|
Prostatitis
Prostatitis is an umbrella term for a variety of medical conditions that incorporate bacterial and non-bacterial origin illnesses in the pelvic region. In contrast with the plain meaning of the word (which means "inflammation of the prostate"), the diagnosis may not always include inflammation. Prostatitis is classified into acute, chronic, asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis, and chronic pelvic pain syndrome. In the United States, prostatitis is diagnosed in 8% of all male urologist visits and 1% of all primary care physician visits for male genitourinary symptoms. Classification The term ''prostatitis'' refers to inflammation of the tissue of the prostate gland. It may occur as an appropriate physiological response to an infection, or it may occur in the absence of infection. In 1999, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) devised a new classification system. For more specifics about each type of prostatitis, including information on sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostatodynia
Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS), previously known as chronic nonbacterial prostatitis, is long-term pelvic pain and lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) without evidence of a bacterial infection. It affects about 2–6% of men. Together with IC/BPS, it makes up urologic chronic pelvic pain syndrome (UCPPS). The cause is unknown. Diagnosis involves ruling out other potential causes of the symptoms such as bacterial prostatitis, benign prostatic hypertrophy, overactive bladder, and cancer. Recommended treatments include multimodal therapy, physiotherapy, and a trial of alpha blocker medication or antibiotics in certain newly diagnosed cases. Some evidence supports some non medication based treatments. Signs and symptoms Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS) is characterized by pelvic or perineal pain without evidence of urinary tract infection, lasting longer than 3 months, as the key symptom. Symptoms may wax and wane. Pain can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
Chronic bacterial prostatitis is a bacterial infection of the prostate gland. It should be distinguished from other forms of prostatitis such as acute bacterial prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS). Signs and symptoms Chronic bacterial prostatitis is a relatively rare condition that usually presents with an intermittent UTI-type picture. It is defined as recurrent urinary tract infections in men originating from a chronic infection in the prostate. Symptoms may be completely absent until there is also bladder infection, and the most troublesome problem is usually recurrent cystitis. It has been said that recurrent and relapsing UTIs (i.e., UTIs due to the same pathogen) are a hallmark of chronic bacterial prostatitis. Chronic bacterial prostatitis occurs in less than 5% of patients with prostate-related non- BPH lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). Dr. Weidner, Professor of Medicine, Department of Urology, University of Gießen, has stated: "In studies of 656 me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Prostatitis
Acute prostatitis is a serious bacterial infection of the prostate gland. This infection is a medical emergency. It should be distinguished from other forms of prostatitis such as chronic bacterial prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS). Signs and symptoms Men with acute prostatitis often have chills, fever, pain in the lower back, perineum, or genital area, urinary frequency and urgency often at night, burning or painful urination, body aches, and a demonstrable infection of the urinary tract, as evidenced by white blood cells and bacteria in the urine. Acute prostatitis may be a complication of prostate biopsy. Often, the prostate gland is very tender to palpation through the rectum. Diagnosis Acute prostatitis is relatively easy to diagnose due to its symptoms that suggest infection. The organism may be found in blood or urine, and sometimes in both. Common bacteria are ''Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Proteus, Pseudomonas, Enterobacter, Enterococcus, Ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostate Massage
Prostate massage is the massage or stimulation of the male prostate gland for medical purposes or sexual stimulation. The prostate takes part in the sexual response cycle, and is essential for the production of semen. Due to its proximity to the anterior rectal wall, it can be stimulated from the anterior wall of the rectum or externally via the perineum. Medical uses Digital rectal examination Prostate massage is part of the digital rectal examination (DRE) routinely given to men by urologists in order to look for nodules of prostate cancer and to obtain an expressed prostatic secretion (EPS) specimen for microscopy and microbiological culture to screen for prostatitis. Therapy for prostatitis In the late 1990s, a small number of doctors tried prostate massage in conjunction with antibiotics for the treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis with uncertain results. In recent trials, however, prostate massage was not shown to improve outcomes compared to antibiotics alone. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymptomatic Inflammatory Prostatitis
Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis is a painless inflammation of the prostate gland where there is no evidence of infection. It should be distinguished from the other categories of prostatitis characterised by either pelvic pain or evidence of infection, such as chronic bacterial prostatitis, acute bacterial prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS). It is a common finding in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Signs and symptoms These patients have no history of genitourinary pain complaints, but leukocytosis is noted, usually during evaluation for other conditions. Diagnosis Diagnosis is through tests of semen, expressed prostatic secretion (EPS) or prostate tissue that reveal inflammation in the absence of symptoms. Treatment No treatment required. It is standard practice for men with infertility and category IV prostatitis to be given a trial of antibiotics and/or anti-inflammatories, although evidence of efficacy are weak. Since signs of asymptomatic prosta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
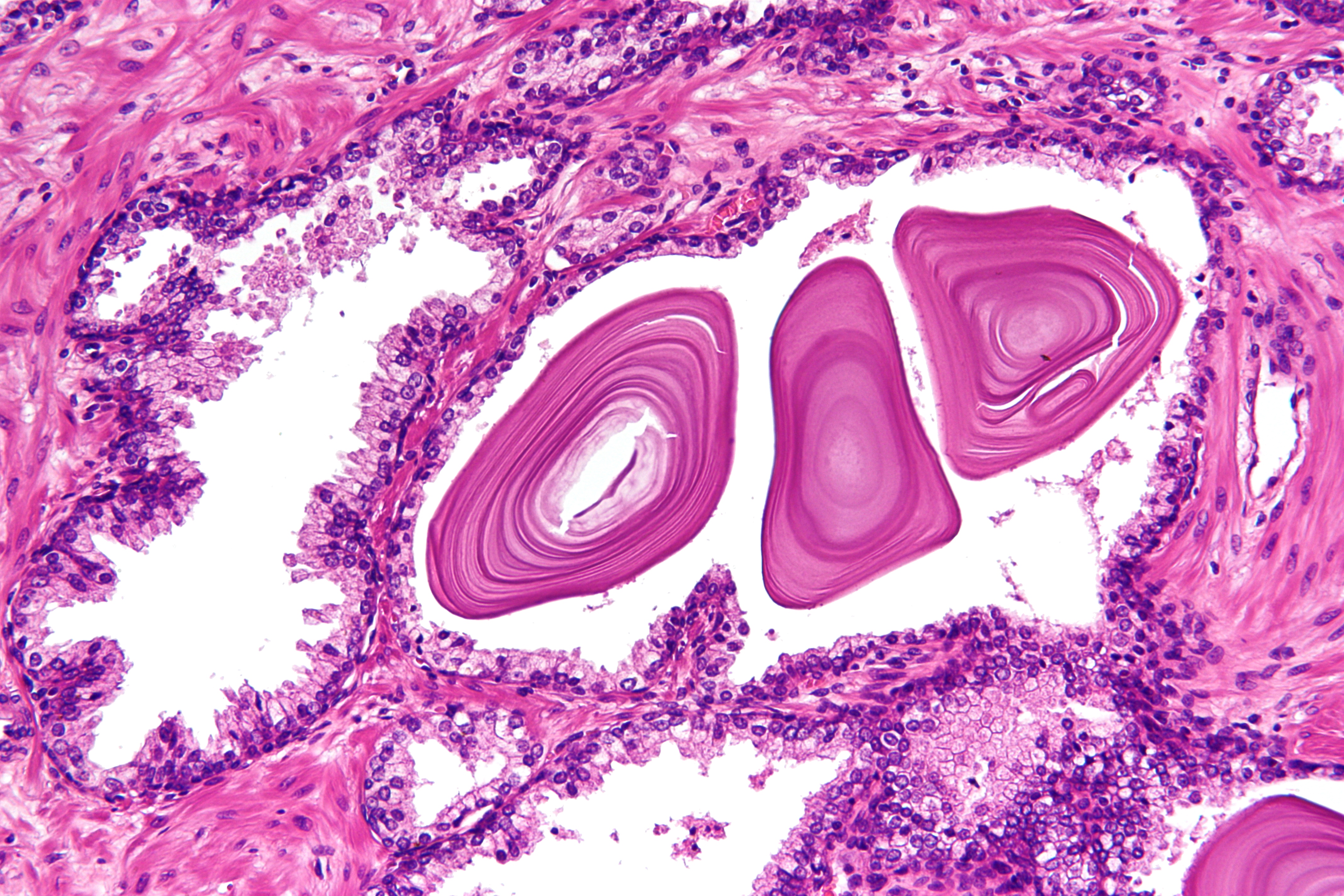
Prostate Gland
The prostate is both an accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found only in some mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemically, and physiologically. Anatomically, the prostate is found below the bladder, with the urethra passing through it. It is described in gross anatomy as consisting of lobes and in microanatomy by zone. It is surrounded by an elastic, fibromuscular capsule and contains glandular tissue as well as connective tissue. The prostate glands produce and contain fluid that forms part of semen, the substance emitted during ejaculation as part of the male sexual response. This prostatic fluid is slightly alkaline, milky or white in appearance. The alkalinity of semen helps neutralize the acidity of the vaginal tract, prolonging the lifespan of sperm. The prostatic fluid is expelled in the first part of ejaculate, together with most of the sperm, because of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstitial Cystitis
Interstitial cystitis (IC), a type of bladder pain syndrome (BPS), is chronic pain in the bladder and pelvic floor of unknown cause. It is the urologic chronic pelvic pain syndrome of women. Symptoms include feeling the need to urinate right away, needing to urinate often, and pain with sex. IC/BPS is associated with depression and lower quality of life. Many of those affected also have irritable bowel syndrome and fibromyalgia. The cause of interstitial cystitis is unknown. While it can, it does not typically run in a family. The diagnosis is usually based on the symptoms after ruling out other conditions. Typically the urine culture is negative. Ulceration or inflammation may be seen on cystoscopy. Other conditions which can produce similar symptoms include overactive bladder, urinary tract infection (UTI), sexually transmitted infections, prostatitis, endometriosis in females, and bladder cancer. There is no cure for interstitial cystitis and management of this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IgG4-related Prostatitis
IgG4-related prostatitis is prostate involvement in men with IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), which is an emerging fibroinflammatory disease entity which is characterised (i) by a tendency to mass forming lesions in multiple sites of the body and (ii) by usually a prompt response to steroid therapy. Men with IgG4-related prostatitis may also present with manifestations of IgG4-RD at other sites anywhere in the body; involvement of different areas of the body can occur either at the same time (synchronously) or at different periods of time (metachronously). Presentation Several case studies on IgG4-related prostatitis have been reported. Patients have been noted to commonly present with lower urinary tract symptoms such as dysuria, pollakisuria, urinary urgency, and a feeling of incomplete emptying. The clinical presentation is similar to that in benign prostatic hyperplasia or chronic prostatitis, although pain, as occurs in CP/CPPS, does not usually appear to be significant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)