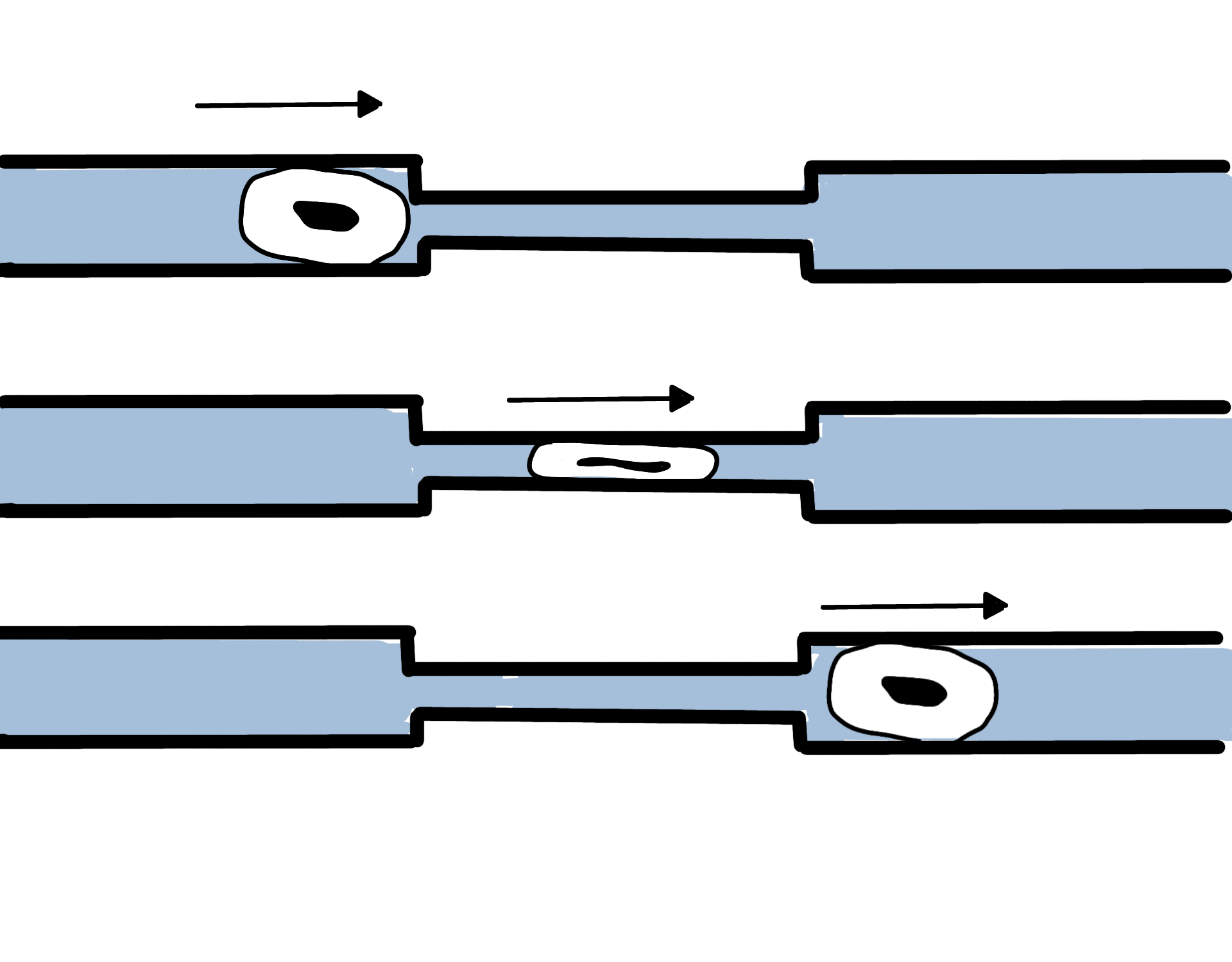
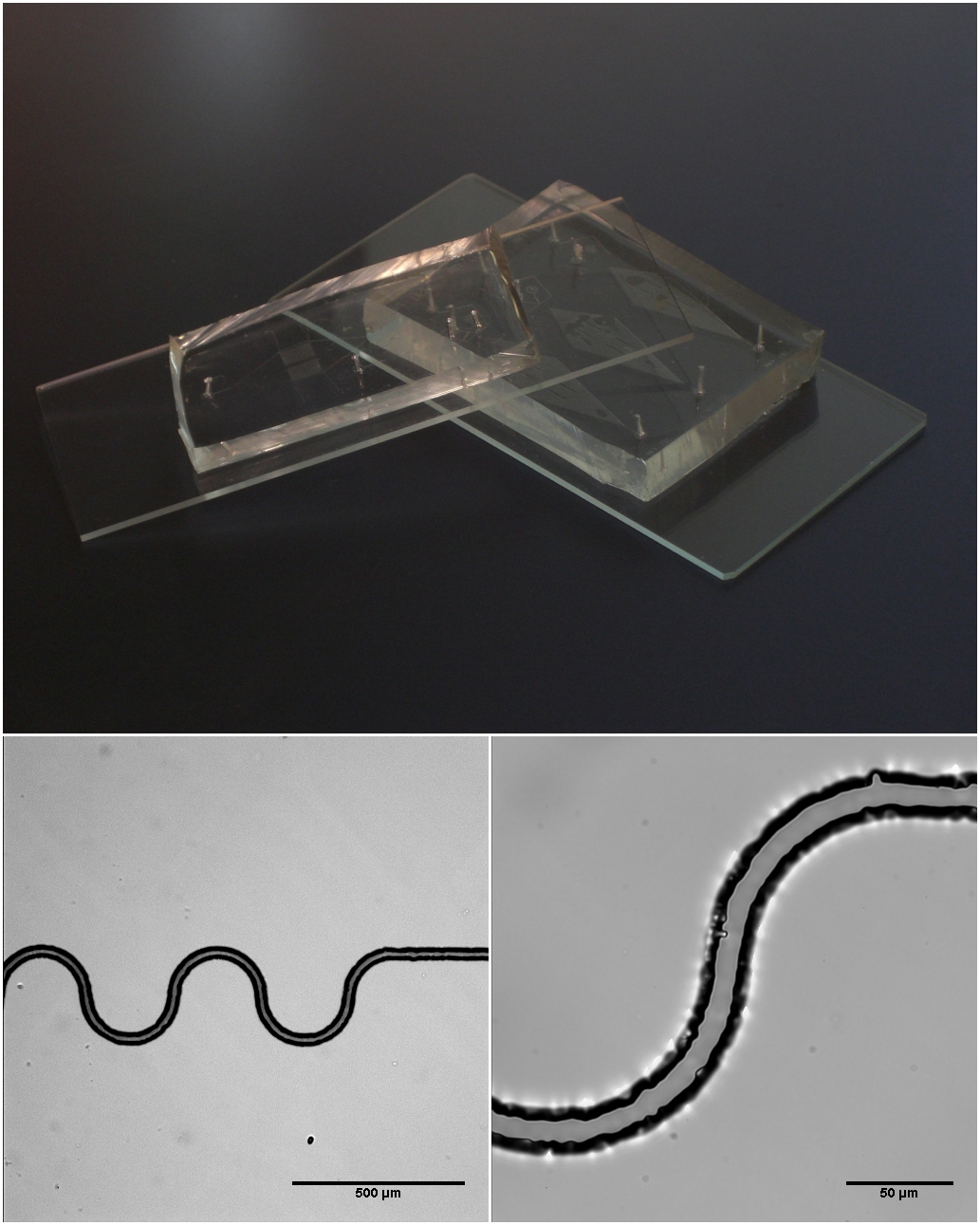
|
Microchannel (microtechnology)
Microchannel in microtechnology is a channel with a hydraulic diameter below 1 mm, usually 1–99 μm. Microchannels are used in fluid control (see Microfluidics), heat transfer (see Micro heat exchanger) and cell migration observation. They are more efficient than their 'marco' counterparts, because of a high surface-area to volume ratio yet pose a multitude of challenges due to their small size. Materials Different types of materials are required for the different uses of microchannels. These are the three main categories. Polymeric and glass substrates polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is used as a solution to a wide range of microfluidic devices due to its low cost and easier fabricating methods. Silicon elastomers can be used for situations in which elasticity and deformation is necessary. Metallic substrates Metallic substrates are often chosen for their advantageous metallic properties, such as withstanding high temperatures and transferring heat faster. They can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell In A Microchannel
Cell most often refers to: * Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life Cell may also refer to: Locations * Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery with only a few monks or nuns * Prison cell, a room used to hold people in prisons Groups of people * Cell, a group of people in a cell group, a form of Christian church organization * Cell, a unit of a clandestine cell system, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization * Cellular organizational structure, such as in business management Science, mathematics, and technology Computing and telecommunications * Cell (EDA), a term used in an electronic circuit design schematics * Cell (microprocessor), a microprocessor architecture developed by Sony, Toshiba, and IBM * Memory cell (computing), the basic unit of (volatile or non-volatile) computer memory * Cell, a unit in a Table (database), database table or spreadsheet, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microtechnology
Microtechnology deals with technology whose features have dimensions of the order of one micrometre (one millionth of a metre, or 10−6 metre, or 1μm). It focuses on physical and chemical processes as well as the production or manipulation of structures with one-micrometre magnitude. Development Around 1970, scientists learned that by arraying large numbers of microscopic transistors on a single chip, microelectronic circuits could be built that dramatically improved performance, functionality, and reliability, all while reducing cost and increasing volume. This development led to the Information Revolution. More recently, scientists have learned that not only electrical devices, but also mechanical devices, may be miniaturized and batch-fabricated, promising the same benefits to the mechanical world as integrated circuit technology has given to the electrical world. While electronics now provide the ‘brains’ for today's advanced systems and products, micro-mechanical devic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydraulic Diameter
The hydraulic diameter, , is a commonly used term when handling flow in non-circular tubes and channels. Using this term, one can calculate many things in the same way as for a round tube. When the cross-section is uniform along the tube or channel length, it is defined as : D_\text = \frac, where : is the cross-sectional area of the flow, : is the wetted perimeter of the cross-section. More intuitively, the hydraulic diameter can be understood as a function of the hydraulic radius , which is defined as the cross-sectional area of the channel divided by the wetted perimeter. Here, the wetted perimeter includes all surfaces acted upon by shear stress from the fluid. : R_\text = \frac, : D_\text = 4R_\text, Note that for the case of a circular pipe, : D_\text =\frac=2R The need for the hydraulic diameter arises due to the use of a single dimension in case of dimensionless quantity such as Reynolds number, which prefer a single variable for flow analysis rather than the set of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microfluidics
Microfluidics refers to the behavior, precise control, and manipulation of fluids that are geometrically constrained to a small scale (typically sub-millimeter) at which surface forces dominate volumetric forces. It is a multidisciplinary field that involves engineering, physics, chemistry, biochemistry, nanotechnology, and biotechnology. It has practical applications in the design of systems that process low volumes of fluids to achieve multiplexing, automation, and high-throughput screening. Microfluidics emerged in the beginning of the 1980s and is used in the development of inkjet printheads, DNA chips, lab-on-a-chip technology, micro-propulsion, and micro-thermal technologies. Typically, micro means one of the following features: * Small volumes (μL, nL, pL, fL) * Small size * Low energy consumption * Microdomain effects Typically microfluidic systems transport, mix, separate, or otherwise process fluids. Various applications rely on passive fluid control using capillary fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micro Heat Exchanger
Micro heat exchangers, Micro-scale heat exchangers, or microstructured heat exchangers are heat exchangers in which (at least one) fluid flows in lateral confinements with typical dimensions below 1 mm. The most typical such confinement are microchannel (microtechnology), microchannels, which are channels with a hydraulic diameter below 1 mm. Microchannel heat exchangers can be made from metal or ceramic. Microchannel heat exchangers can be used for many applications including: * high-performance aircraft gas turbine engines * heat pumps * Microprocessor and microchip cooling * air conditioning Background Investigation of microscale thermal devices is motivated by the single phase internal flow correlation for convective heat transfer: :h=\mathit_c \frac Where h is the heat transfer coefficient, \mathit_c is the Nusselt number, k is the thermal conductivity of the fluid and d is the hydraulic diameter of the channel or duct. In internal laminar flows, the Nusselt number b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Migration
Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. Tissue formation during embryonic development, wound healing and immune responses all require the orchestrated movement of cells in particular directions to specific locations. Cells often migrate in response to specific external signals, including chemical signals and mechanical signals. Errors during this process have serious consequences, including intellectual disability, vascular disease, tumor formation and metastasis. An understanding of the mechanism by which cells migrate may lead to the development of novel therapeutic strategies for controlling, for example, invasive tumour cells. Due to the highly viscous environment (low Reynolds number), cells need to continuously produce forces in order to move. Cells achieve active movement by very different mechanisms. Many less complex prokaryotic organisms (and sperm cells) use flagella or cilia to propel themselves. Eukaryot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poly(methyl Methacrylate)
Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) belongs to a group of materials called engineering plastics. It is a transparent thermoplastic. PMMA is also known as acrylic, acrylic glass, as well as by the trade names and brands Crylux, Plexiglas, Acrylite, Astariglas, Lucite, Perclax, and Perspex, among several others ( see below). This plastic is often used in sheet form as a lightweight or shatter-resistant alternative to glass. It can also be used as a casting resin, in inks and coatings, and for many other purposes. Although not a type of familiar silica-based glass, the substance, like many thermoplastics, is often technically classified as a type of glass, in that it is a non-crystalline vitreous substance—hence its occasional historic designation as ''acrylic glass''. Chemically, it is the synthetic polymer of methyl methacrylate. It was developed in 1928 in several different laboratories by many chemists, such as William Chalmers, Otto Röhm, and Walter Bauer, and first brought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicone Rubber
Silicone rubber is an elastomer (rubber-like material) composed of silicone—itself a polymer—containing silicon together with carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Silicone rubbers are widely used in industry, and there are multiple formulations. Silicone rubbers are often one- or two-part polymers, and may contain fillers to improve properties or reduce cost. Silicone rubber is generally non-reactive, stable, and resistant to extreme environments and temperatures from while still maintaining its useful properties. Due to these properties and its ease of manufacturing and shaping, silicone rubber can be found in a wide variety of products, including voltage line insulators; automotive applications; cooking, baking, and food storage products; apparel such as undergarments, sportswear, and footwear; electronics; medical devices and implants; and in home repair and hardware, in products such as silicone sealants. Curing In its uncured state, silicone rubber is a highly adhesive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Properties Of Metals, Metalloids And Nonmetals
can be broadly divided into metals, metalloids and nonmetals according to their shared physical and chemical properties. All metals have a shiny appearance (at least when freshly polished); are good conductors of heat and electricity; form alloys with other metals; and have at least one basic oxide. Metalloids are metallic-looking brittle solids that are either semiconductors or exist in semiconducting forms, and have amphoteric or weakly acidic oxides. Typical nonmetals have a dull, coloured or colourless appearance; are brittle when solid; are poor conductors of heat and electricity; and have acidic oxides. Most or some elements in each category share a range of other properties; a few elements have properties that are either anomalous given their category, or otherwise extraordinary. Properties Metals Metals appear lustrous (beneath any patina); form mixtures (alloys) when combined with other metals; tend to lose or share electrons when they react with other substan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engineering is the field dedicated to controlling and preventing corrosion. In the most common use of the word, this means electrochemical oxidation of metal in reaction with an oxidant such as oxygen, hydrogen or hydroxide. Rusting, the formation of iron oxides, is a well-known example of electrochemical corrosion. This type of damage typically produces oxide(s) or salt(s) of the original metal and results in a distinctive orange colouration. Corrosion can also occur in materials other than metals, such as ceramics or polymers, although in this context, the term "degradation" is more common. Corrosion degrades the useful properties of materials and structures including strength, appearance and permeability to liquids and gases. Many structural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micro Process Engineering
{{Unreferenced, date=June 2019, bot=noref (GreenC bot) Micro process engineering is the science of conducting chemical or physical processes (unit operations) inside small volumina, typically inside channels with diameters of less than 1 mm (microchannels) or other structures with sub-millimeter dimensions. These processes are usually carried out in continuous flow mode, as opposed to batch production, allowing a throughput high enough to make micro process engineering a tool for chemical production. Micro process engineering is therefore not to be confused with microchemistry, which deals with very small overall quantities of matter. The subfield of micro process engineering that deals with chemical reactions, carried out in microstructured reactors or " microreactors", is also known as microreaction technology. The unique advantages of microstructured reactors or '' microreactors'' are enhanced heat transfer due to the large surface area-to-volume ratio, and enhanced mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microreactor
A microreactor or microstructured reactor or microchannel reactor is a device in which chemical reactions take place in a confinement with typical lateral dimensions below 1 mm; the most typical form of such confinement are microchannels.''Recent advances in synthetic micro reaction technology'' Paul Watts and Charlotte Wiles Chem. Commun., 2007, 443 - 467, Microreactors are studied in the field of micro process engineering, together with other devices (such as micro heat exchangers) in which physical processes occur. The microreactor is usually a continuous flow reactor (contrast with/to a batch reactor). Microreactors offer many advantages over conventional scale reactors, including vast improvements in energy efficiency, reaction speed and yield, safety, reliability, scalability, on-site/on-demand production, and a much finer degree of process control. History Gas-phase microreactors have a long history but those involving liquids started to appear in the late 1990s. On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |