|
Miller Oilfield
The Miller oilfield is a deep reservoir under the North Sea, 240 kilometres north-east of Peterhead in UKCS Blocks 16/7b and 16/8b. It was discovered in 1983 by BP in a water depth of 100 metres. Production from Miller field started in June 1992, and plateau production was from late 1992 to 1997 at rates of up to of oil and of gas per day at standard conditions. Miller produced some of oil during its lifetime. The field is named after Hugh Miller who contributed to Scottish geology in the early nineteenth century. The Miller field reached the end of its economic oil and gas producing life in 2007 when Cessation of Production (CoP) approval was received from the UK government. Preparations are currently under way to decommission the Miller platform, but the oil and gas pipelines will be preserved for future opportunities. On 1 April 2009, sixteen people were killed in the crash of a helicopter carrying workers from the Miller field back to Aberdeen. Geology The reservo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the northeast and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. It also contains more than 790 islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. Most of the population, including the capital Edinburgh, is concentrated in the Central Belt—the plain between the Scottish Highlands and the Southern Uplands—in the Scottish Lowlands. Scotland is divided into 32 administrative subdivisions or local authorities, known as council areas. Glasgow City is the largest council area in terms of population, with Highland being the largest in terms of area. Limited self-governing power, covering matters such as education, social services and roads and transportation, is devolved from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
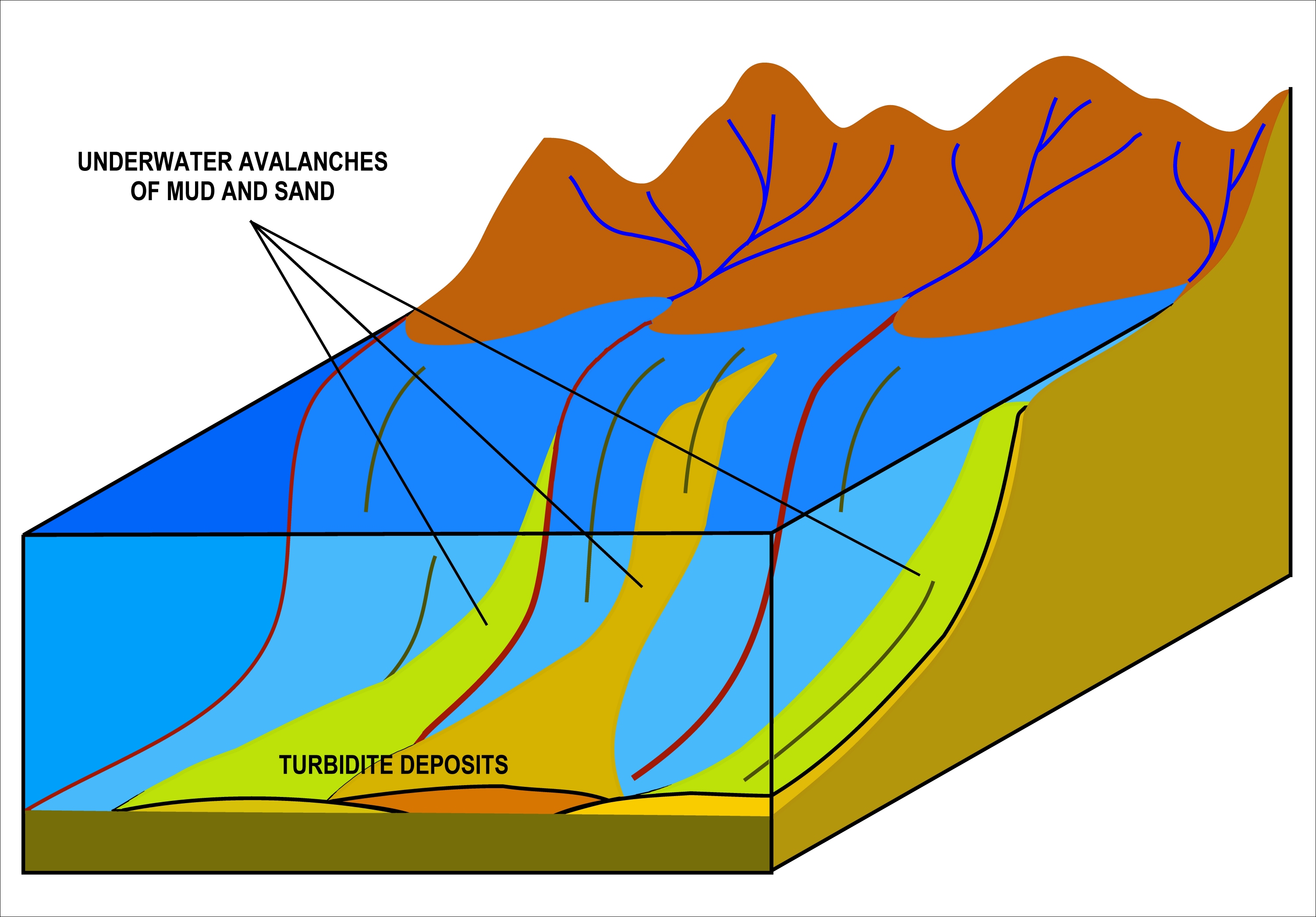
Turbidite
A turbidite is the geologic deposit of a turbidity current, which is a type of amalgamation of fluidal and sediment gravity flow responsible for distributing vast amounts of clastic sediment into the deep ocean. Sequencing Turbidites were first properly described by Arnold H. Bouma (1962), who studied deepwater sediments and recognized particular "fining-up intervals" within deep water, fine-grained shales, which were anomalous because they started at pebble conglomerates and terminated in shales. This was anomalous because within the deep ocean it had historically been assumed that there was no mechanism by which tractional flow could carry and deposit coarse-grained sediments into the abyssal depths. Bouma cycles begin with an erosional contact of a coarse lower bed of pebble to granule conglomerate in a sandy matrix, and grade up through coarse then medium plane parallel sandstone; through cross-bedded sandstone; rippled cross-bedded sand/silty sand, and finally la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bond Offshore Helicopters
Offshore Helicopter Services (OHS) (known as Bond Offshore Helicopters until April 2016) is a British helicopter operator, specialising in providing offshore helicopter transportation services to North Sea and Irish Sea oil and gas platforms. CHC operates a mixed fleet of helicopters on behalf of more than 10 major customers. Annually they transport around 200,000 men and women to and from offshore oil and gas platforms from bases at Aberdeen, Norwich and Sumburgh airports. Babcock also operates two specialist Search and Rescue (SAR) aircraft to support the Oil and Gas industry. These two AW139 helicopters are based at Aberdeen airport and equipped with specialist search and rescue equipment and provide 24-hour SAR coverage for the central North Sea. Bond Offshore Helicopters became a Babcock International Group company when Babcock acquired the Avincis group in May 2014. In September 2021, Babcock sold its oil and gas aviation business to CHC Group. History David Bond (1920 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of Energy And Climate Change
The Department of Energy and Climate Change (DECC) was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom created on 3 October 2008, by Prime Minister Gordon Brown to take over some of the functions related to energy of the Department for Business, Enterprise and Regulatory Reform, and those relating to climate change of the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs. It was led at time of closure by the Secretary of State for Energy and Climate Change, Amber Rudd MP. Following Theresa May's appointment as Prime Minister in July 2016, the department was disbanded and merged with the Department for Business, Innovation and Skills, to form the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy under Greg Clark MP. The department released a major White Paper in July 2009, setting out its purpose and plans. The majority of DECC's budget was spent on managing the historic nuclear sites in the United Kingdom, in 2012/13 this being 69% of its budget spent through the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enhanced Oil Recovery
Enhanced oil recovery (abbreviated EOR), also called tertiary recovery, is the extraction of crude oil from an oil field that cannot be extracted otherwise. EOR can extract 30% to 60% or more of a reservoir's oil, compared to 20% to 40% using primary and secondary recovery. According to the US Department of Energy, carbon dioxide and water are injected along with one of three EOR techniques: thermal injection, gas injection, and chemical injection. More advanced, speculative EOR techniques are sometimes called quaternary recovery. Methods There are three primary techniques of EOR: gas injection, thermal injection, and chemical injection. Gas injection, which uses gases such as natural gas, nitrogen, or carbon dioxide (CO2), accounts for nearly 60 percent of EOR production in the United States. Thermal injection, which involves the introduction of heat, accounts for 40 percent of EOR production in the United States, with most of it occurring in California. Chemical injection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forties Pipeline System
The Forties pipeline system (FPS) is a major pipeline transport network in the North Sea. It is owned and operated by Ineos and carries 30% of the UK's oil, or about of oil per day, to shore. It carries liquids production from 85 fields in the North Sea and several Norwegian fields on behalf of around 40 companies. The system has a capacity of 575,000 barrels of oil a day. FPS consists of a pipeline originating at APA Corporation's Forties Charlie platform. The pipeline carries crude oil , routing through the Forties Unity riser platform, to the terminal at Cruden Bay. From there unstabilised crude is co-mingled with natural gas condensate from the St Fergus terminal and pumped to the processing facility at Kinneil, Grangemouth. The onshore pipeline has three intermediate pumping stations at Netherley, Brechin and Balbeggie. History The original 32-inch pipeline was opened in 1975 to transport oil from the Forties Oil Field, the UK’s first major offshore oil field. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil In Place
Oil in place (OIP) (not to be confused with original oil-in-place (OOIP)) is a specialist term in petroleum geology that refers to the total oil content of an oil reservoir. As this quantity cannot be measured directly, it has to be estimated from other parameters measured prior to drilling or after production has begun. Prior to oil production from a new reservoir, ''volumetric'' methods are used to estimate oil-in-place. A series of test drills are used to map the rock conditions at and around the drilling site and to estimate the size of the oil-bearing rock field. The oil in place is calculated as the product of the volume of porous oil-bearing rock, the porosity of the rock, and its saturation. Correction factors have to be applied for the difference between the volume of the same mass of oil in the reservoir to its volume when brought to the surface, which is caused by the different physical conditions (temperature, pressure) there. Oil-in-place is also known as stock tank o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kimmeridge Clay
The Kimmeridge Clay is a sedimentary deposit of fossiliferous marine clay which is of Late Jurassic to lowermost Cretaceous age and occurs in southern and eastern England and in the North Sea. This rock formation is the major source rock for North Sea oil. The fossil fauna of the Kimmeridge Clay includes turtles, crocodiles, sauropods, plesiosaurs, pliosaurs and ichthyosaurs, as well as a number of invertebrate species. Description Kimmeridge Clay is named after the village of Kimmeridge on the Dorset coast of England, where it is well exposed and forms part of the Jurassic Coast World Heritage Site. Onshore, it is of Late Jurassic (Kimmeridgian) age and outcrops across England, in a band stretching from Dorset in the south-west, north-east to North Yorkshire. Offshore, it extends into the Lower Cretaceous ( Berriasian Stage) and it is found throughout the Southern, Central and Northern North Sea. The foundations of the Humber Bridge on the southern (Barton) side of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graben
In geology, a graben () is a depressed block of the crust of a planet or moon, bordered by parallel normal faults. Etymology ''Graben'' is a loan word from German, meaning 'ditch' or 'trench'. The word was first used in the geologic context by Eduard Suess in 1883. The plural form is either ''graben'' or ''grabens''. Formation A graben is a valley with a distinct escarpment on each side caused by the displacement of a block of land downward. Graben often occur side by side with horsts. Horst and graben structures indicate tensional forces and crustal stretching. Graben are produced from parallel normal faults, where the displacement of the hanging wall is downward, while that of the footwall is upward. The faults typically dip toward the center of the graben from both sides. Horsts are parallel blocks that remain between graben; the bounding faults of a horst typically dip away from the center line of the horst. Single or multiple graben can produce a rift valley. Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brae Formation
:''"Brae" is also the Lowland Scots language word for the slope or brow of a hill.'' Brae (Old Norse: ''Breiðeið'', meaning "the wide isthmus") is a village on the island of Mainland in Shetland, Scotland, United Kingdom. Description Brae was historically a fishing village, but with the construction of the nearby Sullom Voe Oil Terminal in the 1970s it grew rapidly, merging with the nearby village of Northbrae. It is located at the northern end of Busta Voe, on the narrow isthmus that joins Northmavine to the rest of the Mainland. The village stages its own Up Helly Aa. The A970 which connects Lerwick to Northmavine forms the main street of Brae. Brae's police and fire stations, schools, and NHS clinic service much of the northern part of the Mainland. Etymology ''Brae'' is the Lowland Scots word for the slope or brow of a hill. The word 'Brae' in Shetland dialect has a different meaning; it may come from the Old Norse word ''breiðr'' meaning broad. The village may take it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Sea in the north. It is more than long and wide, covering . It hosts key north European shipping lanes and is a major fishery. The coast is a popular destination for recreation and tourism in bordering countries, and a rich source of energy resources, including wind and wave power. The North Sea has featured prominently in geopolitical and military affairs, particularly in Northern Europe, from the Middle Ages to the modern era. It was also important globally through the power northern Europeans projected worldwide during much of the Middle Ages and into the modern era. The North Sea was the centre of the Vikings' rise. The Hanseatic League, the Dutch Republic, and the British each sought to gain command of the North Sea and access ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic, Mesozoic Era and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic magmatic province, Central Atlantic Magmatic Province. The beginning of the Toarcian Stage started around 183 million years ago and is marked by an extinction event associated with widespread Anoxic event, oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated temperatures likely caused by the eruption of the Karoo-Ferrar, Karoo-Ferrar large igneous provinces. The end of the Jurassic, however, has no clear boundary with the Cretaceous and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |