|
Mustafa Raza Khan
Mustafa Raza Khan Qadri (1892–1981) was an Indian Muslim scholar and author, and leader of the Sunni Barelvi movement following the death of its founder, his father Ahmed Raza Khan. He was known as ''Mufti-Azam-i-Hind'' to his followers. In a biography compiled by Muhammad Afthab Cassim Razvi he is referred to as ''Mufti-e-Azam-e-Hind''. Lineage Life He wrote books on Islam in Arabic, Urdu, Persian, and announced judgments on several thousand Islamic problems in his compilation of fatawa ''Fatawa-e-Mustafwia''. Thousands of Islamic scholars were counted as his spiritual successors. He was the main leader of the Jama'at Raza-e-Mustafa in Bareilly, which opposed the Shuddhi movement to convert Muslims to Hinduism in pre-Partition India. During the time of emergency in 1977 in India, he issued a fatwa against vasectomy which was made compulsory and 6.2 million Indian men were sterilized in just a year. In such circumstances Mustafa Raza Khan argued this order of Indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
His Eminence
His Eminence (abbreviation H.Em. or H.E. or HE) is a style (manner of address), style of reference for high nobility, still in use in various religious contexts. Catholicism The style remains in use as the official style or standard form of address in reference to a cardinal (Catholicism), cardinal of the Catholic Church, reflecting his status as a Prince of the Church. A longer, and more formal, title is "His (or Your when addressing the cardinal directly) Most Reverend Eminence". Patriarchs of Eastern Catholic Churches who are also cardinals may be addressed as "His Eminence" or by the style particular to Catholic patriarchs, His Beatitude. When the Grand master (order), Grand Master of the Sovereign Military Order of Malta, the head of state of their sovereign territorial state comprising the island of Malta until 1797, who had already been made a Reichsfürst (i.e., prince of the Holy Roman Empire) in 1607, became (in terms of honorary order of precedence, not in the act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanafi
The Hanafi school ( ar, حَنَفِية, translit=Ḥanafiyah; also called Hanafite in English), Hanafism, or the Hanafi fiqh, is the oldest and one of the four traditional major Sunni schools ( maddhab) of Islamic Law (Fiqh). It is named after the 8th century Kufan scholar, Abu Hanifa, a Tabi‘i of Persian origin whose legal views were preserved primarily by his two most important disciples, Imam Abu Yusuf and Muhammad al-Shaybani. It is considered one of the most widely accepted maddhab amongst Sunni Muslim community and is called the ''Madhhab of Jurists'' (maddhab ahl al-ray). The importance of this maddhab lies in the fact that it is not just a collection of rulings or sayings of Imam Abu Hanifa alone, but rather the rulings and sayings of the council of judges he established belong to it. It had a great excellence and advantage over the establishment of Sunni Islamic legal science. No one before Abu Hanifa preceded in such works. He was the first to solve the cases an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatawa
A fatwā ( ; ar, فتوى; plural ''fatāwā'' ) is a legal ruling on a point of Islamic law (''sharia'') given by a qualified ''Faqīh, Faqih'' (Islamic jurist) in response to a question posed by a private individual, judge or government. A jurist issuing fatwas is called a ''mufti'', and the act of issuing fatwas is called ''iftāʾ''. Fatwas have played an important role throughout Islamic history, taking on new forms in the modern era. Resembling ''jus respondendi'' in Roman law and History of responsa in Judaism, rabbinic ''responsa'', privately issued fatwas historically served to inform Muslim populations about Islam, advise courts on difficult points of Islamic law, and elaborate substantive law. In later times, public and political fatwas were issued to take a stand on doctrinal controversies, legitimize government policies or articulate grievances of the population. During the era of European colonialism, fatwas played a part in mobilizing resistance to foreign domina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hassan Raza Khan
Hassan Raza Khan Bareilwi was an Islamic scholar, Sufi and poet and the younger brother of Imam Ahmed Raza Khan, the main leader of the Ahle Sunnat movement. He was a disciple of Sha Ale Rasool Marehrvi in to Sufism, revered Sufi master from Marehra, Etah, Uttar Pradesh. He was a disciple of Dagh Dehlvi, a learned poet from Delhi. Hasrat Mohani praised Hassan Raza Khan's poetic greatness. Birth and family Hassan Raza was born in 1859 ( Rabi' al-awwal 1276 Hijri), in Bareilly, India. His name at the time of his '' aqeeqah'' was Muhammad, as it was family tradition. Lineage Khan was the brother of Ahmad Raza Khan, the son of Naqi Ali Khan, the son of Raza Ali Khan. Poetry works He has written following books. His famous book of poetry is ''Zauq-e-Naat''. *''Ayina e Qayamat'' *''Rasayel e Hassan'' *''Qitat e Ashar o Ahsan'' *''Samar Fasahat'' *''Qand Parsi'' *''Samamam Hasan Baradbar fitan'' *''Wasaail Bakhshish'' *''Zoq e Naat- Naatia Kalam'' *''Kuliyat e Hassan'' Death ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naqi Ali Khan
Naqi Ali Khan (1830-1880) (urdu: نقی علی خان) was an Indian Sunni Hanafi Islamic Scholar, Mufti and father of Ahmed Raza Khan. Naqi Ali wrote 26 books on Seerah and Aqedah and he issued thousand Fatwas. Family tree Publications * Asool Ul Rishaad (اصول الرشاد لقمع مباني الفساد) * Fazayle E Dua (فضائل دعا) * Tafsir e Surah Alamnashrah Explanation of Ayat (تفسیر سورہ الم نشرخ). See also *Ahmed Raza Khan References Further reading Phd Thesis on Naqi khan (urdu)Related Books on Archive.orgRead more on Mufti Naqi Ali Khan from Dawat-e-Islami's magazine {{DEFAULTSORT:Khan, Naqi Ali 1830 births 1880 deaths Barelvi Indian Sufis Critics of Shia Islam Hanafi fiqh scholars Hanafis Maturidis Indian Sunni Muslim scholars of Islam Writers in British India People from Bareilly Scholars from Uttar Pradesh People from Bareilly district 19th-century Indian non-fiction writers 19th-century Muslim scholars of Islam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barelvi Movement
The Barelvi movement ( ur, بَریلوِی, , ), also known as Ahl al-Sunnah wa'l-Jamaah (People of the Prophet's Way and the Community) is a Sunni revivalist movement following the Hanafi and Shafi'i school of jurisprudence, with strong Sufi influences and with over 500-600 million followers in South Asia and in parts of Europe, America and Africa. It is a broad Sufi-oriented movement that encompasses a variety of Sufi orders, including the Chistis, Qadiris, Soharwardis and Naqshbandis. The movement drew inspiration from the Sunni Sufi doctrines of Shah Abdur Rahim (1644-1719) founder of Madrasah-i Rahimiyah and father of Shah Waliullah Dehlawi, Shah Abdul Aziz Muhaddith Dehlavi (1746 –1824) and Fazl-e-Haq Khairabadi (1796–1861) founder of the Khairabad School. It emphasizes personal devotion to God and the Islamic prophet Muhammad, adherence to Sharia, and Sufi practices such as veneration of saints. They are called Sunni Sufis. Ahmed Raza Khan Barelvi (1856–19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sahib-ul-Ma'ali
Sahib-ul-Ma'ali was a style used to address nobility during Egypt's last monarchical era. Meaning As it has no equivalent in English, ''Sahib-ul-Ma'ali'' is generally translated into English as "His Excellency." However, when literally translated from Arabic into English, ''Sahib-ul-Ma'ali'' means "His Excellency the Sublime Lord." Eligibility Holders of the ''Imtiaz'' noble rank, the third highest rank in the Royal Egyptian Court, were treated in the style of ''Sahib-ul-Ma'ali.'' Only holders of the Grand Cordon of Muhammad Ali, former Ministers of State, and eight other distinguished individuals could hold the ''Imtiaz'' rank at any given time. Those holding the ''Imtiaz'' rank also had the title of Pasha, their wives and daughters were given the title of Khanum, and their sons had the courtesy title of Bey. Notable Titleholders * Boutros Ghali Pasha * Saad Zaghloul Pasha * Hussein Refki Pasha * Mostafa El-Nahas Pasha *Aly Maher Pasha *Ahmad Mahir Pasha Ahmad ( ar, أ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
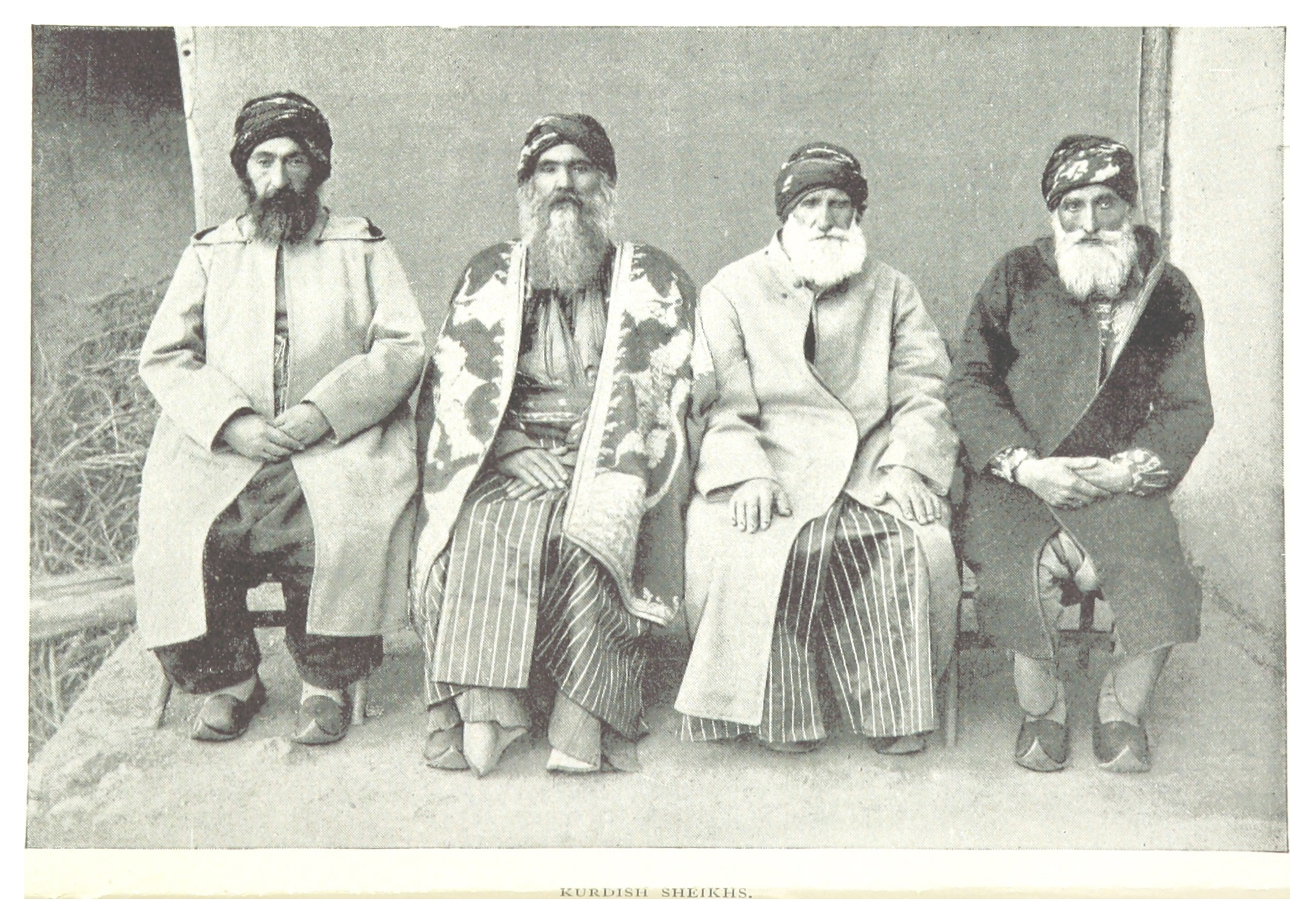
Sheikh
Sheikh (pronounced or ; ar, شيخ ' , mostly pronounced , plural ' )—also transliterated sheekh, sheyikh, shaykh, shayk, shekh, shaik and Shaikh, shak—is an honorific title in the Arabic language. It commonly designates a chief of a tribe or a royal family member in Arabian countries, in some countries it is also given to those of great knowledge in religious affairs as a surname by a prestige religious leader from a chain of Sufi scholars. It is also commonly used to refer to a Muslim religious scholar. It is also used as an honorary title by people claiming to be descended from Hasan ibn Ali and Husayn ibn Ali both patrilineal and matrilineal who are grandsons of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. The term is literally translated to " Elder" (is also translated to "Lord/Master" in a monarchical context). The word 'sheikh' is mentioned in the 23rd verse of Surah Al-Qasas in the Quran. Etymology and meaning The word in Arabic stems from a triliteral root connected with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadrat
''Hazrat, , ,'' or ' ( ar, حَضْرَة, ḥaḍra, pl. ''ḥaḍrāt''; Persian: pronounced or ) is a common Bangladeshi, Indian, Pakistani, Iranian, Afghan, and honorific Arabic and Turkish title used to honour a person. It literally denotes and translates to "presence, appearance." Usage Initially, the title was used for the prophets of the Islamic faith: the twenty-five great Hadhrats include Muhammad, Abraham, Noah, Moses, and Jesus. It carries connotations of the charismatic and is comparable to traditional Western honorifics addressing high officials, such as "Your Honour" (for judges), "Your Majesty" (for monarchs), or "Your Holiness" (for clerics). This word may sometimes also appear after the names of respected Muslim personalities, such as imams, e.g. Turkish ('his Hadrat') in Islamic culture. This is similar to the French honorifics French honorifics are based on the wide use of ''Madame'' for women and ''Monsieur'' for men. Social * "Monsieur" (''M.'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
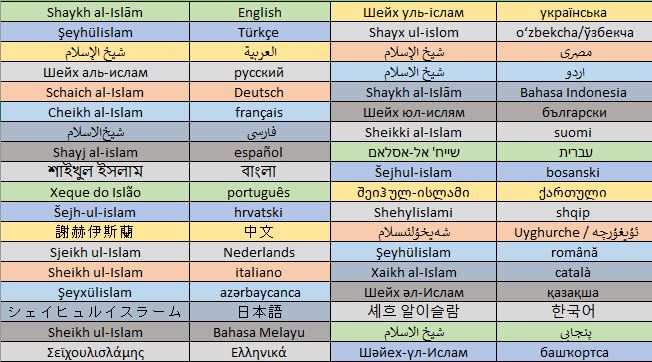
Shaykh Al-Islām
Shaykh al-Islām ( ar, شيخ الإسلام, Šayḫ al-Islām; fa, شِیخُالاسلام ''Sheykh-ol-Eslām''; ota, شیخ الاسلام, Şhaykḫu-l-İslām or ''Sheiklı ul-Islam''; tr, Şeyhülislam) was used in the classical era as an honorific title for outstanding scholars of the Islamic sciences.Gerhard Böwering, Patricia Crone, Mahan Mirza, The Princeton Encyclopedia of Islamic Political Thought, p 509-510. It first emerged in Khurasan towards the end of the 4th Islamic century. In the central and western lands of Islam, it was an informal title given to jurists whose ''fatwas'' were particularly influential, while in the east it came to be conferred by rulers to ''ulama'' who played various official roles but were not generally ''muftis''. Sometimes, as in the case of Ibn Taymiyya, Ibn Taymiyyah, the use of the title was subject to controversy. In the Ottoman Empire, starting from the early modern era, the title came to designate the chief mufti, who over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mufti
A Mufti (; ar, مفتي) is an Islamic jurist qualified to issue a nonbinding opinion ('' fatwa'') on a point of Islamic law (''sharia''). The act of issuing fatwas is called ''iftāʾ''. Muftis and their ''fatwas'' played an important role throughout Islamic history, taking on new roles in the modern era. Tracing its origins to the Quran and early Islamic communities, the practice of ''ifta'' crystallized with the emergence of the traditional legal theory and schools of Islamic jurisprudence (''madhahib''). In the classical legal system, fatwas issued by muftis in response to private queries served to inform Muslim populations about Islam, advise courts on difficult points of Islamic law, and elaborate substantive law. In later times, muftis also issued public and political fatwas that took a stand on doctrinal controversies, legitimized government policies or articulated grievances of the population. Traditionally, a mufti was seen as a scholar of upright character wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Honourable
''The Honourable'' (British English) or ''The Honorable'' (American English; see spelling differences) (abbreviation: ''Hon.'', ''Hon'ble'', or variations) is an honorific style that is used as a prefix before the names or titles of certain people, usually with official governmental or diplomatic positions. Use by governments International diplomacy In international diplomatic relations, representatives of foreign states are often styled as ''The Honourable''. Deputy chiefs of mission, , consuls-general and consuls are always given the style. All heads of consular posts, whether they are honorary or career postholders, are accorded the style according to the State Department of the United States. However, the style ''Excellency'' instead of ''The Honourable'' is used for ambassadors and high commissioners. Africa The Congo In the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the prefix 'Honourable' or 'Hon.' is used for members of both chambers of the Parliament of the Democratic Repu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |