|
Mochizuki-shuku
was the twenty-fifth of the sixty-nine stations of the Nakasendō. It is located in the present-day city of Saku, in Nagano Prefecture, Japan. History Located at the base of Mount Tateshina, Mochizuki has long been known for its horses. The area received its name, which roughly means "desirable moon," because it used to give horses to the Imperial Court and the shogunate on the day of the full moon on the fifteenth day of the eighth month, according to the old calendar.Shinshū no Kaidō Tabō, Nakasendō Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport, Kantō Region. Accessed July 3, 2007. Mimakigahara was located to the northeast of the post town. During the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
69 Stations Of The Nakasendō
The are the rest areas along the Nakasendō, which ran from Nihonbashi in Edo (modern-day Tokyo) to Sanjō Ōhashi in Kyoto.Yama to Keikoku Publishing (2006). Nakasendō o Aruku (Revised ed.). Osaka: Yama to Keikoku Publishing. .Nakasendō Jōhō . NEC Corporation. Accessed August 18, 2007. The route stretched approximately and was an alternate to the Tōkaidō. 
|
Motai-shuku
was a mid-station along the Nakasendō in Edo period Japan. It was in between the post stations of Mochizuki-shuku and Ashida-shuku. It is located in the present-day town of Saku, Nagano Prefecture, Japan. Neighboring post towns ;Nakasendō :Mochizuki-shuku - Motai-shuku - Ashida-shuku was the twenty-sixth of the sixty-nine stations of the Nakasendō. It is located in the present-day town of Tateshina, in the Kitasaku District of Nagano Prefecture, Japan. History Ashida-shuku was formed in 1601, during the Edo period, when the ... References {{coord missing, Nagano Prefecture Stations of the Nakasendo in Nagano Prefecture Stations of the Nakasendō ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashida-shuku
was the twenty-sixth of the sixty-nine stations of the Nakasendō. It is located in the present-day town of Tateshina, in the Kitasaku District of Nagano Prefecture, Japan. History Ashida-shuku was formed in 1601, during the Edo period, when the Nakasendō's route was altered and the government ordered creation of new post towns.Kyū-Ashida-shuku . Town of Tateshina. Accessed August 2, 2007. It was located near the eastern entrance to the Kasadori Pass and was well known for its silk production. Neighboring post towns ;Nakasendō : - Ashida-shuku - |
Ai No Shuku
{{nihongo, Ai no Shuku, 間の宿, mid-station were unofficial post stations along historical routes in Japan. These post stations formed organically along routes (such as the Tōkaidō and the Nakasendō) when the distance between two places was too far or when there were difficult passes nearby. Because they were not officially designated rest areas, travelers along the roads were not allowed to stay in these post stations. Sometimes the Japanese is shortened to 間宿. Notable ''ai no shuku'' Tōkaidō :*Ninomiya-shuku (二宮宿) (between Ōiso-juku and Odawara-juku) ( Ninomiya, Kanagawa Prefecture) :*Hatake-shuku (畑宿) (between Odawara-juku and Hakone-juku) (Hakone, Kanagawa Prefecture) :*Iwabuchi-shuku (岩淵宿) (between Yoshiwara-juku and Kanbara-juku) ( Fujikawa, Shizuoka Prefecture) :*Kikugawa-shuku (菊川宿) (between Kanaya-juku and Nissaka-shuku) ( Shimada, Shizuoka Prefecture) :*Moto-juku (本宿) (between Akasaka-juku and Fujikawa-shuku) ( Okazaki, Aichi Pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yawata-shuku
was the twenty-fourth of the sixty-nine stations of the Nakasendō. It is located in the present-day city of Saku, in Nagano Prefecture, Japan. History Yawata-shuku is located on the west bank of the Shinano River, just across from Shionada-shuku, the preceding post town. Though these two post towns are located not much more than 500 meters away, Yawata-shuku was able to develop during the Keichō era in the early Edo period. It was a comparatively small post town,Yawata-juku JTB Corporation. Accessed August 3, 2007. but its prosperity came from it serving as a rest area at times when the Shinano River could not be crossed and as a distribution center for rice. Neighboring post towns ;Nakasendō : |
History Of Japan
The first human inhabitants of the Japanese archipelago have been traced to prehistoric times around 30,000 BC. The Jōmon period, named after its cord-marked pottery, was followed by the Yayoi period in the first millennium BC when new inventions were introduced from Asia. During this period, the first known written reference to Japan was recorded in the Chinese ''Book of Han'' in the first century AD. Around the 3rd century BC, the Yayoi people from the continent immigrated to the Japanese archipelago and introduced iron technology and agricultural civilization. Because they had an agricultural civilization, the population of the Yayoi began to grow rapidly and ultimately overwhelmed the Jōmon people, natives of the Japanese archipelago who were hunter-gatherers. Between the fourth to ninth century, Japan's many kingdoms and tribes gradually came to be unified under a centralized government, nominally controlled by the Emperor of Japan. The imperial dynasty established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamakura Period
The is a period of Japanese history that marks the governance by the Kamakura shogunate, officially established in 1192 in Kamakura by the first ''shōgun'' Minamoto no Yoritomo after the conclusion of the Genpei War, which saw the struggle between the Taira and Minamoto clans. The period is known for the emergence of the samurai, the warrior caste, and for the establishment of feudalism in Japan. During the early Kamakura period, the shogunate continued warfare against the Northern Fujiwara which was only defeated in 1189. Then, the authority to the Kamakura rulers waned in the 1190s and power was transferred to the powerful Hōjō clan in the early 13th century with the head of the clan as regent (Shikken) under the shogun which became a powerless figurehead. The later Kamakura period saw the invasions of the Mongols in 1274 and again in 1281. To reduce the amount of chaos, the Hōjō rulers decided to decentralize power by allowing two imperial lines – Northern and Southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heian Period
The is the last division of classical Japanese history, running from 794 to 1185. It followed the Nara period, beginning when the 50th emperor, Emperor Kanmu, moved the capital of Japan to Heian-kyō (modern Kyoto). means "peace" in Japanese. It is a period in Japanese history when the Chinese influences were in decline and the national culture matured. The Heian period is also considered the peak of the Japanese imperial court and noted for its art, especially poetry and literature. Two types of Japanese script emerged, including katakana, a phonetic script which was abbreviated into hiragana, a cursive alphabet with a unique writing method distinctive to Japan. This gave rise to Japan's famous vernacular literature, with many of its texts written by court women who were not as educated in Chinese compared to their male counterparts. Although the Imperial House of Japan had power on the surface, the real power was in the hands of the Fujiwara clan, a powerful aristocratic f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
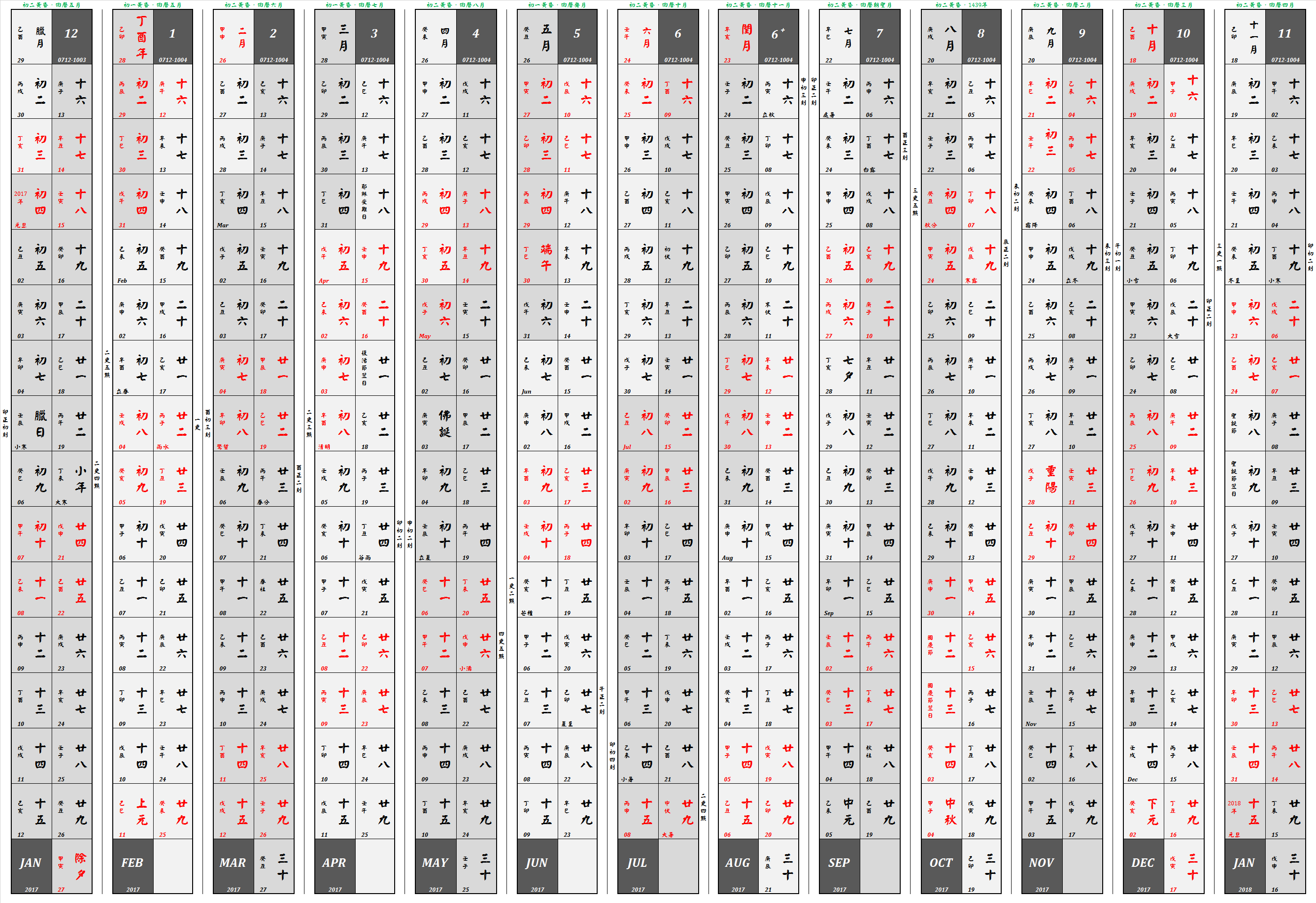
Chinese Calendar
The traditional Chinese calendar (also known as the Agricultural Calendar ��曆; 农历; ''Nónglì''; 'farming calendar' Former Calendar ��曆; 旧历; ''Jiùlì'' Traditional Calendar ��曆; 老历; ''Lǎolì'', is a lunisolar calendar which identifies years, months, and days according to astronomical phenomena. In China, it is defined by the Chinese national standard GB/T 33661–2017, "Calculation and Promulgation of the Chinese Calendar", issued by the Standardization Administration of China on May 12, 2017. Although modern-day China uses the Gregorian calendar, the traditional Chinese calendar governs holidays, such as the Chinese New Year and Lantern Festival, in both China and overseas Chinese communities. It also provides the traditional Chinese nomenclature of dates within a year which people use to select auspicious days for weddings, funerals, moving or starting a business. The evening state-run news program ''Xinwen Lianbo'' in the P.R.C. continues to anno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogunate
, officially , was the title of the military dictators of Japan during most of the period spanning from 1185 to 1868. Nominally appointed by the Emperor, shoguns were usually the de facto rulers of the country, though during part of the Kamakura period, shoguns were themselves figureheads, with real power in hands of the Shikken of the Hōjō clan. The office of shogun was in practice hereditary, though over the course of the history of Japan several different clans held the position. The title was originally held by military commanders during Heian period in the eighth and ninth centuries. When Minamoto no Yoritomo gained political ascendency over Japan in 1185, the title was revived to regularize his position, making him the first shogun in the usually understood sense. The shogun's officials were collectively referred to as the ; they were the ones who carried out the actual duties of administration, while the Imperial court retained only nominal authority.Beasley, William G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |