|
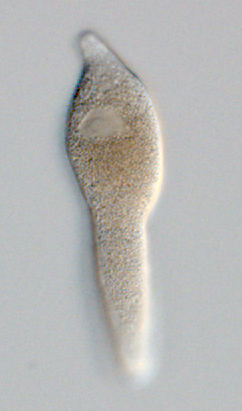
Monocystis
''Monocystis (Gr., monos, ''single'' + kystisis, ''bladder'')'' is a genus (the type of the family Monocystidae) of acephaline gregarines (subclass Gregarinasina) not having the protoplasm divided into segments by septa and including internal parasites of invertebrates (as ''M. agilis'' of the reproductive system of earthworms). Habit and habitat Monocystis lives as an intracellular parasite in its young stage when it lives in the bundle of developing sperms and becomes extracellular in its mature stage when it lives in the contents of seminal vesicles of earthworms. Its infection is so wide that practically all mature earthworms are found parasitized by this parasite. Structure The adult mature of ''Monocystis'' is called trophozoite which is a feeding stage. The young trophozoite lives in the sperm morula (sperm morula is a group of developing sperms) of the host; it feeds and grows at the expense of the protoplasm of the developing sperms until all the protoplasm is exhausted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monocystis Capture
''Monocystis (Gr., monos, ''single'' + kystisis, ''bladder'')'' is a genus (the type of the family Monocystidae) of acephaline gregarines (subclass Gregarinasina) not having the protoplasm divided into segments by septa and including internal parasites of invertebrates (as ''M. agilis'' of the reproductive system of earthworms). Habit and habitat Monocystis lives as an intracellular parasite in its young stage when it lives in the bundle of developing sperms and becomes extracellular in its mature stage when it lives in the contents of seminal vesicles of earthworms. Its infection is so wide that practically all mature earthworms are found parasitized by this parasite. Structure The adult mature of ''Monocystis'' is called trophozoite which is a feeding stage. The young trophozoite lives in the sperm morula A morula (Latin, ''morus'': mulberry) is an early-stage embryo consisting of a solid ball of cells called blastomeres, contained in mammals, and other animals within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monocystinae
The Monocystinae are a subfamily of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa. Taxonomy There are seven genera in this subfamily. The type genus is ''Monocystis''. History This subfamily was created by Bütschli in 1882Bütschli O, Schwager C (1882) Protozoa. Abt. 1, Sarkodina und Sporozoa. Leipzig: F. C. Wintersche Verlagshandlung and modified by Bhatia in 1930.Bhatia BL (1930) Synopsis of the genera and classification of haplocyte gregarines. Parasitol 22: 156-167 Description The species in this subfamily are cylindroid in shape with a mucron at the anterior end. The trophozoites are solitary. Syzygy occurs late in the life cycle. They parasitise the coelom of earthworm An earthworm is a terrestrial invertebrate that belongs to the phylum Annelida. They exhibit a tube-within-a-tube body plan; they are externally segmented with corresponding internal segmentation; and they usually have setae on all segments. T ...s and are spread by the orofaecal route. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregarinasina
The gregarines are a group of Apicomplexan alveolates, classified as the Gregarinasina or Gregarinia. The large (roughly half a millimeter) parasites inhabit the intestines of many invertebrates. They are not found in any vertebrates. However, gregarines are closely related to both ''Toxoplasma'' and ''Plasmodium'', which cause toxoplasmosis and malaria, respectively. Both protists use protein complexes similar to those that are formed by the gregarines for gliding motility and invading target cells. This makes them excellent models for studying gliding motility with the goal of developing treatment options for toxoplasmosis and malaria. Thousands of different species of gregarines are expected to be found in insects, and 99% of these gregarines still need to be described. Each insect can be the host of multiple species. One of the most studied gregarines is ''Gregarina garnhami''. In general, gregarines are regarded as very successful parasites, as their hosts are spread over the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugregarinorida
The ''Eugregarinorida'' are the most large and diverse order of gregarines — parasitic protists belonging to the phylum Apicomplexa. Eugregarines are found in marine, freshwater and terrestrial habitats. These species possess large trophozoites that are significantly different in morphology and behavior from the sporozoites. This taxon contains most of the known gregarine species. These protozoa are common parasites of many invertebrates including insects and polychete worms. Taxonomy Eugregarinorida has three recognised suborders: Aseptatorina, Blastogregarinorina and Septatorina. The intestinal eugregarines are separated into septate — suborder Septatina — and aseptate — suborder Aseptatina — depending on whether the trophozoite is superficially divided by a transverse septum. The marine gregarines are the most poorly studied members of this order. The eugregarines have been classified into 27 families with ~244 genera, 14 of which have more than 25 species each. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthworms
An earthworm is a terrestrial invertebrate that belongs to the phylum Annelida. They exhibit a tube-within-a-tube body plan; they are externally segmented with corresponding internal segmentation; and they usually have setae on all segments. They occur worldwide where soil, water, and temperature allow. Earthworms are commonly found in soil, eating a wide variety of organic matter. This organic matter includes plant matter, living protozoa, rotifers, nematodes, bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms. An earthworm's digestive system runs the length of its body. An earthworm respires (breathes) through its skin. It has a double transport system made of coelomic fluid that moves within the fluid-filled coelom and a simple, closed circulatory system. It has a central and peripheral nervous system. Its central nervous system consists of two ganglia above the mouth, one on either side, connected to a nerve running along its length to motor neurons and sensory cells in each se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protoplasm
Protoplasm (; ) is the living part of a cell that is surrounded by a plasma membrane. It is a mixture of small molecules such as ions, monosaccharides, amino acid, and macromolecules such as proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, etc. In some definitions, it is a general term for the cytoplasm (e.g., Mohl, 1846), but for others, it also includes the nucleoplasm (e.g., Strasburger, 1882). For Sharp (1921), "According to the older usage the extra-nuclear portion of the protoplast 'the entire cell, excluding the cell wall''was called "protoplasm," but the nucleus also is composed of protoplasm, or living substance in its broader sense. The current consensus is to avoid this ambiguity by employing Strasburger's '(1882)''terms cytoplasm Albert_von_Kölliker.html"_;"title="'coined_by_Albert_von_Kölliker">Kölliker_(1863),_originally_as_synonym_for_protoplasm''and_nucleoplasm_([''term_coined_by_Edouard_Van_Beneden.html" ;"title="Albert von Kölliker">Kölliker (1863), originally as syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morula
A morula (Latin, ''morus'': mulberry) is an early-stage embryo consisting of a solid ball of cells called blastomeres, contained in mammals, and other animals within the zona pellucida shell. The blastomeres are the daughter cells of the zygote, and when the blastomeres number from 16–32 the ball of cells is called a morula. At the 8-cell stage the blastomeres are round and only loosely adhered. With further division they begin to become flattened, and develop an inside-out polarity that optimises the cell to cell contact. In the human embryo by day four after fertilisation, the morula at about the 32–cell stage begins to take in fluid. The fluid comes about from sodium-potassium pumps (on trophoblasts) that pump sodium into the morula, drawing in water from the maternal environment to become blastocoelic fluid. Hydrostatic pressure of the fluid creates a large cavity in the morula called a blastocoel or blastocyst cavity. Embryoblast cells also known as the inner cell mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trophozoite
A trophozoite (G. ''trope'', nourishment + ''zoon'', animal) is the activated, feeding stage in the life cycle of certain protozoa such as malaria-causing ''Plasmodium falciparum'' and those of the '' Giardia'' group. (The complement of the trophozoite state is the thick-walled cyst form). Life cycle stages Trophozoite and cyst stages are shown in the life cycle of '' Balantidium coli'' the causative agent of balantidiasis. In the apicomplexan life cycle the trophozoite undergoes schizogony (asexual reproduction) and develops into a schizont which contains merozoites Apicomplexans, a group of intracellular parasites, have life cycle stages that allow them to survive the wide variety of environments they are exposed to during their complex life cycle. Each stage in the life cycle of an apicomplexan organism is .... The trophozoite life stage of '' Giardia'' colonizes and proliferates in the small intestine. Trophozoites develop during the course of the infection into cysts whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sperms
Sperm is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, which are known as spermatozoa, while some red algae and fungi produce non-motile sperm cells, known as spermatia. Flowering plants contain non-motile sperm inside pollen, while some more basal plants like ferns and some gymnosperms have motile sperm. Sperm cells form during the process known as spermatogenesis, which in amniotes ( reptiles and mammals) takes place in the seminiferous tubules of the testes. This process involves the production of several successive sperm cell precursors, starting with spermatogonia, which differentiate into spermatocytes. The spermatocytes then undergo meiosis, reducing their chromosome number by half, which produces spermatids. The spermatids then mature and, in animals, construct a tail, or flagellum, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), Disease vector, vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropreda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the Three-domain system, three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard (archaea), Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass (ecology), biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated phagotrophs. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invertebrates
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate subphylum Vertebrata. Familiar examples of invertebrates include arthropods, mollusks, annelids, echinoderms and cnidarians. The majority of animal species are invertebrates; one estimate puts the figure at 97%. Many invertebrate taxa have a greater number and variety of species than the entire subphylum of Vertebrata. Invertebrates vary widely in size, from 50 μm (0.002 in) rotifers to the 9–10 m (30–33 ft) colossal squid. Some so-called invertebrates, such as the Tunicata and Cephalochordata, are more closely related to vertebrates than to other invertebrates. This makes the invertebrates paraphyletic, so the term has little meaning in taxonomy. Etymology The word "invertebrate" comes from the Latin word ''vertebra'', whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |