligonucleotide *RNA Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Guanosine phosphate2 Nucleotides Phosphate esters Purines Pyrophosphates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rho Family Of GTPases
The Rho family of GTPases is a family of small (~21 kDa) signaling G proteins, and is a subfamily of the Ras superfamily. The members of the Rho GTPase family have been shown to regulate many aspects of intracellular actin dynamics, and are found in all eukaryotic kingdoms, including yeasts and some plants. Three members of the family have been studied in detail: Cdc42, Rac1, and RhoA. All G proteins are "molecular switches", and Rho proteins play a role in organelle development, cytoskeletal dynamics, cell movement, and other common cellular functions. History Identification of the Rho family of GTPases began in the mid-1980s. The first identified Rho member was RhoA, isolated serendipitously in 1985 from a low stringency cDNA screening. Rac1 and Rac2 were identified next, in 1989 followed by Cdc42 in 1990. Eight additional mammalian Rho members were identified from biological screenings until the late 1990s, a turning point in biology where availability of complete genome seq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor
Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) are proteins or protein domains that activate monomeric GTPases by stimulating the release of guanosine diphosphate (GDP) to allow binding of guanosine triphosphate (GTP). A variety of unrelated structural domains have been shown to exhibit guanine nucleotide exchange activity. Some GEFs can activate multiple GTPases while others are specific to a single GTPase. Function Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) are proteins or protein domains involved in the activation of small GTPases. Small GTPases act as molecular switches in intracellular signaling pathways and have many downstream targets. The most well-known GTPases comprise the Ras superfamily and are involved in essential cell processes such as cell differentiation and proliferation, cytoskeletal organization, vesicle trafficking, and nuclear transport. GTPases are active when bound to GTP and inactive when bound to GDP, allowing their activity to be regulated by GEFs and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AKAP13
A-kinase anchor protein 13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AKAP13'' gene. This protein is also called AKAP-Lbc because it encodes the lymphocyte blast crisis (Lbc) oncogene, and ARHGEF13/RhoGEF13 because it contains a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) domain for the RhoA small GTP-binding protein. Function A-kinase anchor protein 13/Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 13 is guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for the RhoA small GTPase protein. Rho is a small GTPase protein that is inactive when bound to the guanine nucleotide GDP. But when acted on by Rho GEF proteins such as AKAP13, this GDP is released and replaced by GTP, leading to the active state of Rho. In this active, GTP-bound conformation, Rho can bind to and activate specific effector proteins and enzymes to regulate cellular functions. In particular, active Rho is a major regulator of the cell actin cytoskeleton. AKAP13 is a member of a group of four RhoGEF proteins known to be activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NFAT5 Osmotic Response Activation Pathway3
Nuclear factor of activated T-cells 5, also known as NFAT5 and sometimes TonEBP, is a human gene that encodes a transcription factor that regulates the expression of genes involved in the osmotic stress. The product of this gene is a member of the nuclear factors of activated T cells (NFAT) family of transcription factors. Proteins belonging to this family play a central role in inducible gene transcription during the immune response. This protein regulates gene expression induced by osmotic stress in mammalian cells. Unlike monomeric members of this protein family, this protein exists as a homodimer and forms stable dimers with DNA elements. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Osmotic stress Tissues that comprise the kidneys, skin, and eyes are often subjected to osmotic stresses. When the extracellular environment is hypertonic, cells lose water and consequently, shrink. To counteract this, cells increase their sodium uptake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinases
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases are a class of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) that are responsive to stress stimuli, such as cytokines, ultraviolet irradiation, heat shock, and osmotic shock, and are involved in cell differentiation, apoptosis and autophagy. Persistent activation of the p38 MAPK pathway in muscle satellite cells (muscle stem cells) due to ageing, impairs muscle regeneration. p38 MAP Kinase (MAPK), also called RK or CSBP (Cytokinin Specific Binding Protein), is the mammalian orthologue of the yeast Hog1p MAP kinase, which participates in a signaling cascade controlling cellular responses to cytokines and stress. Four p38 MAP kinases, p38-α (MAPK14), -β (MAPK11), -γ ( MAPK12 / ERK6), and -δ ( MAPK13 / SAPK4), have been identified. Similar to the SAPK/JNK pathway, p38 MAP kinase is activated by a variety of cellular stresses including osmotic shock, inflammatory cytokines, lipopolysaccharides (LPS), ultraviolet light, and growth facto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
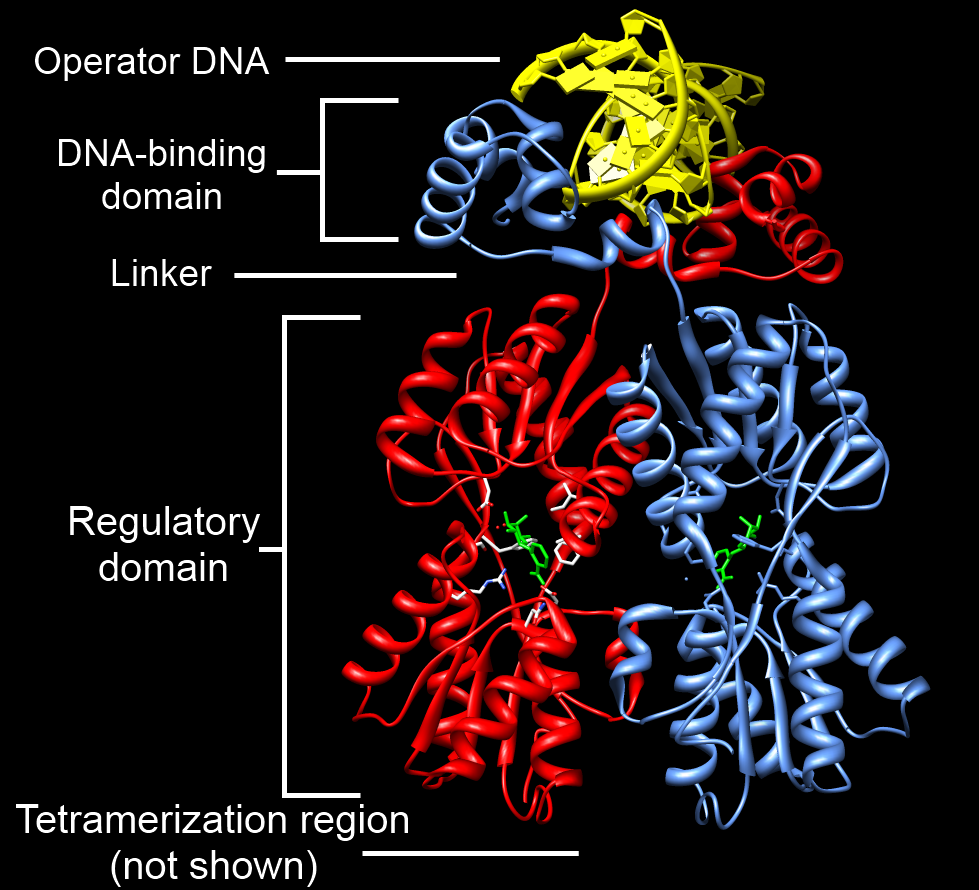
DNA-binding Domain
A DNA-binding domain (DBD) is an independently folded protein domain that contains at least one structural motif that recognizes double- or single-stranded DNA. A DBD can recognize a specific DNA sequence (a recognition sequence) or have a general affinity to DNA. Some DNA-binding domains may also include nucleic acids in their folded structure. Function One or more DNA-binding domains are often part of a larger protein consisting of further protein domains with differing function. The extra domains often regulate the activity of the DNA-binding domain. The function of DNA binding is either structural or involves transcription regulation, with the two roles sometimes overlapping. DNA-binding domains with functions involving DNA structure have biological roles in DNA replication, repair, storage, and modification, such as methylation. Many proteins involved in the regulation of gene expression contain DNA-binding domains. For example, proteins that regulate transcription by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rel Homology Domain
The Rel homology domain (RHD) is a protein domain found in a family of eukaryotic transcription factors, including both NF-κB and NFAT, among others. Some of these transcription factors appear to form multi-protein DNA-bound complexes. Phosphorylation of the RHD appears to play a role in the regulation of some of these transcription factors, acting to modulate the expression of their target genes. The RHD is composed of two immunoglobulin-like beta barrel subdomains that grip the DNA in the major groove. The N-terminal specificity domain resembles the core domain of the p53 transcription factor, and contains a recognition loop that interacts with DNA bases. In the case of NF-κB, the C-terminal dimerization subdomain determines dimerization propensity with other proteins in the NF-κB Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) is a protein complex that controls transcription of DNA, cytokine production and cell survival. NF-κB is found in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |