|
N-Oxalylglycine
''N''-Oxalylglycine is the organic compound with the formula HO2CC(O)NHCH2CO2H. This colourless solid is used as an inhibitor of α-ketoglutarate-dependent enzymes.Hausinger, R. P."Fe(II)/α-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases and related enzymes" Critical Reviews of Biochemical Molecular Biology 2004, 39: pp 21-68. It is isosteric with α-ketoglutaric acid α-Ketoglutaric acid (2-oxoglutaric acid) is one of two ketone derivatives of glutaric acid. The term "ketoglutaric acid," when not further qualified, almost always refers to the alpha variant. β-Ketoglutaric acid varies only by the position o .... Such enzymes are pervasive and, for example, are required for the synthesis of 4-hydroxyproline. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Oxalylglycine, N- Carboxamides Dicarboxylic acids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-Acetylglycinamide
''N''-Acetylglycinamide is a glycine derivative. See also * Acetylglycinamide chloral hydrate Acetylglycinamide chloral hydrate is a hypnotic/sedative. It is a combination of acetylglycinamide and chloral hydrate Chloral hydrate is a geminal diol with the formula . It is a colorless solid. It has limited use as a sedative and hypnot ... * ''N''-Acetylglycine References Acetamides {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycylglycine
Glycylglycine is the dipeptide of glycine, making it the simplest peptide. The compound was first synthesized by Emil Fischer and Ernest Fourneau Ernest Fourneau (4 October 1872 – 5 August 1949) was a French pharmacist graduated in Pharmacy 1898 for the Paris university specialist in medicinal chemical and pharmacology who played a major role in the discovery of synthetic local anesthetic ... in 1901 by boiling 2,5-diketopiperazine (glycine anhydride) with hydrochloric acid. Shaking with alkali and other synthesis methods have been reported. Because of its low toxicity, it is useful as a buffer for biological systems with effective ranges between pH 2.5–3.8 and 7.5–8.9; however, it is only moderately stable for storage once dissolved. It is used in the synthesis of more complex peptides. Glycylglycine has also been reported to be helpful in solubilizing recombinant proteins in ''E. coli''. Using different concentrations of the glycylglycine improvement in protein solubil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxalyldiaminopropionic Acid
Oxalyldiaminopropionic acid (ODAP) is a structural analogue of the neurotransmitter glutamate found in the grass pea ''Lathyrus sativus''. It is the neurotoxin responsible for the motor neuron degeneration syndrome lathyrism. Sources ODAP is found in the seeds of the legume ''L. sativus'', a grass pea plant, in the range of .5% w/w. ''L. sativus'' can be found in areas of Southern, Central, and Eastern Europe, the Mediterranean Basin, Iraq and Afghanistan as well as areas of Asia and Africa.Heuzé V., Tran G., Hassoun P., Lessire M., Lebas F., 2016. Grass pea (Lathyrus sativus). Feedipedia, a programme by INRA, CIRAD, AFZ and FAO. https://www.feedipedia.org/node/285 Last updated on April 19, 2016, 15:36 History In some regions, including the Indian subcontinent, Bangladesh, Ethiopia and Nepal, the grass pea has become a staple food item. The plant has a high tolerance of environmental conditions which results in it being the only available food source in times of famine or drought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, hydrogen cyanide), are not classified as organic compounds and are considered inorganic. Other than those just named, little consensus exists among chemists on precisely which carbon-containing compounds are excluded, making any rigorous definition of an organic compound elusive. Although organic compounds make up only a small percentage of Earth's crust, they are of central importance because all known life is based on organic compounds. Living t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Formula
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and ''plus'' (+) and ''minus'' (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include Subscript and superscript, subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical nomenclature, chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae. The simplest types of chemical formulae are called ''empirical formulae'', which use letters and numbers ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
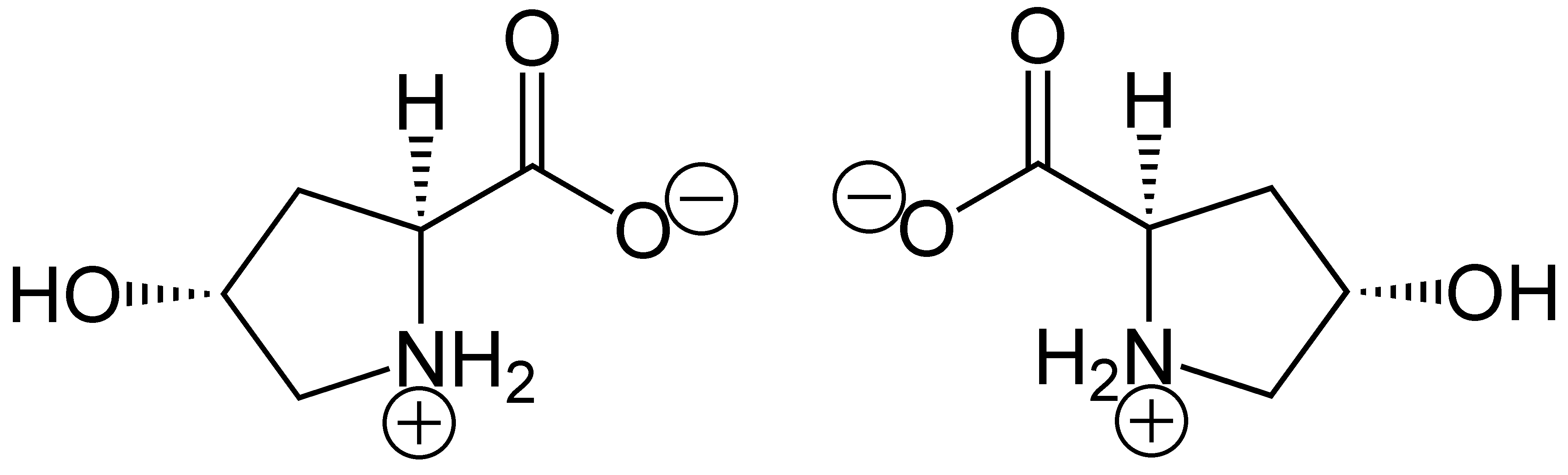
Hydroxyproline
(2''S'',4''R'')-4-Hydroxyproline, or L-hydroxyproline ( C5 H9 O3 N), is an amino acid, abbreviated as Hyp or O, ''e.g.'', in Protein Data Bank. Structure and discovery In 1902, Hermann Emil Fischer isolated hydroxyproline from hydrolyzed gelatin. In 1905, Hermann Leuchs synthesized a racemic mixture of 4-hydroxyproline. Hydroxyproline differs from proline by the presence of a hydroxyl (OH) group attached to the gamma carbon atom. Production and function Hydroxyproline is produced by hydroxylation of the amino acid proline by the enzyme prolyl hydroxylase following protein synthesis (as a post-translational modification). The enzyme catalyzed reaction takes place in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. Although it is not directly incorporated into proteins, hydroxyproline comprises roughly 4% of all amino acids found in animal tissue, an amount greater than seven other amino acids that are translationally incorporated. Animals Collagen Hydroxyproline is a major compon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |