|
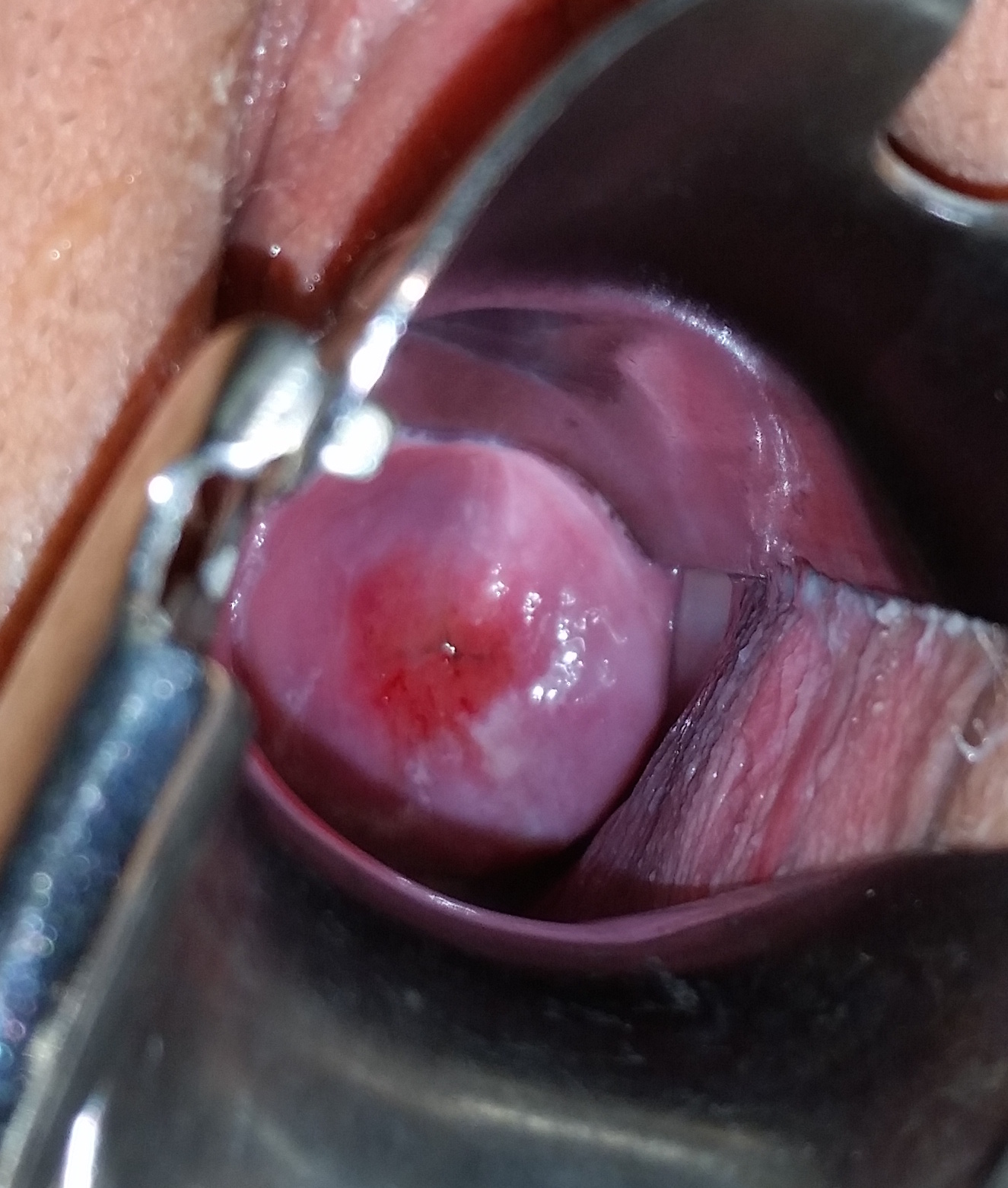
Mucopurulent Cervicitis
Cervicitis is inflammation of the uterine cervix. Cervicitis in women has many features in common with urethritis in men and many cases are caused by sexually transmitted infections. Non-infectious causes of cervicitis can include intrauterine devices, contraceptive diaphragms, and allergic reactions to spermicides or latex condoms. Cervicitis affects over half of all women during their adult life. Cervicitis may ascend and cause endometritis and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). Cervicitis may be acute or chronic. Symptoms and signs Cervicitis may have no symptoms. If symptoms do manifest, they may include: * Abnormal vaginal bleeding after intercourse between periods * Unusual gray, white, or yellow vaginal discharge * Painful sexual intercourse * Pain in the vagina * Pressure or heaviness in the pelvis * Frequent, painful urination Causes Cervicitis can be caused by any of a number of infections, of which the most common are chlamydia and gonorrhea, with chlamydia acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out necrotic cells and tissues damaged from the original insult and the inflammatory process, and initiate tissue repair. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and Functio laesa, loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore it is considered as a mechanism of innate immune system, innate immunity, as compared to adaptive immune system, adaptive immunity, which is specific for each pathogen. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydia Infection
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Chlamydia trachomatis''. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear they may occur only several weeks after infection; the incubation period between exposure and being able to infect others is thought to be on the order of two to six weeks. Symptoms in women may include vaginal discharge or burning with urination. Symptoms in men may include discharge from the penis, burning with urination, or pain and swelling of one or both testicles. The infection can spread to the upper genital tract in women, causing pelvic inflammatory disease, which may result in future infertility or ectopic pregnancy. Chlamydia infections can occur in other areas besides the genitals, including the anus, eyes, throat, and lymph nodes. Repeated chlamydia infections of the eyes that go without treatment can result in trachoma, a common cause of blindness i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorganism fighting another), whereas non-antibiotic antibacterials (such as sulfonamides and antiseptics) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydia
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Chlamydia trachomatis''. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear they may occur only several weeks after infection; the incubation period between exposure and being able to infect others is thought to be on the order of two to six weeks. Symptoms in women may include vaginal discharge or burning with urination. Symptoms in men may include discharge from the penis, burning with urination, or pain and swelling of one or both testicles. The infection can spread to the upper genital tract in women, causing pelvic inflammatory disease, which may result in future infertility or ectopic pregnancy. Chlamydia infections can occur in other areas besides the genitals, including the anus, eyes, throat, and lymph nodes. Repeated chlamydia infections of the eyes that go without treatment can result in trachoma, a common cause of blindness in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
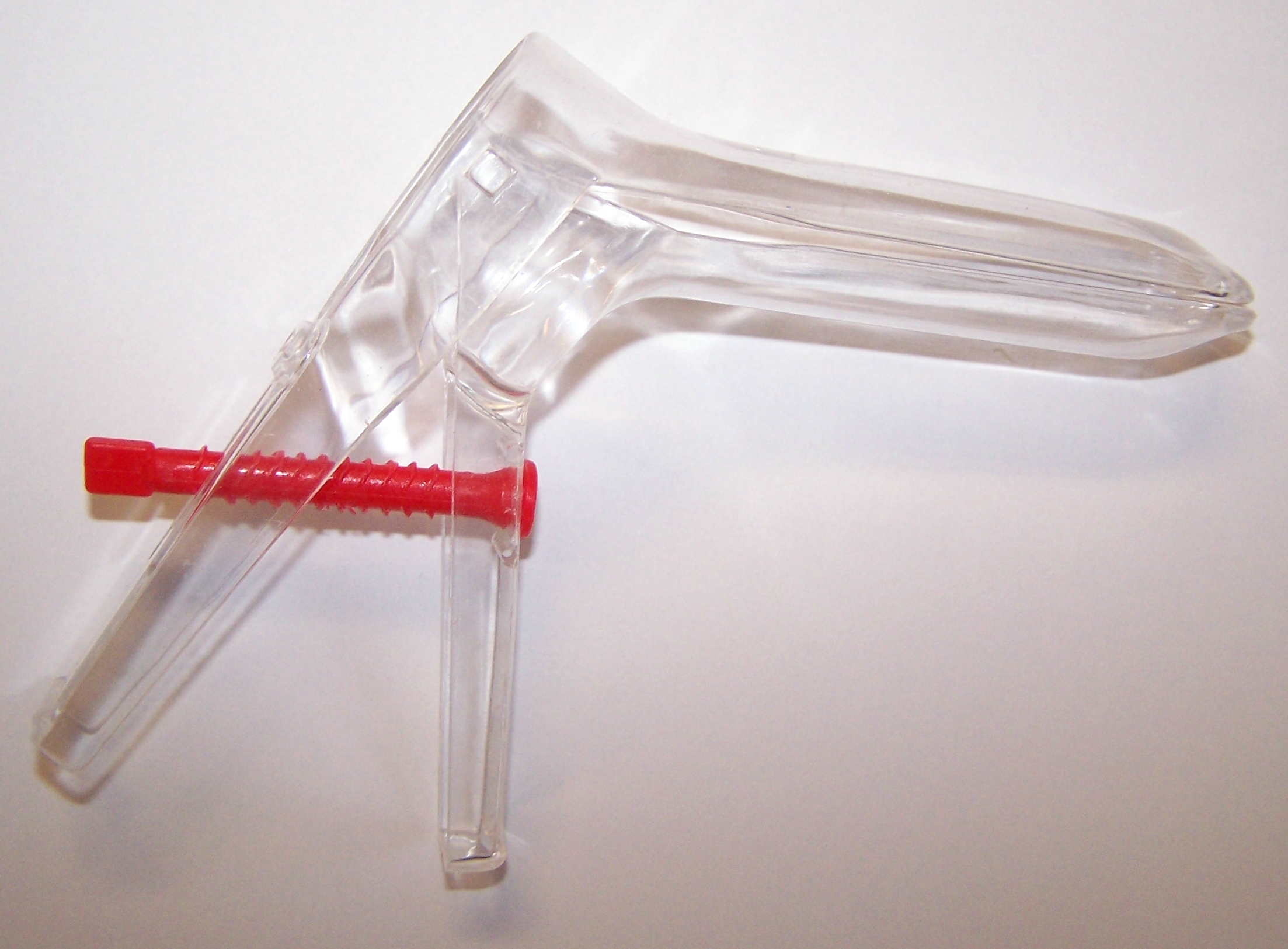
Speculum (medical)
A speculum (Latin for 'mirror'; plural specula or speculums) is a medical tool for investigating body orifices, with a form dependent on the orifice for which it is designed. In old texts, the speculum may also be referred to as a diopter or dioptra. Like an endoscope, a speculum allows a view inside the body; endoscopes, however, tend to have optics while a speculum is intended for direct vision. History Vaginal and anal specula were used by the ancient Greeks and Romans, and speculum artifacts have been found in Pompeii. A vaginal speculum, developed by J. Marion Sims, consists of a hollow cylinder with a rounded end that is divided into two hinged parts, somewhat like the beak of a duck. This speculum is inserted into the vagina to dilate it for examination of the vagina and cervix. The modern vaginal speculum was developed by J. Marion Sims, a plantation doctor in Lancaster County, South Carolina. Between 1845 and 1849, Sims performed dozens of surgeries, without anesthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvic Exam
A pelvic examination is the physical examination of the external and internal female pelvic organs. It is frequently used in gynecology for the evaluation of symptoms affecting the female reproductive and urinary tract, such as pain, bleeding, discharge, urinary incontinence, or trauma (e.g. sexual assault). It can also be used to assess a woman's anatomy in preparation for procedures. The exam can be done awake in the clinic and emergency department, or under anesthesia in the operating room. The most commonly performed components of the exam are 1) the external exam, to evaluate the external genitalia 2) the internal exam with palpation (commonly called the bimanual exam) to examine the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes, and 3) the internal exam using the speculum to visualize the vaginal walls and cervix. During the pelvic exam, sample of cells and fluids may be collected to screen for sexually transmitted infections or cancer. Some clinicians perform a pelvic exam as part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrauterine Device
An intrauterine device (IUD), also known as intrauterine contraceptive device (IUCD or ICD) or coil, is a small, often T-shaped birth control device that is inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. IUDs are one form of long-acting reversible birth control (LARC). One study found that female family planning providers choose LARC methods more often (41.7%) than the general public (12.1%). Among birth control methods, IUDs, along with other contraceptive implants, result in the greatest satisfaction among users. IUDs are safe and effective in adolescents as well as those who have not previously had children. Once an IUD is removed, even after long-term use, fertility returns to normal rapidly. Copper devices have a failure rate of about 0.8% while hormonal ( levonorgestrel) devices fail about 0.2% of the time within the first year of use. In comparison, male sterilization and male condoms have a failure rate of about 0.15% and 15%, respectively. Copper IUDs can also be u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycoplasma Genitalium
''Mycoplasma genitalium'' (''MG'', commonly known as Mgen) is a sexually transmitted, small and pathogenic bacterium that lives on the mucous epithelial cells of the urinary and genital tracts in humans. Medical reports published in 2007 and 2015 state that Mgen is becoming increasingly common. Resistance to multiple antibiotics is becoming prevalent, including to azithromycin, which until recently was the most reliable treatment. The bacteria was first isolated from the urogenital tract of humans in 1981, and was eventually identified as a new species of ''Mycoplasma'' in 1983. It can cause negative health effects in men and women. It also increases the risk factor for HIV spread with higher occurrences in those previously treated with the azithromycin antibiotics. Specifically, it causes urethritis in both men and women, and also cervicitis and pelvic inflammation in women. It presents clinically similar symptoms to that of ''Chlamydia trachomatis'' infection and has shown hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
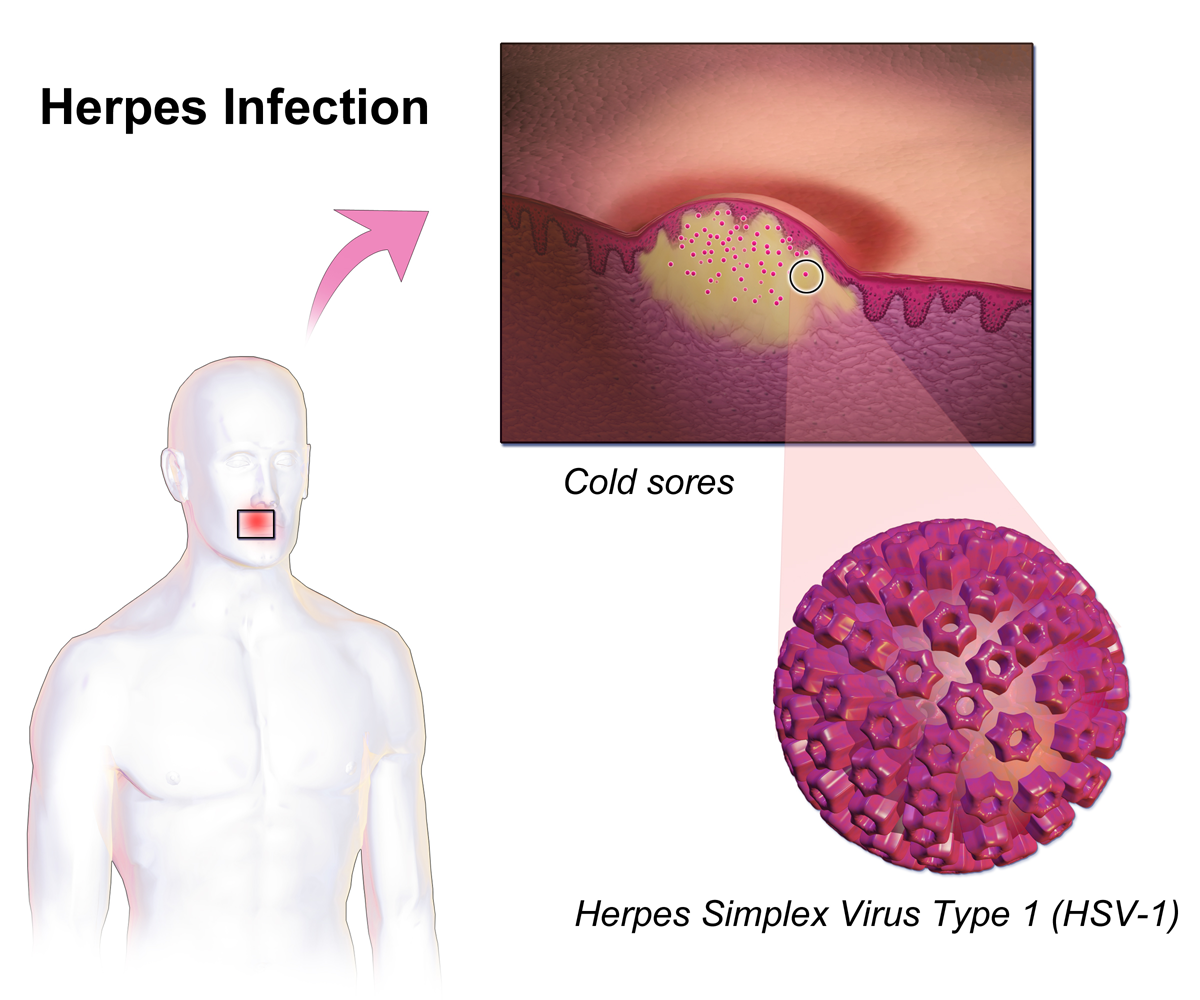
Herpes Simplex
Herpes simplex is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. Infections are categorized based on the part of the body infected. Oral herpes involves the face or mouth. It may result in small blisters in groups often called cold sores or fever blisters or may just cause a sore throat. Genital herpes, often simply known as herpes, involves the genitalia. It may have minimal symptoms or form blisters that break open and result in small ulcers. These typically heal over two to four weeks. Tingling or shooting pains may occur before the blisters appear. Herpes cycles between periods of active disease followed by periods without symptoms. The first episode is often more severe and may be associated with fever, muscle pains, swollen lymph nodes and headaches. Over time, episodes of active disease decrease in frequency and severity. Herpetic whitlow typically involves the fingers or thumb. Herpes simplex keratitis involves the eye. Herpesviral encephalitis involves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichomonas Vaginalis
''Trichomonas vaginalis'' is an anaerobic, flagellated protozoan parasite and the causative agent of a sexually transmitted disease called trichomoniasis. It is the most common pathogenic protozoan that infects humans in industrialized countries. Infection rates in men and women are similar but women are usually symptomatic, while infections in men are usually asymptomatic. Transmission usually occurs via direct, skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual, most often through vaginal intercourse. The WHO has estimated that 160 million cases of infection are acquired annually worldwide. The estimates for North America alone are between 5 and 8 million new infections each year, with an estimated rate of asymptomatic cases as high as 50%. Usually treatment consists of metronidazole and tinidazole. Clinical History Alfred Francois Donné (1801–1878) was the first to describe a procedure to diagnose trichomoniasis through "the microscopic observation of motile protozoa i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea, colloquially known as the clap, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium '' Neisseria gonorrhoeae''. Infection may involve the genitals, mouth, or rectum. Infected men may experience pain or burning with urination, discharge from the penis, or testicular pain. Infected women may experience burning with urination, vaginal discharge, vaginal bleeding between periods, or pelvic pain. Complications in women include pelvic inflammatory disease and in men include inflammation of the epididymis. Many of those infected, however, have no symptoms. If untreated, gonorrhea can spread to joints or heart valves. Gonorrhea is spread through sexual contact with an infected person. This includes oral, anal, and vaginal sex. It can also spread from a mother to a child during birth. Diagnosis is by testing the urine, urethra in males, or cervix in females. Testing all women who are sexually active and less than 25 years of age each year as well as thos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)
