genitals
A sex organ (or reproductive organ) is any part of an animal or plant that is involved in sexual reproduction. The reproductive organs together constitute the reproductive system. In animals, the testis in the male, and the ovary in the female, ...
, mouth, or rectum
The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the gut in others. The adult human rectum is about long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction (the end of the sigmoid colon) at the l ...
. Infected men may experience pain or burning with urination, discharge from the penis
A penis (plural ''penises'' or ''penes'' () is the primary sexual organ that male animals use to inseminate females (or hermaphrodites) during copulation. Such organs occur in many animals, both vertebrate and invertebrate, but males d ...
, or testicular pain. Infected women may experience burning with urination, vaginal discharge, vaginal bleeding between periods, or pelvic pain
Pelvic pain is pain in the area of the pelvis. Acute pain is more common than chronic pain. If the pain lasts for more than six months, it is deemed to be chronic pelvic pain. It can affect both the male and female pelvis.
Common causes in incl ...
. Complications in women include pelvic inflammatory disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease, also known as pelvic inflammatory disorder (PID), is an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system, namely the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, and inside of the pelvis. Often, there may be no ...
and in men include inflammation of the epididymis. Many of those infected, however, have no symptoms. If untreated, gonorrhea can spread to joints
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw- ...
or heart valves.
Gonorrhea is spread through sexual contact with an infected person. This includes oral, anal, and vaginal sex. It can also spread from a mother to a child during birth. Diagnosis is by testing the urine, urethra
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ''ourḗthrā'') is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra c ...
in males, or cervix
The cervix or cervix uteri (Latin, 'neck of the uterus') is the lower part of the uterus (womb) in the human female reproductive system. The cervix is usually 2 to 3 cm long (~1 inch) and roughly cylindrical in shape, which changes durin ...
in females. Testing all women who are sexually active and less than 25 years of age each year as well as those with new sexual partners is recommended; the same recommendation applies in men who have sex with men (MSM).
Gonorrhea can be prevented with the use of condom
A condom is a sheath-shaped barrier device used during sexual intercourse to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a sexually transmitted infection (STI). There are both male and female condoms. With proper use—and use at every act of inte ...
s, having sex with only one person who is uninfected, and by not having sex. Treatment is usually with ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone, sold under the brand name Rocephin, is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. These include middle ear infections, endocarditis, meningitis, pneumonia, bone and joint ...
by injection and azithromycin
Azithromycin, sold under the brand names Zithromax (in oral form) and Azasite (as an eye drop), is an antibiotic medication used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes middle ear infections, strep throat, pneum ...
by mouth. Resistance
Resistance may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Comics
* Either of two similarly named but otherwise unrelated comic book series, both published by Wildstorm:
** ''Resistance'' (comics), based on the video game of the same title
** ''T ...
has developed to many previously used antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, ...
s and higher doses of ceftriaxone are occasionally required. Retesting is recommended three months after treatment. Sexual partners from the last two months should also be treated.
Gonorrhea affects about 0.8% of women and 0.6% of men. An estimated 33 to 106 million new cases occur each year, out of the 498 million new cases of curable STI – which also includes syphilis, chlamydia
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium '' Chlamydia trachomatis''. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear they may occur only several w ...
, and trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis (trich) is an infectious disease caused by the parasite '' Trichomonas vaginalis''. About 70% of affected people do not have symptoms when infected. When symptoms occur, they typically begin 5 to 28 days after exposure. Symptoms c ...
. Infections in women most commonly occur when they are young adults. In 2015, it caused about 700 deaths. Descriptions of the disease date back to before the Common Era
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the ...
within the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tān ...
/''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tān ...
Old Testament
The Old Testament (often abbreviated OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew writings by the Israelites. The ...
(). The current name was first used by the Greek physician Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be on ...
before AD 200 who referred to it as "an unwanted discharge of semen".
Signs and symptoms
Gonorrhea infections of mucosal membranes can cause swelling, itching, pain, and the formation of pus. The time from exposure to symptoms is usually between two and 14 days, with most symptoms appearing between four and six days after infection, if they appear at all. Both men and women with infections of the throat may experience asore throat
Sore throat, also known as throat pain, is pain or irritation of the throat. Usually, causes of sore throat include
* viral infections
* group A streptococcal infection (GAS) bacterial infection
* pharyngitis (inflammation of the throat)
* t ...
, though such infection does not produce symptoms in 90% of cases. Other symptoms may include swollen lymph nodes around the neck. Either sex can become infected in the eyes or rectum if these tissues are exposed to the bacterium.
Women
Half of women with gonorrhea areasymptomatic
In medicine, any disease is classified asymptomatic if a patient tests as carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. Whenever a medical condition fails to show noticeable symptoms after a diagnosis it might be considered as ...
but the other half experience vaginal discharge, lower abdominal pain, or pain with sexual intercourse associated with inflammation of the uterine cervix. Common medical complications of untreated gonorrhea in women include pelvic inflammatory disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease, also known as pelvic inflammatory disorder (PID), is an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system, namely the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, and inside of the pelvis. Often, there may be no ...
which can cause scars to the fallopian tubes
The fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes, oviducts or salpinges (singular salpinx), are paired tubes in the human female that stretch from the uterus to the ovaries. The fallopian tubes are part of the female reproductive system. In ...
and result in later ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy is a complication of pregnancy in which the embryo attaches outside the uterus. Signs and symptoms classically include abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding, but fewer than 50 percent of affected women have both of these sympt ...
among those women who become pregnant.
Men
Most infected men with symptoms have inflammation of the penile urethra associated with a burning sensation during urination and discharge from the penis. In men, discharge with or without burning occurs in half of all cases and is the most common symptom of the infection. This pain is caused by a narrowing and stiffening of the urethral lumen. The most common medical complication of gonorrhea in men is inflammation of the epididymis. Gonorrhea is also associated with increased risk ofprostate cancer
Prostate cancer is cancer of the prostate. Prostate cancer is the second most common cancerous tumor worldwide and is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related mortality among men. The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system that su ...
.
Infants
 If not treated, gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum will develop in 28% of infants born to women with gonorrhea.
If not treated, gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum will develop in 28% of infants born to women with gonorrhea.
Spread
If left untreated, gonorrhea can spread from the original site of infection and infect and damage the joints, skin, and other organs. Indications of this can include fever, skin rashes, sores, and joint pain and swelling. In advanced cases, gonorrhea may cause a general feeling of tiredness similar to other infections. It is also possible for an individual to have anallergic reaction
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, refer a number of conditions caused by the hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic derm ...
to the bacteria, in which case any appearing symptoms will be greatly intensified. Very rarely it may settle in the heart, causing endocarditis
Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves the heart valves. Other structures that may be involved include the interventricular septum, the chordae tendineae, the mural endocardium, or the ...
, or in the spinal column, causing meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, headache, and neck stiffness. Other symptoms include confusion ...
. Both are more likely among individuals with suppressed immune systems, however.
Cause
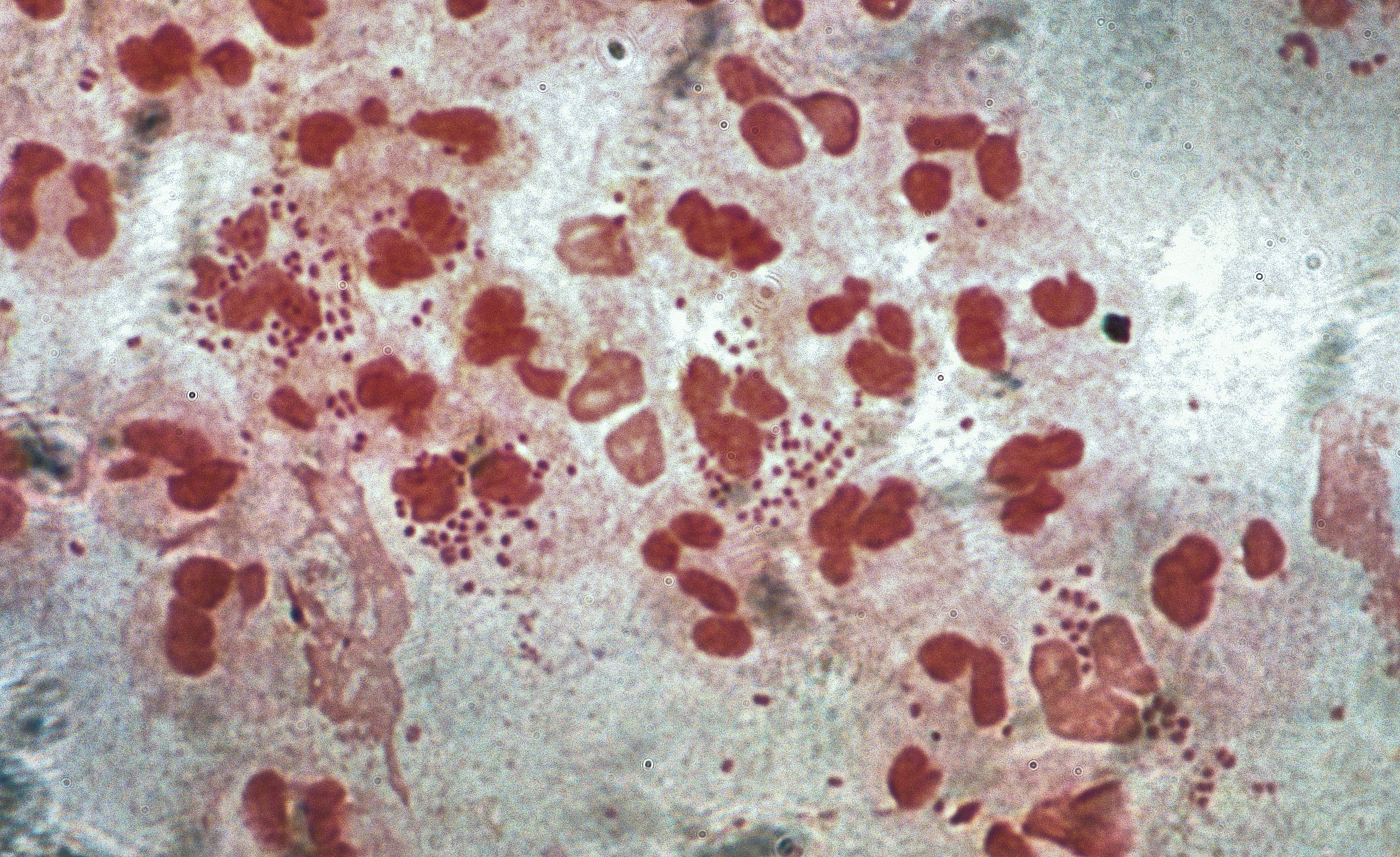
 Gonorrhea is caused by the bacterium '' Neisseria gonorrhoeae''. Previous infection does not confer immunity – a person who has been infected can become infected again by exposure to someone who is infected. Infected persons may be able to infect others repeatedly without having any signs or symptoms of their own.
Gonorrhea is caused by the bacterium '' Neisseria gonorrhoeae''. Previous infection does not confer immunity – a person who has been infected can become infected again by exposure to someone who is infected. Infected persons may be able to infect others repeatedly without having any signs or symptoms of their own.
Spread
The infection is usually spread from one person to another through vaginal, oral, oranal sex
Anal sex or anal intercourse is generally the insertion and thrusting of the erect penis into a person's anus, or anus and rectum, for sexual pleasure.Sepages 270–271for anal sex information, anpage 118for information about the clitoris. O ...
. Men have a 20% risk of getting the infection from a single act of vaginal intercourse with an infected woman. The risk for men who have sex with men (MSM) is higher.Howard Brown Health Center: STI Annual Report, 2009 Insertive MSM may get a penile infection from anal intercourse, while receptive MSM may get anorectal gonorrhea. Women have a 60–80% risk of getting the infection from a single act of vaginal intercourse with an infected man.National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases; National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services (20 July 2001). "Workshop Summary: Scientific Evidence on Condom Effectiveness for Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) Prevention". Hyatt Dulles Airport, Herndon, Virginia. pp14
A mother may transmit gonorrhea to her newborn during childbirth; when affecting the infant's eyes, it is referred to as ophthalmia neonatorum. It may be able to spread through the objects contaminated with body fluid from an infected person. The bacteria typically does not survive long outside the body, typically dying within minutes to hours.
Risk factors
It is discovered that sexually active women younger than 25 and men who have sex with men are at increased risk of getting gonorrhea. Other risk factors include: * Having a new sex partner * Having a sex partner who has other partners * Having more than one sex partner * Having had gonorrhea or another sexually transmitted infection *Complications
Medically it has been said that Untreated gonorrhea can lead to major complications, such as: * Infertility in women. Gonorrhea can spread into the uterus and fallopian tubes, causing pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). PID can result in scarring of the tubes, greater risk of pregnancy complications and infertility. PID requires immediate treatment. * Infertility in men. Gonorrhea can cause a small, coiled tube in the rear portion of the testicles where the sperm ducts are located (epididymis) to become inflamed (epididymitis). Untreated epididymitis can lead to infertility. * Infection that spreads to the joints and other areas of the body. The bacterium that causes gonorrhea can spread through the bloodstream and infect other parts of the body, including the joints. Fever, rash, skin sores, joint pain, swelling and stiffness are possible results. * Increased risk of HIV/AIDS. Having gonorrhea increases the susceptibility to infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the virus that leads to AIDS. People who have both gonorrhea and HIV (untreated by anti-retroviral therapy) are able to pass both diseases more readily to their partners. * Complications in babies. Babies who contract gonorrhea from their mothers during birth can develop blindness, sores on the scalp and infections.Diagnosis
Traditionally, gonorrhea was diagnosed with Gram stain andculture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these grou ...
; however, newer polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) ...
(PCR)-based testing methods are becoming more common. In those failing initial treatment, culture should be done to determine sensitivity to antibiotics.
Tests that use PCR (aka nucleic acid amplification) to identify genes unique to ''N. gonorrhoeae'' are recommended for screening and diagnosis of gonorrhea infection. These PCR-based tests require a sample of urine, urethral swabs, or cervical/vaginal swabs. Culture (growing colonies of bacteria in order to isolate and identify them) and Gram-stain (staining of bacterial cell walls to reveal morphology) can also be used to detect the presence of ''N. gonorrhoeae'' in all specimen types except urine.
If Gram-negative, oxidase-positive diplococci are visualized on direct Gram stain of urethral pus (male genital infection), no further testing is needed to establish the diagnosis of gonorrhea infection. However, in the case of female infection direct Gram stain of cervical swabs is not useful because the ''N. gonorrhoeae'' organisms are less concentrated in these samples. The chances of false positives are increased as Gram-negative diplococci native to the normal vaginal flora cannot be distinguished from ''N. gonorrhoeae.'' Thus, cervical swabs must be cultured under the conditions described above. If oxidase positive, Gram-negative diplococci are isolated from a culture of a cervical/vaginal swab specimen, then the diagnosis is made. Culture is especially useful for diagnosis of infections of the throat, rectum, eyes, blood, or joints—areas where PCR-based tests are not well established in all labs. Culture is also useful for antimicrobial sensitivity testing, treatment failure, and epidemiological purposes (outbreaks, surveillance).
In patients who may have disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI), all possible mucosal sites should be cultured (e.g., pharynx, cervix, urethra, rectum).https://www.cdc.gov/std/tg2015/clinical.htm section on prevention methods Three sets of blood cultures should also be obtained. Synovial fluid should be collected in cases of septic arthritis.
All people testing positive for gonorrhea should be tested for other sexually transmitted diseases such as chlamydia
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium '' Chlamydia trachomatis''. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear they may occur only several w ...
, syphilis, and human immunodeficiency virus. Studies have found co-infection with chlamydia ranging from 46 to 54% in young people with gonorrhea. Among persons in the United States between 14 and 39 years of age, 46% of people with gonorrheal infection also have chlamydial infection. For this reason, gonorrhea and chlamydia testing are often combined. People diagnosed with gonorrhea infection have a fivefold increase risk of HIV transmission. Additionally, infected persons who are HIV positive are more likely to shed and transmit HIV to uninfected partners during an episode of gonorrhea.
Screening
The United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends screening for gonorrhea in women at increased risk of infection, which includes all sexually active women younger than 25 years. Extragenital gonorrhea and chlamydia are highest in men who have sex with men (MSM). Additionally, the USPSTF also recommends routine screening in people who have previously tested positive for gonorrhea or have multiple sexual partners and individuals who use condoms inconsistently, provide sexual favors for money, or have sex while under the influence of alcohol or drugs. Screening for gonorrhea in women who are (or intend to become) pregnant, and who are found to be at high risk forsexually transmitted disease
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), also referred to as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and the older term venereal diseases, are infections that are Transmission (medicine), spread by Human sexual activity, sexual activity, especi ...
s, is recommended as part of prenatal care in the United States.
Prevention
As with most sexually transmitted diseases, the risk of infection can be reduced significantly by the correct use ofcondom
A condom is a sheath-shaped barrier device used during sexual intercourse to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a sexually transmitted infection (STI). There are both male and female condoms. With proper use—and use at every act of inte ...
s, not having sex, or can be removed almost entirely by limiting sexual activities to a mutually monogamous relationship with an uninfected person.
Those previously infected are encouraged to return for follow up care to make sure that the infection has been eliminated. In addition to the use of phone contact, the use of email and text messaging have been found to improve the re-testing for infection.
Newborn babies coming through the birth canal are given erythromycin
Erythromycin is an antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes respiratory tract infections, skin infections, chlamydia infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, and syphilis. It may also be used du ...
ointment in the eyes to prevent blindness from infection. The underlying gonorrhea should be treated; if this is done then usually a good prognosis will follow.
Treatment
Antibiotics
 Antibiotics are used to treat gonorrhea infections. As of 2016, both
Antibiotics are used to treat gonorrhea infections. As of 2016, both ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone, sold under the brand name Rocephin, is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. These include middle ear infections, endocarditis, meningitis, pneumonia, bone and joint ...
by injection and azithromycin
Azithromycin, sold under the brand names Zithromax (in oral form) and Azasite (as an eye drop), is an antibiotic medication used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes middle ear infections, strep throat, pneum ...
by mouth are most effective. However, due to increasing rates of antibiotic resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistanc ...
, local susceptibility patterns must be taken into account when deciding on treatment. Ertapenem is a potential effective alternative treatment for ceftriaxone-resistant gonorrhea.
Adults may have eyes infected with gonorrhoea and require proper personal hygiene and medications. Addition of topical antibiotics have not been shown to improve cure rates compared to oral antibiotics alone in treatment of eye infected gonorrhea. For newborns, erythromycin
Erythromycin is an antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes respiratory tract infections, skin infections, chlamydia infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, and syphilis. It may also be used du ...
ointment is recommended as a preventative measure for gonococcal infant conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis, also known as pink eye, is inflammation of the outermost layer of the white part of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelid. It makes the eye appear pink or reddish. Pain, burning, scratchiness, or itchiness may occur. The ...
.
Infections of the throat can be especially problematic, as antibiotics have difficulty becoming sufficiently concentrated there to destroy the bacteria. This is amplified by the fact that pharyngeal gonorrhoea is mostly asymptomatic, and gonococci and commensal ''Neisseria'' species can coexist for long time periods in the pharynx and share anti-microbial resistance genes. Accordingly, an enhanced focus on early detection (i.e., screening of high-risk populations, such as men who have sex with men, PCR testing
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) ...
should be considered) and appropriate treatment of pharyngeal gonorrhoea is important.
Sexual partners
It is recommended that sexual partners be tested and potentially treated. One option for treating sexual partners of people infected is patient-delivered partner therapy (PDPT), which involves providing prescriptions or medications to the person to take to his/her partner without the health care provider's first examining him/her."Expedited partner therapy in the management of sexually transmitted diseases". February 2006. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The United States'
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georg ...
(CDC) currently recommend that individuals who have been diagnosed and treated for gonorrhea avoid sexual contact with others until at least one week past the final day of treatment in order to prevent the spread of the bacterium.
Antibiotic resistance
Many antibiotics that were once effective includingpenicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using ...
, tetracycline
Tetracycline, sold under various brand names, is an oral antibiotic in the tetracyclines family of medications, used to treat a number of infections, including acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague, malaria, and syphilis.
Common side effects ...
, and fluoroquinolones are no longer recommended because of high rates of resistance. Resistance to cefixime
Cefixime, sold under the brand name Suprax among others, is an antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections. These infections include otitis media, strep throat, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, gonorrhea, and Lyme d ...
has reached a level such that it is no longer recommended as a first-line agent in the United States, and if it is used a person should be tested again after a week to determine whether the infection still persists. Public health officials are concerned that an emerging pattern of resistance may predict a global epidemic. In 2016, the WHO published new guidelines for treatment, stating "There is an urgent need to update treatment recommendations for gonococcal infections to respond to changing antimicrobial resistance (AMR) patterns of ''N. gonorrhoeae''. High-level resistance to previously recommended quinolones is widespread and decreased susceptibility to the extended-spectrum (third-generation) cephalosporins, another recommended first-line treatment in the 2003 guidelines, is increasing and several countries have reported treatment failures."
Prognosis
meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, headache, and neck stiffness. Other symptoms include confusion ...
, or endocarditis
Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves the heart valves. Other structures that may be involved include the interventricular septum, the chordae tendineae, the mural endocardium, or the ...
. This occurs in between 0.6 and 3% of infected women and 0.4 and 0.7% of infected men.
In men, inflammation of the epididymis, prostate gland, and urethra
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ''ourḗthrā'') is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra c ...
can result from untreated gonorrhea.Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; & Mitchell, Richard N. (2007). ''Robbins Basic Pathology'' (8th ed.). Saunders Elsevier. pp. 705–706 In women, the most common result of untreated gonorrhea is pelvic inflammatory disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease, also known as pelvic inflammatory disorder (PID), is an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system, namely the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, and inside of the pelvis. Often, there may be no ...
. Other complications include inflammation of the tissue surrounding the liver, a rare complication associated with Fitz-Hugh–Curtis syndrome; septic arthritis in the fingers, wrists, toes, and ankles; septic abortion; chorioamnionitis
Chorioamnionitis, also known as intra-amniotic infection (IAI), is inflammation of the fetal membranes (amnion and chorion), usually due to bacterial infection. In 2015, a National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Workshop expert p ...
during pregnancy; neonatal or adult blindness from conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis, also known as pink eye, is inflammation of the outermost layer of the white part of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelid. It makes the eye appear pink or reddish. Pain, burning, scratchiness, or itchiness may occur. The ...
; and infertility
Infertility is the inability of a person, animal or plant to reproduce by natural means. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy adult, except notably among certain eusocial species (mostly haplodiploid insects). It is the normal st ...
. Men who have had a gonorrhea infection have an increased risk of getting prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is cancer of the prostate. Prostate cancer is the second most common cancerous tumor worldwide and is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related mortality among men. The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system that su ...
.
Epidemiology
 About 88 million cases of gonorrhea occur each year, out of the 448 million new cases of curable STI each year – that also includes syphilis, chlamydia and
About 88 million cases of gonorrhea occur each year, out of the 448 million new cases of curable STI each year – that also includes syphilis, chlamydia and trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis (trich) is an infectious disease caused by the parasite '' Trichomonas vaginalis''. About 70% of affected people do not have symptoms when infected. When symptoms occur, they typically begin 5 to 28 days after exposure. Symptoms c ...
. The prevalence was highest in the Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
n region, the Americas, and Western Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
, and lowest in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
. In 2013, it caused about 3,200 deaths, up from 2,300 in 1990.
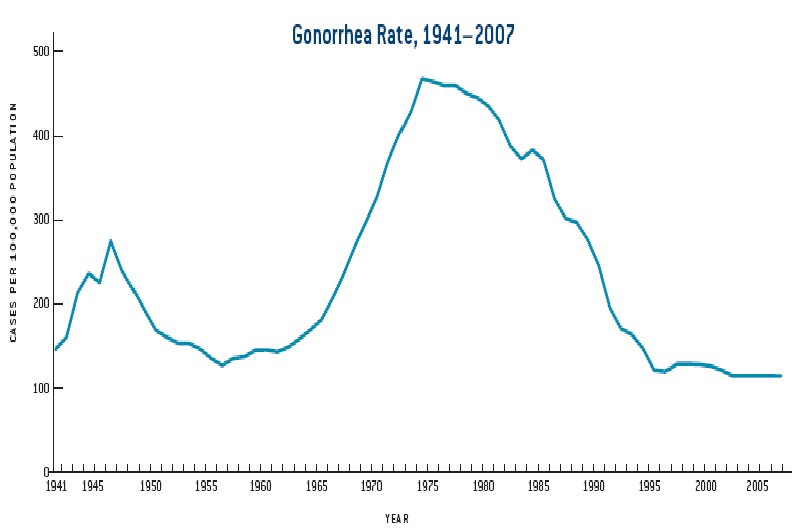
In the United Kingdom, 196 per 100,000 males 20 to 24 years old and 133 per 100,000 females 16 to 19 years old were diagnosed in 2005. In 2013, the CDC estimated that more than 820,000 people in the United States get a new gonorrheal infection each year. Fewer than half of these infections are reported to CDC. In 2011, 321,849 cases of gonorrhea were reported to the CDC. After the implementation of a national gonorrhea control program in the mid-1970s, the national gonorrhea rate declined from 1975 to 1997. After a small increase in 1998, the gonorrhea rate has decreased slightly since 1999. In 2004, the rate of reported gonorrheal infections was 113. 5 per 100,000 persons.
In the US, it is the second-most-common bacterial sexually transmitted infections
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), also referred to as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and the older term venereal diseases, are infections that are spread by sexual activity, especially vaginal intercourse, anal sex, and ora ...
; chlamydia
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium '' Chlamydia trachomatis''. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear they may occur only several w ...
remains first. According to the CDC African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an Race and ethnicity in the United States, ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American ...
s are most affected by gonorrhea, accounting for 69% of all gonorrhea cases in 2010.
The World Health Organization warned in 2017 of the spread of untreatable strains of gonorrhea, following analysis of at least three cases in Japan, France and Spain, which survived all antibiotic treatment.
History
 Some scholars translate the biblical terms ''zav'' (for a male) and ''zavah'' (for a female) as gonorrhea.
It has been suggested that mercury was used as a treatment for gonorrhea. Surgeons' tools on board the recovered English warship the ''
Some scholars translate the biblical terms ''zav'' (for a male) and ''zavah'' (for a female) as gonorrhea.
It has been suggested that mercury was used as a treatment for gonorrhea. Surgeons' tools on board the recovered English warship the ''Mary Rose
The ''Mary Rose'' (launched 1511) is a carrack-type warship of the English Tudor navy of King Henry VIII. She served for 33 years in several wars against France, Scotland, and Brittany. After being substantially rebuilt in 1536, she saw her ...
'' included a syringe
A syringe is a simple reciprocating pump consisting of a plunger (though in modern syringes, it is actually a piston) that fits tightly within a cylindrical tube called a barrel. The plunger can be linearly pulled and pushed along the inside o ...
that, according to some, was used to inject the mercury via the urinary meatus
The urinary meatus, (, ) also known as the external urethral orifice, is the opening of the urethra. It is the point where urine exits the urethra in both sexes and where semen exits the urethra in males. The meatus has varying degrees of sensiti ...
into crewmen with gonorrhea. The name "the clap", in reference to the disease, is recorded as early as the sixteenth century, referring to a medieval red-light district
A red-light district or pleasure district is a part of an urban area where a concentration of prostitution and sex-oriented businesses, such as sex shops, strip clubs, and adult theaters, are found. In most cases, red-light districts are parti ...
in Paris, Les Clapiers. Translating to "The rabbit holes", it was so named for the small huts in which prostitutes worked. as cited in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' entry for "clap"
In 1854, Dr. Wilhelm Gollmann
Wilhelm may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* William Charles John Pitcher, costume designer known professionally as "Wilhelm"
* Wilhelm (name), a list of people and fictional characters with the given name or surname
Other uses
* Moun ...
addressed gonorrhea in his book, ''Homeopathic Guide to all Diseases Urinary and Sexual Organs''. He noted that the disease was common in prostitutes and homosexuals in large cities. Gollmann recommended the following as cures: aconite to cure "shooting pains with soreness and inflammation;" mercury "for stitching pain with purulent discharge;" ''nux vomica
''Strychnos nux-vomica'', the strychnine tree, also known as nux vomica, poison fruit, semen strychnos, and quaker buttons, is a deciduous tree native to India and to southeast Asia. It is a medium-sized tree in the family Loganiaceae that grows ...
'' and sulphur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
"when the symptoms are complicated with hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids (or haemorrhoids), also known as piles, are vascular structures in the anal canal. In their normal state, they are cushions that help with stool control. They become a disease when swollen or inflamed; the unqualified term '' ...
and stricture of the rectum
The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the gut in others. The adult human rectum is about long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction (the end of the sigmoid colon) at the l ...
. Other remedies include argentum, ''aurum'' (gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
), belladonna, calcarea, ignatia, phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ea ...
, and sepia.
Silver nitrate
Silver nitrate is an inorganic compound with chemical formula . It is a versatile precursor to many other silver compounds, such as those used in photography. It is far less sensitive to light than the halides. It was once called ''lunar caustic ...
was one of the widely used drugs in the 19th century. However, it became replaced by Protargol Silver proteinate (brand name: Protargol) is used in electron microscopy with periodic acid and thiocarbohydrazide or thiosemicarbohydrazide as a positive stain for carbohydrates such as glycogen. It can also be used for light microscopy to stain ne ...
. Arthur Eichengrün invented this type of colloidal silver, which was marketed by Bayer
Bayer AG (, commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer's areas of business include pharmaceutica ...
from 1897 onward. The silver-based treatment was used until the first antibiotics came into use in the 1940s.
The exact time of onset of gonorrhea as prevalent disease or epidemic cannot be accurately determined from the historical record. One of the first reliable notations occurs in the Acts of the (English) Parliament. In 1161, this body passed a law to reduce the spread of "... the perilous infirmity of burning". The symptoms described are consistent with, but not diagnostic of, gonorrhea. A similar decree was passed by Louis IX in France in 1256, replacing regulation with banishment. Similar symptoms were noted at the siege of Acre by Crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were ...
.
Coincidental to, or dependent on, the appearance of a gonorrhea epidemic, several changes occurred in European medieval society. Cities hired public health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the det ...
doctors to treat affected patients without right of refusal. Pope Boniface There have been eight popes and one antipope named Boniface.
*Pope Boniface I (r. 418–422)
*Pope Boniface II (530–532)
*Pope Boniface III (607)
*Pope Boniface IV (608–615)
*Pope Boniface V (619–625)
*Pope Boniface VI (896)
**Antipope Bonifa ...
rescinded the requirement that physicians complete studies for the lower orders of the Catholic priesthood.
Medieval public health physicians in the employ of their cities were required to treat prostitutes infected with the "burning", as well as lepers and other epidemic patients. After Pope Boniface completely secularized the practice of medicine, physicians were more willing to treat a sexually transmitted disease.
Research
A vaccine for gonorrhea has been developed that is effective in mice. It will not be available for human use until further studies have demonstrated that it is both safe and effective in the human population. Development of a vaccine has been complicated by the ongoing evolution of resistant strains and antigenic variation (the ability of ''N. gonorrhoeae'' to disguise itself with different surface markers to evade the immune system). As '' N. gonorrhoeae'' is closely related to ''N. meningitidis
''Neisseria meningitidis'', often referred to as meningococcus, is a Gram-negative bacterium that can cause meningitis and other forms of meningococcal disease such as meningococcemia, a life-threatening sepsis. The bacterium is referred to as a ...
'' and they have 80–90% homology in their genetic sequences some cross-protection by meningococcal vaccines is plausible. A study published in 2017 showed that MeNZB
MeNZB was a vaccine against a specific strain of group B meningococcus, used to control an epidemic of meningococcal disease in New Zealand. Most people are able to carry the meningococcus bacteria safely with no ill effects. However, meningoco ...
group B meningococcal vaccine provided a partial protection against gonorrhea. The vaccine efficiency was calculated to be 31%.
References
External links
*"Gonorrhea – CDC Fact Sheet"
{{Authority control Bacterium-related cutaneous conditions Gonorrhea Infectious causes of cancer Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate