|
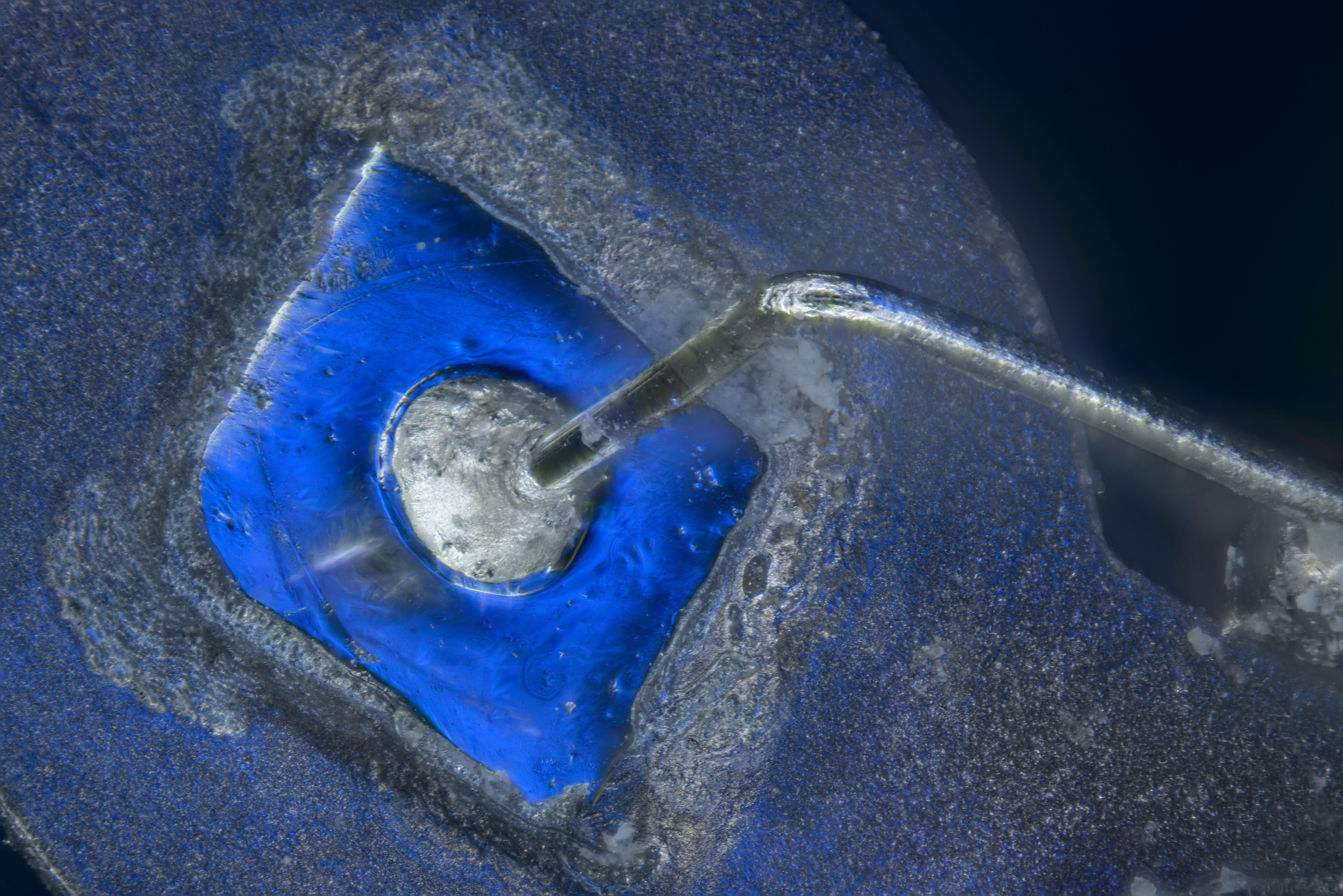
Micro-alloy Transistor
The germanium alloy-junction transistor, or alloy transistor, was an early type of bipolar junction transistor, developed at General Electric and RCA in 1951 as an improvement over the earlier grown-junction transistor. The usual construction of an alloy-junction transistor is a germanium crystal forming the base, with emitter and collector alloy beads fused on opposite sides. Indium and antimony were commonly used to form the alloy junctions on a bar of N-type germanium. The collector junction pellet would be about 50 mils (thousandths of an inch) in diameter, and the emitter pellet about 20 mils. The base region would be on the order of 1 mil (0.001 inches, 25 μm) thick. There were several types of improved alloy-junction transistors developed over the years that they were manufactured. All types of alloy-junction transistors became obsolete in the early 1960s, with the introduction of the planar transistor which could be mass-produced easily while alloy-junction transisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2N140 PNP Germanium Alloy Junction Transistor Closeup
N14 may refer to: Roads * N14 road (Belgium), a a national road in Belgium * Route nationale 14, in France * N14 road (Ireland) * N14 expressway (Netherlands) * N14 (South Africa) * A14 motorway (Switzerland) * Nebraska Highway 14, in the United States Vehicles * LNER Class N14, a British steam locomotive * Nissan Pulsar (N14), a Japanese automobile * , a submarine of the Royal Navy Other uses * N14 (Long Island bus) * BMW N14, an automobile engine * Flying W Airport in Burlington County, New Jersey, United States * Nitrogen-14, an isotope of nitrogen * N14, a postcode district in the N postcode area N, or n, is the fourteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''en'' (pronounced ), plural ''ens''. History ... See also * 14N (other) {{Letter-NumberCombDisambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffused-base Transistor
A diffused junction transistor is a transistor formed by diffusing dopants into a semiconductor substrate. The diffusion process was developed later than the alloy junction and grown junction processes for making bipolar junction transistors (BJTs). Bell Labs developed the first prototype diffused junction bipolar transistors in 1954. Diffused-base transistor The earliest diffused junction transistors were diffused-base transistors. These transistors still had alloy emitters and sometimes alloy collectors like the earlier alloy-junction transistors. Only the base was diffused into the substrate. Sometimes the substrate formed the collector, but in transistors like Philco's micro-alloy diffused transistors the substrate was the bulk of the base. Double diffusion At Bell Labs Calvin Souther Fuller produced basic physical understanding of a means of directly forming the emitter, base, and collector by double diffusion. The method was summarized in a history of science at Bell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1951 Introductions
Events January * January 4 – Korean War: Third Battle of Seoul – Chinese and North Korean forces capture Seoul for the second time (having lost the Second Battle of Seoul in September 1950). * January 9 – The Government of the United Kingdom announces abandonment of the Tanganyika groundnut scheme for the cultivation of peanuts in the Tanganyika Territory, with the writing off of £36.5M debt. * January 15 – In a court in West Germany, Ilse Koch, The "Witch of Buchenwald", wife of the commandant of the Buchenwald concentration camp, is sentenced to life imprisonment. * January 20 – Winter of Terror: Avalanches in the Alps kill 240 and bury 45,000 for a time, in Switzerland, Austria and Italy. * January 21 – Mount Lamington in Papua New Guinea 1951 eruption of Mount Lamington, erupts catastrophically, killing nearly 3,000 people and causing great devastation in Oro Province. * January 25 – Dutch author Anne de Vries releases the first volume of his children's nove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrode Transistor
A tetrode transistor is any transistor having four active terminals. Early tetrode transistors There were two types of tetrode transistor developed in the early 1950s as an improvement over the point-contact transistor and the later grown-junction transistor and alloy-junction transistor. Both offered much higher speed than earlier transistors. *Point-contact transistor having two emitters. It became obsolete in the middle 1950s. *Modified grown-junction transistor or alloy-junction transistor having two connections at opposite ends of the base. It achieved its high speed by reducing the input to output capacitance. It became obsolete in the early 1960s with the development of the diffusion transistor. Modern tetrode transistors *Dual emitter transistor, used in two-input transistor-transistor logic gates *Dual collector transistor, used in two-output integrated injection logic gates * Diffused planar silicon bipolar junction transistor, - ''Tetrode transistor memory logic cell'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philips
Koninklijke Philips N.V. (), commonly shortened to Philips, is a Dutch multinational conglomerate corporation that was founded in Eindhoven in 1891. Since 1997, it has been mostly headquartered in Amsterdam, though the Benelux headquarters is still in Eindhoven. Philips was formerly one of the largest electronics companies in the world, but is currently focused on the area of health technology, having divested its other divisions. The company was founded in 1891 by Gerard Philips and his father Frederik, with their first products being light bulbs. It currently employs around 80,000 people across 100 countries. The company gained its royal honorary title (hence the ''Koninklijke'') in 1998 and dropped the "Electronics" in its name in 2013, due to its refocusing from consumer electronics to healthcare technology. Philips is organized into three main divisions: Personal Health (formerly Philips Consumer Electronics and Philips Domestic Appliances and Personal Care), Connecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drift-field Transistor
The drift-field transistor, also called the drift transistor or graded base transistor, is a type of high-speed bipolar junction transistor having a doping-engineered electric field in the base to reduce the charge carrier base transit time. Invented by Herbert Kroemer at the Central Bureau of Telecommunications Technology of the German Postal Service, in 1953, it continues to influence the design of modern high-speed bipolar junction transistors. Early drift transistors were made by diffusing the base dopant in a way that caused a higher doping concentration near the emitter reducing towards the collector. This graded base happens automatically with the double diffused planar transistor (so they aren't usually called drift transistors). Similar high speed transistors Another way to speed the base transit time of this type of transistor is to vary the band gap across the base, e.g. in the SiGe pitaxial baseBJT the base of Si1−ηGeη can be grown with η approx 0.2 by the colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge Carrier
In physics, a charge carrier is a particle or quasiparticle that is free to move, carrying an electric charge, especially the particles that carry electric charges in electrical conductors. Examples are electrons, ions and holes. The term is used most commonly in solid state physics. In a conducting medium, an electric field can exert force on these free particles, causing a net motion of the particles through the medium; this is what constitutes an electric current. In conducting media, particles serve to carry charge: *In many metals, the charge carriers are electrons. One or two of the valence electrons from each atom are able to move about freely within the crystal structure of the metal. The free electrons are referred to as conduction electrons, and the cloud of free electrons is called a Fermi gas. Many metals have electron and hole bands. In some, the majority carriers are holes. *In electrolytes, such as salt water, the charge carriers are ions, which are atoms or molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Field
An electric field (sometimes E-field) is the physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles and exerts force on all other charged particles in the field, either attracting or repelling them. It also refers to the physical field for a system of charged particles. Electric fields originate from electric charges and time-varying electric currents. Electric fields and magnetic fields are both manifestations of the electromagnetic field, one of the four fundamental interactions (also called forces) of nature. Electric fields are important in many areas of physics, and are exploited in electrical technology. In atomic physics and chemistry, for instance, the electric field is the attractive force holding the atomic nucleus and electrons together in atoms. It is also the force responsible for chemical bonding between atoms that result in molecules. The electric field is defined as a vector field that associates to each point in space the electrostatic ( Coulomb) for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doping (semiconductor)
In semiconductor production, doping is the intentional introduction of impurities into an intrinsic semiconductor for the purpose of modulating its electrical, optical and structural properties. The doped material is referred to as an extrinsic semiconductor. Small numbers of dopant atoms can change the ability of a semiconductor to conduct electricity. When on the order of one dopant atom is added per 100 million atoms, the doping is said to be ''low'' or ''light''. When many more dopant atoms are added, on the order of one per ten thousand atoms, the doping is referred to as ''high'' or ''heavy''. This is often shown as ''n+'' for n-type doping or ''p+'' for p-type doping. (''See the article on semiconductors for a more detailed description of the doping mechanism.'') A semiconductor doped to such high levels that it acts more like a conductor than a semiconductor is referred to as a degenerate semiconductor. A semiconductor can be considered i-type semiconductor if it has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface-barrier Transistor
The surface-barrier transistor is a type of transistor developed by Philco in 1953 as an improvement to the alloy-junction transistor and the earlier point-contact transistor. Like the modern Schottky transistor, it offered much higher speed than earlier transistors and used metal–semiconductor junctions (instead of p-n junction, semiconductor–semiconductor junctions), but unlike the schottky transistor, both junctions were metal–semiconductor junctions. Production process Philco used a patented process of applying two tiny electrochemical jet streams of liquid indium sulfate (electrolyte solution) on opposite sides of a thin strip of N-type germanium base material. This process would etch away and form circular well depressions on each side of the N-type germanium base material, until the germanium base material was ultra thin and having a thickness of approximately a few ten-thousandths of an inch. After the etching process was finished, the polarity applied to the electrol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2N1307 Transistor Die With Bond Wires Attached
{{Letter-NumberCombDisambig ...
N13 may refer to Roads * N13 road (Ireland) * National Route 13 (Morocco) * Nebraska Highway 13, United States * Route 13 (Laos) * Route nationale 13, France Other uses * Bloomsburg Municipal Airport, in Pennsylvania, United States * BMW N13, an automobile engine * LNER Class N13, a steam locomotive * London Buses route N13 * Nissan Pulsar (N13), an automobile * Nitrogen-13, an isotope of nitrogen * N13, a postcode district in the N postcode area N, or n, is the fourteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''en'' (pronounced ), plural ''ens''. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philco
Philco (an acronym for Philadelphia Battery Company) is an American electronics industry, electronics manufacturer headquartered in Philadelphia. Philco was a pioneer in battery, radio, and television production. In 1961, the company was purchased by Ford Motor Company, Ford and, from 1966, renamed "Philco-Ford". Ford sold the company to GTE in 1974, and it was purchased by Philips in 1981. In North America, the Philco brand is currently owned by Philips. In other markets, the Philco International brand is owned by Electrolux. In the early 1920s, Philco made storage batteries, "socket power" battery eliminator units (plug-in transformers), and battery chargers. With the invention of the rectifier tube, which made it practical to power radios by electrical outlets, in 1928, Philco entered the radio business. They followed other radio makers such as RCA, Atwater-Kent, Zenith Electronics, Freshman Masterpiece, FADA Radio (Frank A. D'Andrea Radio), and AH Grebe into the battery-powere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |