|
Micromyrtus Stenocalyx
''Micromyrtus stenocalyx'' is a species of flowering plant in the family Myrtaceae and is endemic to the inland of Western Australia. It is a straggly or widely spreading shrub with oblong or club-shaped leaves pressed against the stem, and cream-coloured to yellow flowers with 10 stamens. Description ''Micromyrtus stenocalyx'' is a straggly or widely spreading shrub that typically grows to a height of . Its leaves are oblong or club-shaped and more or less pressed against the stem, long on a petiole about long with a few oil glands on the lower surface. The flowers are arranged singly in leaf axils and are long on a peduncle about long. The floral tube is cylindrical and about long, the sepals less than long and wide and the petals are cream-coloured to yellow, about long with several oil glands. Flowering has been recorded July to November. Taxonomy This species was first formally described in 1876 by Ferdinand von Mueller who gave it the name ''Thryptomene stenocalyx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myrtaceae
Myrtaceae, the myrtle family, is a family of dicotyledonous plants placed within the order Myrtales. Myrtle, pōhutukawa, bay rum tree, clove, guava, acca (feijoa), allspice, and eucalyptus are some notable members of this group. All species are woody, contain essential oils, and have flower parts in multiples of four or five. The leaves are evergreen, alternate to mostly opposite, simple, and usually entire (i.e., without a toothed margin). The flowers have a base number of five petals, though in several genera, the petals are minute or absent. The stamens are usually very conspicuous, brightly coloured, and numerous. Evolutionary history Scientists hypothesize that the family Myrtaceae arose between 60 and 56 million years ago (Mya) during the Paleocene era. Pollen fossils have been sourced to the ancient supercontinent Gondwana. The breakup of Gondwana during the Cretaceous period (145 to 66 Mya) geographically isolated disjunct taxa and allowed for rapid speciation; i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Green (botanist)
John William Green (born 10 July 1930) is an Australian botanist. Career Green began his botanical career in 1954 as assistant botanist in the Western Australian Herbarium. He remained in that position until 1958, in his final year serving as botanical adviser to phytochemical surveys in the southwest Australia, southwest. He then took up a position at the University of New England, Australia, University of New England at Armidale, New South Wales until 1963, when he moved to Canberra, initially as an academic, and after 1966 as a researcher at the Forest Research Institute (Australia), Forest Research Institute. In 1970 he moved to Ontario, Canada, taking up a post as professor at the Laurentian University. In 1975, Green returned to Australia, taking on the post of curator to the Western Australian Herbarium. He held that position until 1987. During this time he oversaw the introduction of database systems for management of collections. Plant taxa publications Green has pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Western Australia
The flora of Western Australia comprises 10,551 published native vascular plant species and a further 1,131 unpublished species. They occur within 1,543 genera from 211 families; there are also 1,317 naturalised alien or invasive plant species more commonly known as weeds. There are an estimated 150,000 cryptogam species or nonvascular plants which include lichens, and fungi although only 1,786 species have been published, with 948 algae and 672 lichen the majority. History Indigenous Australians have a long history with the flora of Western Australia. They have for over 50,000 years obtained detailed information on most plants. The information includes its uses as sources for food, shelter, tools and medicine. As Indigenous Australians passed the knowledge along orally or by example, most of this information has been lost, along many of the names they gave the flora. It was not until Europeans started to explore Western Australia that systematic written details of the flora comme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of Biodiversity, Conservation And Attractions (Western Australia)
The Department of Biodiversity, Conservation and Attractions (DBCA) is the Government of Western Australia, Western Australian government department responsible for managing lands and waters described in the ''Conservation and Land Management Act 1984'', the ''Rottnest Island Authority Act 1987'', the ''Swan and Canning Rivers Management Act 2006'', the ''Botanic Gardens and Parks Authority Act 1998'', and the ''Zoological Parks Authority Act 2001'', and implementing the state's conservation and environment legislation and regulations. The Department reports to the Minister for Environment and the Minister for Tourism. DBCA was formed on 1 July 2017 by the merger of the Department of Parks and Wildlife (Western Australia), Department of Parks and Wildlife (DPaW), the Botanic Gardens and Parks Authority, the Zoological Parks Authority and the Rottnest Island Authority. The former DPaW became the Parks and Wildlife Service. Status Parks and Wildlife Service The Formerly the Depar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murchison Bioregion
The Murchison is an Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia, interim Australian bioregion located within the Mid West region of Western Australia, Mid West of Western Australia. The bioregion is loosely related to the catchment area of the Murchison River, Western Australia, Murchison River and has an area of . Traditionally the region is known as ''The Murchison''. Geography The landscape is characterised by low hills and mesas, separated by colluvium flats and alluvial plains. The western portion of the bioregion is drained by the upper Murchison River (Western Australia), Murchison and Wooramel River, Wooramel rivers, which drain westwards towards the coast.Anthony Desmond, Mark Cowan and Alanna Chant (2001). "Murchison 2 (MUR2 – Western Murchison subregion)", in ''A Biodiversity Audit of Western Australia’s 53 Biogeographical Subregions in 2002''. The Department of Conservation and Land Management, Government of Western Australia, November 2001/ref> Toget ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Victoria Desert
The Great Victoria Desert is a sparsely populated desert ecoregion and interim Australian bioregion in Western Australia and South Australia. History In 1875, British-born Australian explorer Ernest Giles became the first European to cross the desert. He named the desert after the then-reigning monarch, Queen Victoria. In 1891, David Lindsey's expedition traveled across this area from north to south. Frank Hann was looking for gold in this area between 1903 and 1908. Len Beadell explored the area in the 1960s. Location and description The Great Victoria is the largest desert in Australia, and consists of many small sandhills, grassland plains, areas with a closely packed surface of pebbles (called desert pavement or gibber plains), and salt lakes. It is over wide (from west to east) and covers an area of from the Eastern Goldfields region of Western Australia to the Gawler Ranges in South Australia. The Western Australian mulga shrublands ecoregion lies to the west, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
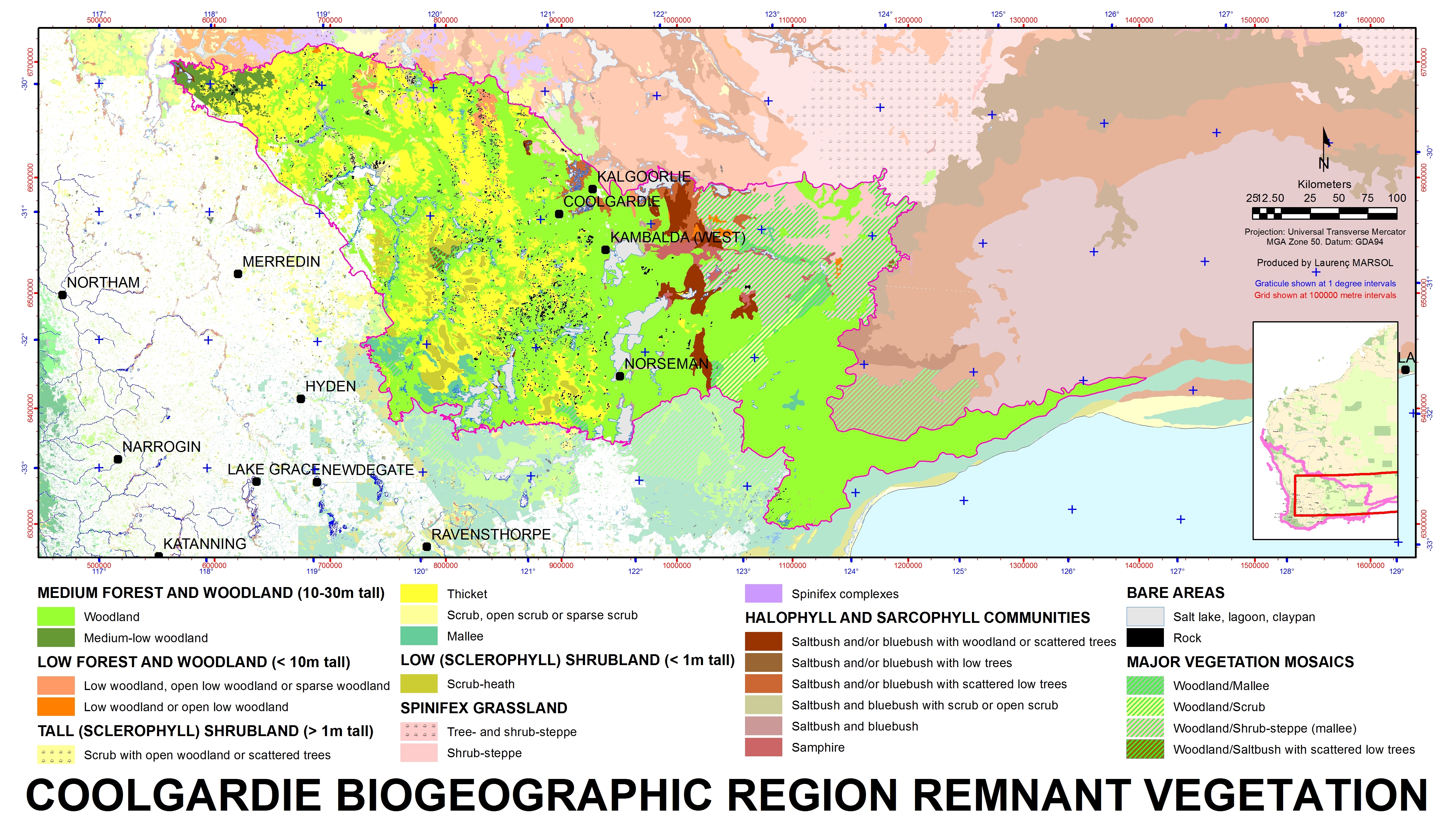
Coolgardie Bioregion
Coolgardie is an Australian bioregion consisting of an area of low hills and plains of infertile sandy soil in Western Australia. It has an area of . It includes much of the Great Western Woodlands. Location and description This is a transition zone between the Mediterranean climate of Australia's south-west coast and the country's dry interior. The poor soil makes it unsuitable for agriculture but Coolgardie has been a gold and nickel mining area. It is bounded on the north by the arid Murchison bioregion, characterised by open Mulga woodlands and steppe. The low shrublands of the arid Nullarbor Plain lie to the east. The Mallee bioregion adjoins Coolgardie on the south. The Avon Wheatbelt bioregion is to the west. The Coolgardie bioregion, together with the coastal Hampton bioregion to the southeast, constitute the Coolgardie woodlands ecoregion defined by the World Wildlife Fund. Flora and fauna The low hills are home to woodland of endemic species of eucalyptus whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binomial Nomenclature
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name (which may be shortened to just "binomial"), a binomen, name or a scientific name; more informally it is also historically called a Latin name. The first part of the name – the '' generic name'' – identifies the genus to which the species belongs, whereas the second part – the specific name or specific epithet – distinguishes the species within the genus. For example, modern humans belong to the genus ''Homo'' and within this genus to the species ''Homo sapiens''. ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' is likely the most widely known binomial. The ''formal'' introduction of this system of naming species is credit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuytsia (journal)
''Nuytsia'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Western Australian Herbarium. It publishes papers on systematic botany, giving preference to papers related to the flora of Western Australia. Nearly twenty percent of Western Australia's plant taxa have been published in ''Nuytsia''. The journal was established in 1970 and has appeared irregularly since. The editor-in-chief is Kevin Thiele. ''Nuytsia'' is named after the monospecific genus ''Nuytsia'', whose only species is '' Nuytsia floribunda'', the Western Australian Christmas tree. Occasionally, the journal has published special issues, such as an issue in 2007 substantially expanding described species from Western Australia. Publication details The record of the issues published is found at the ''FloraBase ''FloraBase'' is a public access web-based database of the flora of Western Australia. It provides authoritative scientific information on 12,978 taxa, including descriptions, maps, images, conservati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micromyrtus
''Micromyrtus'' is a genus of shrubs, in the family Myrtaceae, described as a genus in 1865. The entire genus is endemic to Australia. Species The following is a list of species accepted by the Australian Plant Census as at March 2020: * '' Micromyrtus acuta'' Rye * '' Micromyrtus albicans'' A.R.Bean * '' Micromyrtus arenicola'' Rye * '' Micromyrtus barbata'' J.W.Green * '' Micromyrtus blakelyi'' J.W.Green * '' Micromyrtus capricornia'' A.R.Bean * '' Micromyrtus carinata'' A.R. Bean * '' Micromyrtus chrysodema'' Rye * '' Micromyrtus ciliata'' (Sm.) Druce - fringed heath-myrtle * '' Micromyrtus clavata'' J.W.Green ex Rye * '' Micromyrtus collina'' Rye * '' Micromyrtus delicata'' A.R.Bean * '' Micromyrtus elobata'' (F.Muell.) Benth. ** ''Micromyrtus elobata'' (F.Muell.) Benth. subsp. ''elobata'' ** ''Micromyrtus elobata'' subsp. ''scopula'' Rye * '' Micromyrtus erichsenii'' Hemsl. * '' Micromyrtus fimbrisepala'' J.W.Green * '' Micromyrtus flaviflora'' (F.Muell.) J.M.Blac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jess Young
Jess Young (Jesse) (1851–1909) was an English traveller. He is best known as an explorer who accompanied Ernest Giles during his fourth expedition, making some important botanical collections along the way. Life He was a younger son of Richard Young of Wisbech, England. He attended the Abbey Park School of David James Smeaton in St Andrews, Fifeshire, Scotland, as Jesse Young. He accompanied Richard Bourke, 6th Earl of Mayo on his 1872 inspection of Port Blair in the Andaman Islands, where Lord Mayo was assassinated. In May 1875 Giles, in listing the members of his expedition party, referred to him as "Mr Jess Young, a young friend of Sir Thomas Elder, lately arrived from England." Giles's party left Beltana, South Australia on 6 May, and arrived in Perth, Western Australia on 13 November. During the expedition, Young collected the specimens of a number of new plant species, including ''Eucalyptus salubris'', ''Eucalyptus youngiana'' and '' Eremophila youngii'', all from the vic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_W_IMG_2431.jpg)



.jpg)