|
N-Acetylmuramic Acid
''N''-Acetylmuramic acid (NAM or MurNAc) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is a monomer of peptidoglycan in most bacterial cell walls, which is built from alternating units of ''N''-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) and ''N''-acetylmuramic acid, cross-linked by oligopeptides at the lactic acid residue of MurNAc. MurNAc is a monosaccharide derivative of ''N''-acetylglucosamine. Formation of NAM NAM is an addition product of phosphoenolpyruvate and ''N''-acetylglucosamine. This addition happens exclusively in the cell cytoplasm. Clinical significance ''N''-Acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) is part of the peptidoglycan polymer of bacterial cell walls. MurNAc is covalently linked to ''N''-acetylglucosamine and may also be linked through the hydroxyl on carbon number 4 to the carbon of L-alanine. A pentapeptide composed of L-alanyl-D-isoglutaminyl-L-lysyl-D-alanyl-D-alanine is added to the MurNAc in the process of making the peptidoglycan strands of the cell wall. Synth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like peptidoglycan layer outside the plasma membrane, the rigid cell wall (murein sacculus) characteristic of most bacteria (domain ''Bacteria''). The sugar component consists of alternating residues of β-(1,4) linked ''N''-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and ''N''-acetylmuramic acid (NAM). Attached to the ''N''-acetylmuramic acid is a oligopeptide chain made of three to five amino acids. The peptide chain can be cross-linked to the peptide chain of another strand forming the 3D mesh-like layer. Peptidoglycan serves a structural role in the bacterial cell wall, giving structural strength, as well as counteracting the osmotic pressure of the cytoplasm. This repetitive linking results in a dense peptidoglycan layer which is critical for maintaining cell form and withstanding high osmotic pressures, and it is regularly replaced by peptidoglycan production. Pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fosfomycin
Fosfomycin, sold under the brand name Monurol among others, is an antibiotic primarily used to treat lower UTI. It is not indicated for kidney infections. Occasionally it is used for prostate infections. It is generally taken by mouth. Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, headache, and vaginal yeast infections. Severe side effects may include anaphylaxis and ''Clostridium difficile''-associated diarrhea. While use during pregnancy has not been found to be harmful, such use is not recommended. A single dose when breastfeeding appears safe. Fosfomycin works by interfering with the production of the bacterial cell wall. Fosfomycin was discovered in 1969 and approved for medical use in the United States in 1996 . It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. The World Health Organization classifies fosfomycin as critically important for human medicine. It is available as a generic medication. It was originally produced by certain types of ''Stre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
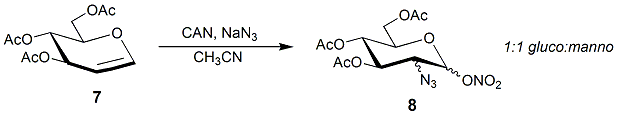
Monosaccharide Derivatives
Monosaccharides (from Greek ''monos'': single, '' sacchar'': sugar), also called simple sugars, are the simplest forms of sugar and the most basic units (monomers) from which all carbohydrates are built. They are usually colorless, water-soluble, and crystalline solids. Contrary to their name (sugars), only some monosaccharides have a sweet taste. Most monosaccharides have the formula (though not all molecules with this formula are monosaccharides). Examples of monosaccharides include glucose (dextrose), fructose (levulose), and galactose. Monosaccharides are the building blocks of disaccharides (such as sucrose and lactose) and polysaccharides (such as cellulose and starch). The table sugar used in everyday vernacular is itself a disaccharide sucrose comprising one molecule of each of the two monosaccharides D-glucose and D-fructose. Each carbon atom that supports a hydroxyl group is chiral, except those at the end of the chain. This gives rise to a number of isomeric forms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Sugars
In organic chemistry, an amino sugar (or more technically a 2-amino-2-deoxysugar) is a sugar molecule in which a hydroxyl group has been replaced with an amine group. More than 60 amino sugars are known, with one of the most abundant being ''N''-Acetyl--glucosamine, which is the main component of chitin. Derivatives of amine containing sugars, such as ''N''-acetylglucosamine and sialic acid, whose nitrogens are part of more complex functional groups rather than formally being amines, are also considered amino sugars. Aminoglycosides are a class of antimicrobial compounds that inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. These compounds are conjugates of amino sugars and aminocyclitols. Synthesis From glycals Glycals are cyclic enol ether derivatives of monosaccharides, having a double bond between carbon atoms 1 and 2 of the ring. ''N''-functionalized of glycals at the C2 position, combined with glycosidic bond formation at C1 is a common strategy for the synthesis of amino sugars. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucosamine
Glucosamine (C6H13NO5) is an amino sugar and a prominent precursor in the biochemical synthesis of glycosylated proteins and lipids. Glucosamine is part of the structure of two polysaccharides, chitosan and chitin. Glucosamine is one of the most abundant monosaccharides. Produced commercially by the hydrolysis of shellfish exoskeletons or, less commonly, by fermentation of a grain such as corn or wheat, glucosamine has many names depending on country. Although a common dietary supplement, there is little evidence that it is effective for relief of arthritis or pain, and is not an approved prescription drug. Dietary supplement Oral glucosamine is a dietary supplement and is not a prescription drug. Glucosamine is marketed as a supplement to support the structure and function of joints, and the marketing is targeted to people with osteoarthritis. Commonly sold forms of glucosamine are glucosamine sulfate, glucosamine chondroitin, glucosamine hydrochloride, and ''N''-acetylglucos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Sugar
In organic chemistry, an amino sugar (or more technically a 2-amino-2-deoxysugar) is a sugar molecule in which a hydroxyl group has been replaced with an amine group. More than 60 amino sugars are known, with one of the most abundant being ''N''-Acetyl--glucosamine, which is the main component of chitin. Derivatives of amine containing sugars, such as ''N''-acetylglucosamine and sialic acid, whose nitrogens are part of more complex functional groups rather than formally being amines, are also considered amino sugars. Aminoglycosides are a class of antimicrobial compounds that inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. These compounds are conjugates of amino sugars and aminocyclitols. Synthesis From glycals Glycals are cyclic enol ether derivatives of monosaccharides, having a double bond between carbon atoms 1 and 2 of the ring. ''N''-functionalized of glycals at the C2 position, combined with glycosidic bond formation at C1 is a common strategy for the synthesis of amino sugars. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorganism fighting another), whereas non-antibiotic antibacterials (such as sulfonamides and antiseptics) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy
The ''Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy'' is a peer-reviewed medical journal which covers antimicrobial chemotherapy, including laboratory aspects and clinical use of antimicrobial agents. It is published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy and was established in 1975. In January 2015 J. Peter Donnelly ( Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre) became the eighth editor-in-chief replacing Alan P. Johnson (Health Protection Agency, London, United Kingdom). The journal has had two previous publishers. All content is available for free after 12 months while authors also have the option to have their articles published immediately as open access. History The ''Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy'' was founded by David Williams in 1975, who was also its editor for its first six years. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal received a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are cytosol (a gel-like substance), the organelles (the cell's internal sub-structures), and various cytoplasmic inclusions. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance or cytoplasmic matrix which remains after exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, the plant plastids, lipid droplets, and vacuoles. Most cellular activities take place within the cytoplasm, such as many metabolic pathways including glycolysis, and proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphoenolpyruvate
Phosphoenolpyruvate (2-phosphoenolpyruvate, PEP) is the ester derived from the enol of pyruvate and phosphate. It exists as an anion. PEP is an important intermediate in biochemistry. It has the highest-energy phosphate bond found (−61.9 kJ/mol) in organisms, and is involved in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. In plants, it is also involved in the biosynthesis of various aromatic compounds, and in carbon fixation; in bacteria, it is also used as the source of energy for the phosphotransferase system. In glycolysis PEP is formed by the action of the enzyme enolase on 2-phosphoglyceric acid. Metabolism of PEP to pyruvic acid by pyruvate kinase (PK) generates adenosine triphosphate (ATP) via substrate-level phosphorylation. ATP is one of the major currencies of chemical energy within cells. In gluconeogenesis PEP is formed from the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate and hydrolysis of one guanosine triphosphate molecule. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |