|
Menomonie, Wisconsin
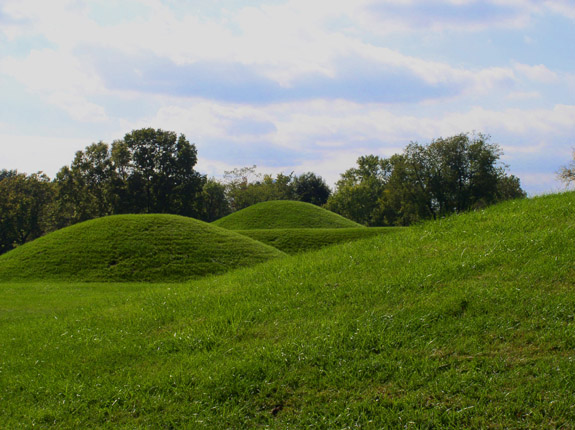
Menomonie () is a city in and the county seat of Dunn County in the western part of the U.S. state of Wisconsin. The city's population was 16,843 as of the 2020 census. Named for the original inhabitants of the area, the Menominee, the city forms the core of the United States Census Bureau's Menomonie Micropolitan Statistical Area (MSA), which includes all of Dunn County (2010 population: 43,857). The Menomonie MSA and the Eau Claire–Chippewa Falls metropolitan area to the east form the Census Bureau's Eau Claire-Menomonie Consolidated Metropolitan Statistical Area. The city center is at the south end of Lake Menomin, a reservoir on the Red Cedar River. History The earliest known residents of the area were people from the Trempealeau Hopewell Culture of the Middle Woodland Period (100–400 CE). Evidence from their culture includes a mound from the Wakanda Mounds Group in Wakanda Park, along the western shore of Lake Menomin. Most of these mounds are thought to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michigan to the northeast, and Lake Superior to the north. The bulk of Wisconsin's population live in areas situated along the shores of Lake Michigan. The largest city, Milwaukee, anchors its largest metropolitan area, followed by Green Bay and Kenosha, the third- and fourth-most-populated Wisconsin cities respectively. The state capital, Madison, is currently the second-most-populated and fastest-growing city in the state. Wisconsin is divided into 72 counties and as of the 2020 census had a population of nearly 5.9 million. Wisconsin's geography is diverse, having been greatly impacted by glaciers during the Ice Age with the exception of the Driftless Area. The Northern Highland and Western Upland along wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eau Claire–Chippewa Falls Metropolitan Area
The Eau Claire–Chippewa Falls metropolitan area refers loosely to the urbanized area along the Chippewa and Eau Claire Rivers, in west-central Wisconsin, with its primary center at Eau Claire and secondary centers at Chippewa Falls and Altoona. At a ribbon-cutting for the opening of the final stretch of the newly 4-laned section of WIS 29 between Green Bay and Elk Mound, in 2005, Gov. Jim Doyle referred to the region, including Menomonie to the west, as "Wisconsin's Golden Triangle." Extent Because the United States Census Bureau uses only counties to define census statistical areas outside New England, the official Eau Claire Metropolitan Statistical Area (which includes Chippewa Falls) encompasses all of Eau Claire and Chippewa Counties. These counties, combined with Dunn County to the west, coextensive with the Menomonie micropolitan area, comprise the Eau Claire-Menomonie Combined Statistical Area, with a 2015 population of 210,133. These three counties, especia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Treaty Of Prairie Du Chien
The Treaty of Prairie du Chien may refer to any of several treaties made and signed in Prairie du Chien, Wisconsin between the United States, representatives from the Sioux, Sac and Fox, Menominee, Ioway, Winnebago and the Anishinaabeg ( Chippewa, Ottawa and Potawatomi) Native American peoples. Description The First Treaty of Prairie du Chien was signed by William Clark and Lewis Cass for the United States and representatives of the Sioux, Sac and Fox, Menominee, Ioway, Winnebago, and Anishinaabeg ( Chippewa and the Council of Three Fires of Chippewa, Ottawa and Potawatomi) on August 19, 1825, proclaimed on February 6, 1826, and codified as . Due to the overall tribal movements toward the western direction under pressure of encroaching settlers, the Sioux Nation resisted and came into conflict with other tribes moving west into their traditional territory. The United States negotiated the treaty to try to reduce inter-tribal warfare. The treaty begins by establi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Kathio
The Battle of Kathio, or Battle of Izatys, was an oral tradition of the Chippewa reporting a battle fought in 1750 between Chippewas and the Sioux at the village of Kathio, or Izatys, on the Rum River next to Mille Lacs Lake. According to tradition an old man, living in a Chippewa village at the Fond du Lac (end of the lake), had four adult sons. They frequently made trips to visit the Sioux and they often returned home with gifts. During one particular trip one of the sons was killed in a quarrel over a Sioux woman. The remaining three brothers returned home for a short while, then returned to the Sioux, convinced the death of their brother was a mistake. However, upon this trip, only one brother returned home to his father safely. The last son, filled with forgiveness, went to seek the Sioux and reconcile their differences, but only met his death in the Sioux village. For two years after, the father hunted and worked hard to obtain enough ammunition and supplies to ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ojibwe
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains. According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of the largest tribal populations among Native American peoples. In Canada, they are the second-largest First Nations population, surpassed only by the Cree. They are one of the most numerous Indigenous Peoples north of the Rio Grande. The Ojibwe population is approximately 320,000 people, with 170,742 living in the United States , and approximately 160,000 living in Canada. In the United States, there are 77,940 mainline Ojibwe; 76,760 Saulteaux; and 8,770 Mississauga, organized in 125 bands. In Canada, they live from western Quebec to eastern British Columbia. The Ojibwe language is Anishinaabemowin, a branch of the Algonquian language family. They are part of the Council of Three Fires (which also include the Odawa and Potawatomi) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santee Dakota
The Dakota (pronounced , Dakota language: ''Dakȟóta/Dakhóta'') are a Native American tribe and First Nations band government in North America. They compose two of the three main subcultures of the Sioux people, and are typically divided into the Eastern Dakota and the Western Dakota. The four bands of Eastern Dakota are the Bdewákaŋthuŋwaŋ, Waȟpéthuŋwaŋ, Waȟpékhute, and Sisíthuŋwaŋ and are sometimes referred to as the Santee (''Isáŋyathi'' or ''Isáŋ-athi''; "knife" + "encampment", "dwells at the place of knife flint"), who reside in the eastern Dakotas, central Minnesota and northern Iowa. They have federally recognized tribes established in several places. The Western Dakota are the Yankton, and the Yanktonai (''Iháŋktȟuŋwaŋ'' and ''Iháŋktȟuŋwaŋna''; "Village-at-the-end" and "Little village-at-the-end"), who reside in the Upper Missouri River area. The Yankton-Yanktonai are collectively also referred to by the endonym ''Wičhíyena'' ("Those Who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effigy Mound
An effigy mound is a raised pile of earth built in the shape of a stylized animal, symbol, religious figure, human, or other figure. The Effigy Moundbuilder culture is primarily associated with the years 550-1200 CE during the Late Woodland Period, although radiocarbon dating has placed the origin of certain mounds as far back as 320 BCE. Effigy mounds were constructed in many Native American cultures. Scholars believe they were primarily for religious purposes, although some also fulfilled a burial mound function. The builders of the effigy mounds are usually referred to as the Mound Builders. Over 3200 animal-shaped effigy mounds have been identified by the Wisconsin Historical Society in the upper midwest. Native North American effigy mounds have been compared to the large-scale geoglyphs such as the Nazca Lines of Peru. History Early European observations Effigy mounds are limited to the Northern and Eastern United States, and most likely the French were the first Europea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Era
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the original Anno Domini (AD) and Before Christ (BC) notations used for the same calendar era. The two notation systems are numerically equivalent: " CE" and "AD " each describe the current year; "400 BCE" and "400 BC" are the same year. The expression traces back to 1615, when it first appeared in a book by Johannes Kepler as the la, annus aerae nostrae vulgaris (), and to 1635 in English as " Vulgar Era". The term "Common Era" can be found in English as early as 1708, and became more widely used in the mid-19th century by Jewish religious scholars. Since the later 20th century, BCE and CE have become popular in academic and scientific publications because BCE and CE are religiously neutral terms. They are used by others who wish to be sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodland Period
In the classification of archaeological cultures of North America, the Woodland period of North American pre-Columbian cultures spanned a period from roughly 1000 BCE to European contact in the eastern part of North America, with some archaeologists distinguishing the Mississippian period, from 1000 CE to European contact as a separate period. The term "Woodland Period" was introduced in the 1930s as a generic term for prehistoric sites falling between the Archaic hunter-gatherers and the agriculturalist Mississippian cultures. The Eastern Woodlands cultural region covers what is now eastern Canada south of the Subarctic region, the Eastern United States, along to the Gulf of Mexico. This period is variously considered a developmental stage, a time period, a suite of technological adaptations or "traits", and a "family tree" of cultures related to earlier Archaic cultures. It can be characterized as a chronological and cultural manifestation without any massive changes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
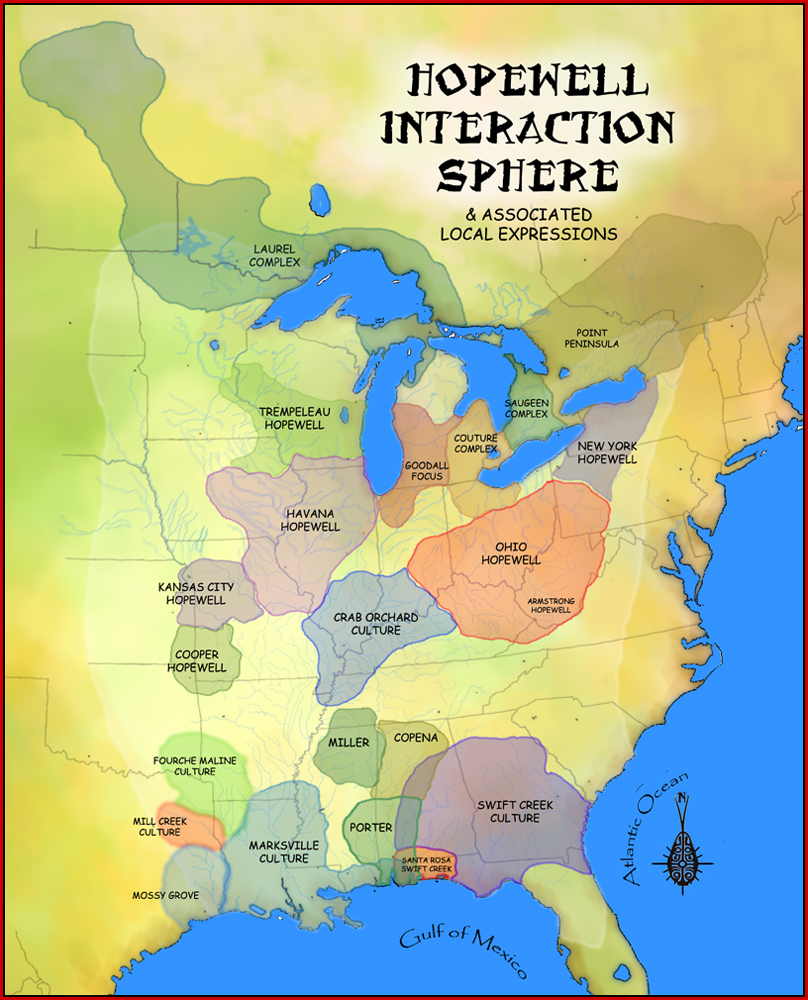
Hopewell Tradition
The Hopewell tradition, also called the Hopewell culture and Hopewellian exchange, describes a network of precontact Native American cultures that flourished in settlements along rivers in the northeastern and midwestern Eastern Woodlands from 100 BCE to 500 CE, in the Middle Woodland period. The Hopewell tradition was not a single culture or society but a widely dispersed set of populations connected by a common network of trade routes. At its greatest extent, the Hopewell exchange system ran from the northern shores of Lake Ontario south to the Crystal River Indian Mounds in modern-day Florida. Within this area, societies exchanged goods and ideas, with the highest amount of activity along waterways, which were the main transportation routes. Peoples within the Hopewell exchange system received materials from all over the territory of what now comprises the mainland United States. Most of the items traded were exotic materials; they were delivered to peoples living in the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
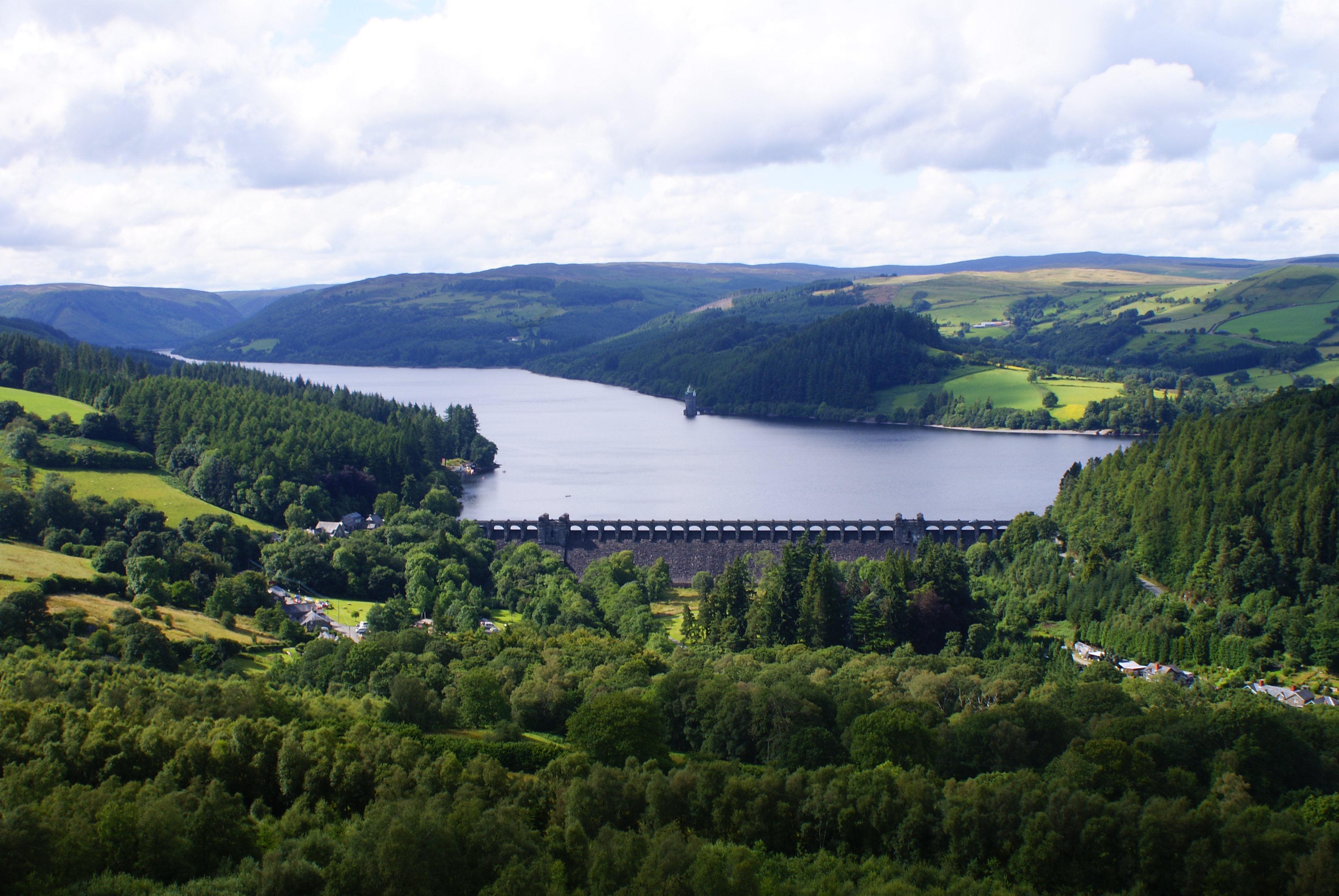
Red Cedar River (Wisconsin)
The Red Cedar River in northwestern Wisconsin is a tributary of the Chippewa River. Its name is translation from the Ojibwe ''Miskwaawaakokaan-ziibi'' meaning "Abundant with Red Cedar River." According to the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources, the river flows approximately 100 miles from southwestern Sawyer County to its confluence with the Chippewa southeast of Dunnville in southern Dunn County. It drains portions of eight Wisconsin counties: Barron, Chippewa, Dunn, Polk, Rusk, St. Croix, Sawyer, and Washburn. Important tributaries include the Chetek River and the Hay River. Important settlements along the river's course include Cameron, Rice Lake, Colfax, and Menomonie. Much of the river's course runs through Dunn County, which it nearly bisects from north to south. The Red Cedar flows through Red Cedar Lake and Rice Lake in Barron County (adjacent to the city of Rice Lake), and two reservoirs in central Dunn County: Tainter Lake and Lake Menomin Lake Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reservoir
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation. Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including controlling a watercourse that drains an existing body of water, interrupting a watercourse to form an embayment within it, through excavation, or building any number of retaining walls or levees. In other contexts, "reservoirs" may refer to storage spaces for various fluids; they may hold liquids or gasses, including hydrocarbons. ''Tank reservoirs'' store these in ground-level, elevated, or buried tanks. Tank reservoirs for water are also called cisterns. Most underground reservoirs are used to store liquids, principally either water or petroleum. Types Dammed valleys Dammed reservoirs are artificial lakes created and controlled by a dam constructed across a valley, and rely on the natural topography to provide most of the basin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)