|
Muireadhach Ua Dubhthaigh
Muireadhach Ua Dubhthaigh (fl. c. 1075–1150) was an Archbishop of Connacht, in Ireland. Background A member of a Connacht ecclesiastical family, Ua Dubhthaigh was born during the reign of King Áed Ua Ruairc (r. 1067–1087). His family were natives of Lissonuffy in what is now north-east County Roscommon, and produced a number of abbots and bishops. One such was Flannagan Ruadh Ua Dubhthaigh, listed in his obituary of 1097 as "successor of Comman, and lector of Tuaim-da-ghualann". Other Ó Dubhthaigh who held high church offices included: * Domnall mac Flannacáin Ua Dubthaig (died 1136) and Flannacán Ua Dubthaig (dead by 1152), Bishops of Elphin; * Dubthaigh Ó Dubhthaigh, Abbot of Cong, died 1223 * Muiredach Ua Dubthaig (''fl''. 1208), Bishop of Killala * Uilliam Ó Dubhthaigh, OFM (fl. 1290–1297), Bishop of Clonmacnoise * Céle Ua Dubthaigh (died 1210), Bishop of Mayo. * Cadla Ua Dubthaig (fl. 1167–1201), Archbishop of Tuam. Archbishop of Connacht At the Syno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishop
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdiocese ( with some exceptions), or are otherwise granted a titular archbishopric. In others, such as the Lutheran Church of Sweden and the Church of England, the title is borne by the leader of the denomination. Etymology The word archbishop () comes via the Latin ''archiepiscopus.'' This in turn comes from the Greek , which has as components the etymons -, meaning 'chief', , 'over', and , 'seer'. Early history The earliest appearance of neither the title nor the role can be traced. The title of "metropolitan" was apparently well known by the 4th century, when there are references in the canons of the First Council of Nicæa of 325 and Council of Antioch of 341, though the term seems to be used generally for all higher ranks of bishop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
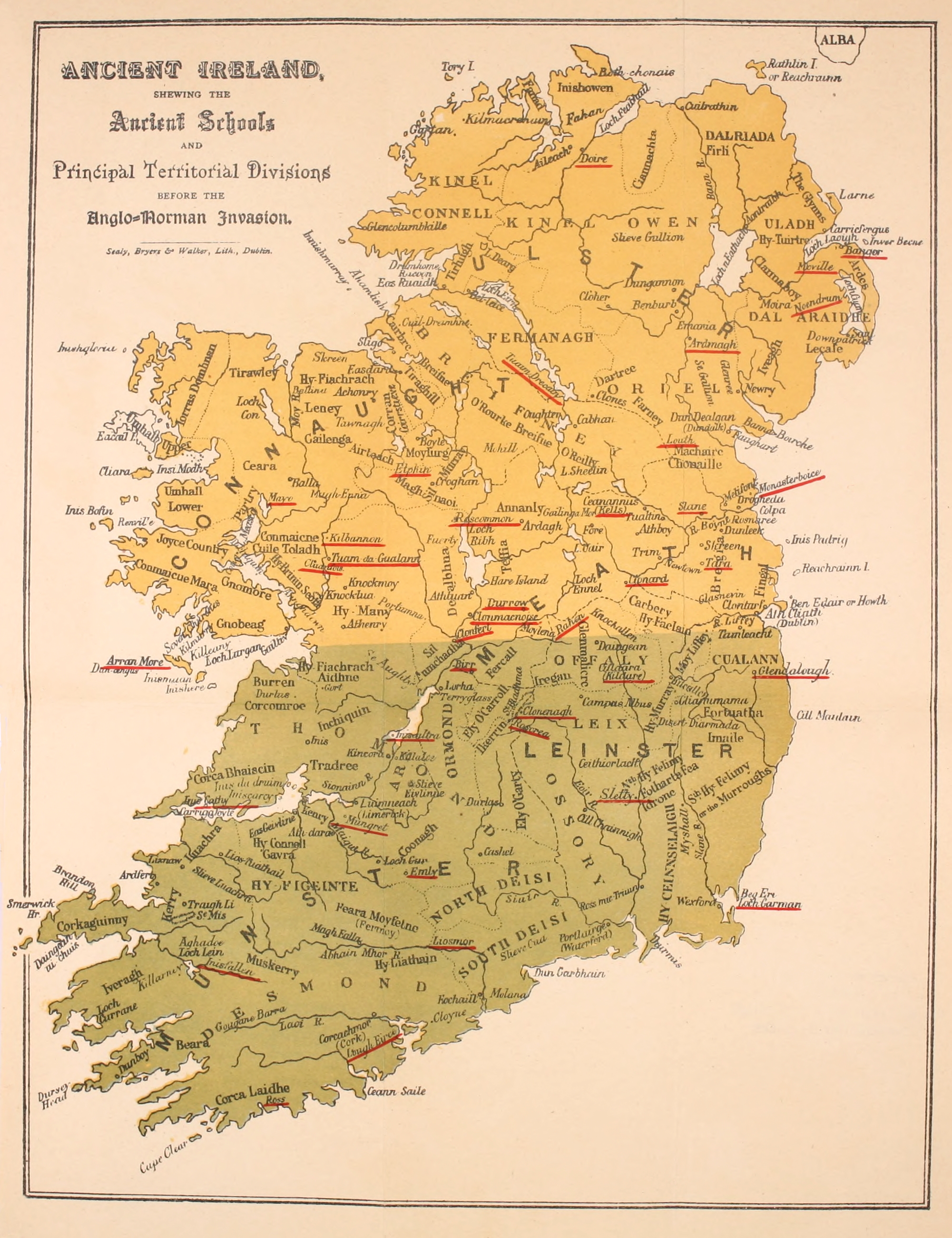
Archbishop Of Tuam
The Archbishop of Tuam ( ; ga, Ard-Easpag Thuama) is an archbishop which takes its name after the town of Tuam in County Galway, Ireland. The title was used by the Church of Ireland until 1839, and is still in use by the Catholic Church. History At the Synod of Rathbreasail in 1111, Tuam was named as the seat of a diocese corresponding roughly with the diocese of Elphin, whilst Cong was chosen as the seat of a diocese corresponding with the later archdiocese of Tuam in west Connacht. There is no record of any bishops of Cong, and no bishop was given the title "bishop of Tuam" in the Irish annals before 1152. However the annals recorded some "archbishops/bishops of Connacht" such as Cathasach Ua Conaill (died 1117), Domhnall Ua Dubhthaigh (1117–1136), Muireadhach Ua Dubhthaigh (1136–1150) – the latter was succeeded by Áed Ua hOissín. At the Synod of Kells in 1152, the archdiocese of Tuam was established with six suffragan dioceses. During the Reformation, the bishopr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leath Cuinn
Leath Cuinn (Conn's Half) and Leath Moga (Mugh's half) are legendary ancient divisions of Ireland. Leath Cuinn was the island north of the Esker Riada (east-west drumlin belt from Dublin to Galway Bay). Conn Cétchathach, for whom this division is named, was a retrospective ancestor of the Connachta and Uí Néill dynasties. Ireland's legendary ancient division into Leath Cuinn (Conn's Half) and Leath Moga (Mugh's half) resulted from the battle of Maigh Nuadad in 123 A.D. Conn, defeated by Eoghan Mor (also known as Mug Nuadat), was forced to accede to the division of Ireland into two halves: * The North - taking in Connacht, Ulster and Meath - would be Conn's Half * The South - taking in Munster, Osraighe and Leinster - would be Eoghan's Half. To solidify the arrangement, Conn's daughter, Sadhbh was married to Ailill Aulom, son of Eoghan. The Eoganacht dynasty in Munster claimed, as descendants of Oiloill Olum, the historical right as overkings of Leath Moga (i.e. overlords ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munster
Munster ( gle, an Mhumhain or ) is one of the provinces of Ireland, in the south of Ireland. In early Ireland, the Kingdom of Munster was one of the kingdoms of Gaelic Ireland ruled by a "king of over-kings" ( ga, rí ruirech). Following the Norman invasion of Ireland, the ancient kingdoms were shired into Counties of Ireland#2.1 Pre-Norman sub-divisions, counties for administrative and judicial purposes. In later centuries, local government legislation has seen further sub-division of the historic counties. Munster has no official function for Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local government purposes. For the purposes of the International Organization for Standardization, ISO, the province is listed as one of the provincial sub-divisions of the State (ISO 3166-2:IE) and coded as "IE-M". Geographically, Munster covers a total area of and has a population of 1,364,098, with the most populated city being Cork (city), Cork. Other significant urban centres in the pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cormac Mac Carthaigh
Cormac is a masculine given name in the Irish and English languages. The name is ancient in the Irish language and is also seen in the rendered Old Norse as ''Kormákr''. Mac is Irish for "son", and can be used as either a prefix or a suffix. The derivation of "cor" is not so clear. The most popular speculation is that it is from "corb," the old Irish for wheel, perhaps designating someone who fought in a cart or chariot as male names are often derived from order of battle. (For instance "Gary, Garth, etc., from "gar" for "spear.") However, some etymologies suggest it derives from the old Irish for "raven", a bird laden with mystical meaning for the Celts, and often used to mean "legend" or "legendary". Similarly, it might refer specifically to Corb, one of the legendary Fomorians of Irish mythology. Today the name is typically listed in baby names books as meaning "raven" or "legend" or sometimes as "charioteer". People with the name Cormac *Cormac Mac Airt, semi-histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair
Toirdhealbhach Mór Ua Conchobhair (old spelling: Tairrdelbach Mór Ua Conchobair; 1088 – 1156) anglicised Turlough Mór O'Conor, was King of Connacht (1106–1156) and High King of Ireland (ca. 1120–1156). Family background and early life Toirdelbhach was born in the year 1088. He was the youngest son of Ruaidrí na Saide Buide (died 1118), and his mother was Mór, daughter of Toirdelbach Ua Briain (1009–14 July 1086). Therefore, through his mother, his great-great-grandfather was Brian Boru. His brothers were Niall (killed 1093), Tadc (killed 1097), Conchobar (murdered 1103), and Domnall, King of Connacht (deposed 1106). There was at least one sister, Dubhchobhlaigh Bean Ua hEaghra of Luighne Connacht (died 1131). Ruaidrí was married to four or more women. According to the Annals of Tigernach, Toirdelbach's mother died the year he was born, suggesting his birth may have been arduous. In 1092, King Ruaidrí was blinded by Flaithbertaigh Ua Flaithbertaigh, an incident w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Áed Ua HOissín
Áed Ua hOissín (Hugh O'Hession) was consecrated first Archbishop of Tuam in 1152 and died in 1161. He was closely associated with Connacht royalty, and had served as abbot of Tuam. Biography Ua hOissín was the first Archbishop of Tuam and one of four bishops granted pallia at the Synod of Kells by the papal legate Cardinal Archbishop Giovanni Paparoni in 1152. He played a part in the period of Cistercian-inspired church reform initiated by St Malachy immediately before the Norman invasion of Ireland. He came from a family with some church connections: Aed Ua Oisin was also the name of a coarb of Iarlaith of Tuam (abbot of Jarlath's Monastery) in the late 11th century – this abbot is said to have died in 1085.Unknown. ''Annals of Clonmacnoise'' With other clergy he actively intervened in the affairs of Connaught and Ireland more broadly, and though Connaught wasn't a centre of Cistercian inspired reform he was part of a renewal of the Church centred on the refoundation of T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synod Of Kells
The Synod of Kells (, ) took place in 1152, under the presidency of Giovanni Cardinal Paparoni, and continued the process begun at the Synod of Ráth Breasail (1111) of reforming the Irish church. The sessions were divided between the abbeys of Kells and Mellifont, and in later times the synod has been called the Synod of Kells-Mellifont and the Synod of Mellifont-Kells. Its main effect was to increase the number of archbishops from two to four, and to redefine the number and size of dioceses. The Primacy of Ireland was granted to the Archdiocese of Armagh. Background Máel Máedóc Ua Morgair (Saint Malachy) was made a priest in 1119, as vicar to Celsus. His first sees were Down and Connor, and he was located at Bangor Abbey. On the death of Celsus in 1129, Malachy was nominated as his successor at Armagh, now the prime see in Ireland. An internal church dispute over the succession and proposals for reform obliged him to concede the position to Gelasius. In 1137, Gelasius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Annals
A number of Irish annals, of which the earliest was the Chronicle of Ireland, were compiled up to and shortly after the end of the 17th century. Annals were originally a means by which monks determined the yearly chronology of feast days. Over time, the obituaries of priests, abbots and bishops were added, along with that of notable political events. Non-Irish models include Bede's ''Chronica maiora'', Marcellinus Comes's ''Chronicle of Marcellinus'' and the '' Liber pontificalis''.Ó Corráin, "annals, Irish", p. 69. Chronology The origins of annalistic compilation can be traced to the occasional recording of notes and events in blank spaces between the '' latercus'', i.e. the 84-year Easter table adopted from Gaulish writer Sulpicius Severus (d. ''c''. 423). Extant Manuscript copies of extant annals include the following: * ''Annals of Boyle'' * ''Annals of Clonmacnoise'' * ''Annals of Connacht'' * '' Annals of Duiske'' * ''Annals of the Four Masters'' * ''Annals of Inisfall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clonmacnoise
Clonmacnoise (Irish: ''Cluain Mhic Nóis'') is a ruined monastery situated in County Offaly in Ireland on the River Shannon south of Athlone, founded in 544 by Saint Ciarán, a young man from Rathcroghan, County Roscommon. Until the 9th century it had close associations with the kings of Connacht. Saint Ciarán founded the monastery in the ancient territory of Uí Maine at a point where the major east–west land route ( Slighe Mhor) meets the River Shannon after crossing the bogs of Central Ireland known as the Esker Riada. The strategic location of the monastery helped it become a major center of religion, learning, craftsmanship and trade by the 9th century;Moss (2014), p. 126 and together with Clonard it was one of the most famous places in Ireland, visited by scholars from all over Europe. From the ninth until the eleventh century it was allied with the kings of Meath. Many of the high kings of Tara ( ''ardrí'') and of Connacht were buried here. Clonmacnoise was l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domhnall Ua Dubhthaigh
Domhnall Ua Dubhthaigh, Archbishop of Connacht, died 1136. The post of Archbishop of Connacht was a precursor to that of Archbishop of Tuam. His death is noted in the Annals of the Four Masters as follows: ''Domhnall Ua Dubhthaigh, Archbishop of Connaught, and successor of Ciaran, head of the wisdom and hospitality of the province, died after mass and celebration at Cluain-fearta-Brenainn.'' The Annals of Loch Cé have his obit ''sub anno'' 1137, describing him as ''"Domhnall Ua Dubhthaigh, bishop of Elphin, and comarb of Ciaran of Cluain-mic-Nois."'' References * http://www.irishtimes.com/ancestor/surname/index.cfm?fuseaction=History&Surname=duffy&UserID= * http://www.ucc.ie/celt/online/T100005B/text025.html * http://www.ucc.ie/celt/online/T100013/text002.html * ''Episcopal Hierarchy in Connacht and Tairdelbach Ua Conchobair'', Colman Etchingham, ''Journal of the Galway Archaeological and Historical Society'', vol. 52, 2000, pp. 13–29. * ''Irish Kings and High Kings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |