|
Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor Of Infancy
Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy is a very rare oral cavity tumor that is seen in patients usually at or around birth. It must be removed to be cured. Definitions: A rare, biphasic, neuroblastic, and pigmented epithelial neoplasm of craniofacial sites, usually involving the oral cavity or gums. Signs and symptoms Most patients present with a very rapidly growing mass that often gives a bluish appearance in the mouth. This is because the pigmentation in the cells appears blue through the overlying epithelium (mucosa). By imaging studies, there is usually a large expansive radiolucent (clear) mass without well defined borders. Calcifications within the mass may be seen. More than 70% involve the maxilla (usually maxillary anterior alveolar ridge), while the mandible and skull are affected less often. There is often an elevated vanilmandelic acid level. Pathogenesis It is considered to be a developmental anomaly, and thus is congenital in presentation. It is though ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Cavity
In animal anatomy, the mouth, also known as the oral cavity, or in Latin cavum oris, is the opening through which many animals take in food and issue vocal sounds. It is also the cavity lying at the upper end of the alimentary canal, bounded on the outside by the lips and inside by the pharynx. In tetrapods, it contains the tongue and, except for some like birds, teeth. This cavity is also known as the buccal cavity, from the Latin ''bucca'' ("cheek"). Some animal phyla, including arthropods, molluscs and chordates, have a complete digestive system, with a mouth at one end and an anus at the other. Which end forms first in ontogeny is a criterion used to classify bilaterian animals into protostomes and deuterostomes. Development In the first multicellular animals, there was probably no mouth or gut and food particles were engulfed by the cells on the exterior surface by a process known as endocytosis. The particles became enclosed in vacuoles into which enzymes were secreted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Crest
Neural crest cells are a temporary group of cells unique to vertebrates that arise from the embryonic ectoderm germ layer, and in turn give rise to a diverse cell lineage—including melanocytes, craniofacial cartilage and bone, smooth muscle, peripheral and enteric neurons and glia. After gastrulation, neural crest cells are specified at the border of the neural plate and the non-neural ectoderm. During neurulation, the borders of the neural plate, also known as the neural folds, converge at the dorsal midline to form the neural tube. Subsequently, neural crest cells from the roof plate of the neural tube undergo an epithelial to mesenchymal transition, delaminating from the neuroepithelium and migrating through the periphery where they differentiate into varied cell types. The emergence of neural crest was important in vertebrate evolution because many of its structural derivatives are defining features of the vertebrate clade. Underlying the development of neural crest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD57
3-beta-glucuronosyltransferase 1 (B3GAT1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''B3GAT1'' gene, whose enzymatic activity creates the CD57 epitope on other cell surface proteins. In immunology, the CD57 antigen (CD stands for cluster of differentiation) is also known as HNK1 (human natural killer-1) or LEU7. It is expressed as a carbohydrate epitope that contains a residue in several adhesion molecules of the nervous system. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the glucuronyltransferase gene family. These enzymes exhibit strict acceptor specificity, recognizing nonreducing terminal sugars and their anomeric linkages. This gene product functions as the key enzyme in a glucuronyl transfer reaction during the biosynthesis of the carbohydrate epitope HNK-1 (human natural killer-1, also known as CD57 and LEU7). Alternate transcriptional splice variants have been characterized. Immunohistochemistry In anatomical pathology, CD57 (immunostaining) is simila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuron Specific Enolase
Gamma-enolase, also known as enolase 2 (ENO2) or neuron specific enolase (NSE), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''ENO2'' gene. Gamma-enolase is a phosphopyruvate hydratase. Gamma-enolase is one of the three enolase isoenzymes found in mammals. This isoenzyme, a homodimer, is found in mature neurons and cells of neuronal origin. A switch from alpha enolase to gamma enolase occurs in neural tissue during development in rats and primates. Interactive pathway map Utility Detection of NSE with antibodies can be used to identify neuronal cells and cells with neuroendocrine differentiation. NSE is produced by small-cell carcinomas, which are neuroendocrine Neuroendocrine cells are cells that receive neuronal input (through neurotransmitters released by nerve cells or neurosecretory cells) and, as a consequence of this input, release messenger molecules (hormones) into the blood. In this way they bri ... in origin. NSE is therefore a useful tumor marker for disting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMB-45
HMB-45 is a monoclonal antibody that reacts against an antigen present in melanocyte, melanocytic tumors such as melanomas, and stands for Human Melanoma Black. It is used in anatomic pathology as a marker for such tumors. The specific antigen recognized by HMB-45 is now known as PMEL_(gene), Pmel 17. History HMB-45 was discovered by Drs. Allen M. Gown and Arthur M. Vogel in 1986. The antibody was generated to an extract of melanoma. Cancer diagnostics In a study to determine diagnostic usefulness of specific antibodies used to identify melanoma, HMB-45 had a 92% sensitivity when used to identify melanoma. The antibody also reacts positively against junctional nevus cells and fetal melanocytes. Despite this relatively high sensitivity—HMB-45 does have its drawbacks. HMB-45 can be detected in only 50-70% of melanomas. HMB-45 does not react well against intradermal nevi, normal adult melanocytes, spindle cell melanomas and desmoplastic melanomas. HMB-45 is nonreactive with almo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vimentin
Vimentin is a structural protein that in humans is encoded by the ''VIM'' gene. Its name comes from the Latin ''vimentum'' which refers to an array of flexible rods. Vimentin is a type III intermediate filament (IF) protein that is expressed in mesenchymal cells. IF proteins are found in all animal cells as well as bacteria. Intermediate filaments, along with tubulin-based microtubules and actin-based microfilaments, comprises the cytoskeleton. All IF proteins are expressed in a highly developmentally-regulated fashion; vimentin is the major cytoskeletal component of mesenchymal cells. Because of this, vimentin is often used as a marker of mesenchymally-derived cells or cells undergoing an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) during both normal development and metastatic progression. Structure A vimentin monomer, like all other intermediate filaments, has a central α-helical domain, capped on each end by non- helical amino (head) and carboxyl (tail) domains. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, horns, claws, hooves, and the outer layer of skin among vertebrates. Keratin also protects epithelial cells from damage or stress. Keratin is extremely insoluble in water and organic solvents. Keratin monomers assemble into bundles to form intermediate filaments, which are tough and form strong unmineralized epidermal appendages found in reptiles, birds, amphibians, and mammals. Excessive keratinization participate in fortification of certain tissues such as in horns of cattle and rhinos, and armadillos' osteoderm. The only other biological matter known to approximate the toughness of keratinized tissue is chitin. Keratin comes in two types, the primitive, softer forms found in all vertebrates and harder, derived forms found only among saur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
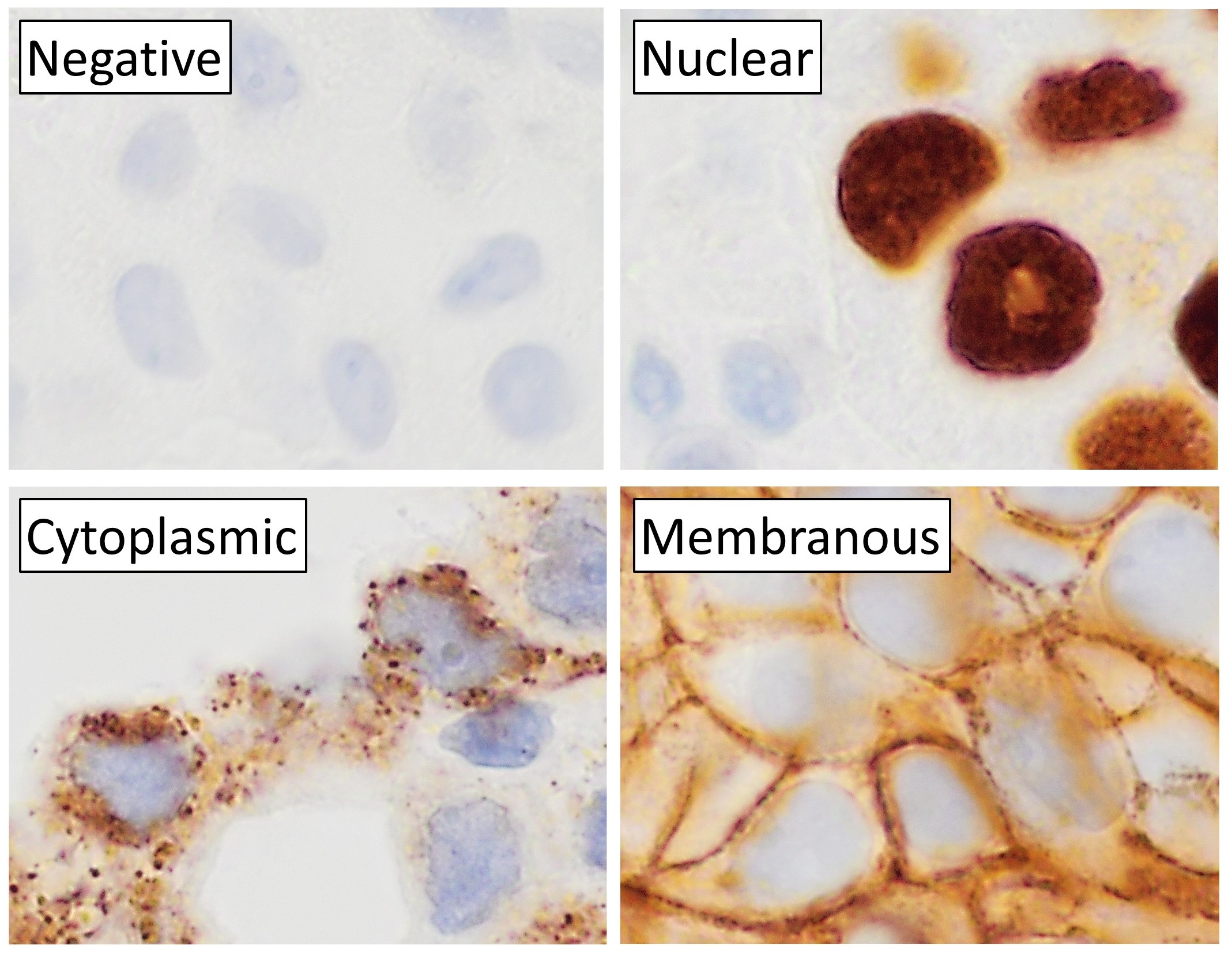
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is the most common application of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens (proteins) in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. IHC takes its name from the roots "immuno", in reference to antibodies used in the procedure, and "histo", meaning tissue (compare to immunocytochemistry). Albert Coons conceptualized and first implemented the procedure in 1941. Visualising an antibody-antigen interaction can be accomplished in a number of ways, mainly either of the following: * ''Chromogenic immunohistochemistry'' (CIH), wherein an antibody is conjugated to an enzyme, such as peroxidase (the combination being termed immunoperoxidase), that can catalyse a colour-producing reaction. * ''Immunofluorescence'', where the antibody is tagged to a fluorophore, such as fluorescein or rhodamine. Immunohistochemical staining is widely used in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor Infancy LDRT 369 08
The word oral may refer to: Relating to the mouth * Relating to the mouth, the first portion of the alimentary canal that primarily receives food and liquid **Oral administration of medicines ** Oral examination (also known as an oral exam or oral test), a practice in many schools and disciplines in which an examiner poses questions to the student in spoken form ** Oral hygiene, practices involved in cleaning the mouth and preventing disease **Oral medication **Oral rehydration therapy, a simple treatment for dehydration associated with diarrhea **Oral sex, sexual activity involving the stimulation of genitalia by use of the mouth, tongue, teeth or throat. **Oral stage, a human development phase in Freudian developmental psychology **Oral tradition, cultural material and tradition transmitted orally from one generation to another **Oralism, the education of deaf students through oral language by using lip reading, and mimicking of mouth shapes and breathing patterns **Speech commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino acid tyrosine is followed by polymerization. The melanin pigments are produced in a specialized group of cells known as melanocytes. Functionally, eumelanin serves as protection against UV radiation. There are five basic types of melanin: eumelanin, pheomelanin, neuromelanin, allomelanin and pyomelanin. The most common type is eumelanin, of which there are two types— brown eumelanin and black eumelanin. Pheomelanin, which is produced when melanocytes are malfunctioning due to derivation of the gene to its recessive format is a cysteine-derivative that contains poly benzothiazine portions that are largely responsible for the of red yellow tint given to some skin or hair colors. Neuromelanin is found in the brain. Research has been unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important roles in reinforcing the DNA during cell division, preventing DNA damage, and regulating gene expression and DNA replication. During mitosis and meiosis, chromatin facilitates proper segregation of the chromosomes in anaphase; the characteristic shapes of chromosomes visible during this stage are the result of DNA being coiled into highly condensed chromatin. The primary protein components of chromatin are histones. An octamer of two sets of four histone cores (Histone H2A, Histone H2B, Histone H3, and Histone H4) bind to DNA and function as "anchors" around which the strands are wound.Maeshima, K., Ide, S., & Babokhov, M. (2019). Dynamic chromatin organization without the 30-nm fiber. ''Current opinion in cell biology, 58,'' 95–104. https://doi.o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor Infancy LDRT 369 13
The word oral may refer to: Relating to the mouth * Relating to the mouth, the first portion of the alimentary canal that primarily receives food and liquid **Oral administration of medicines ** Oral examination (also known as an oral exam or oral test), a practice in many schools and disciplines in which an examiner poses questions to the student in spoken form ** Oral hygiene, practices involved in cleaning the mouth and preventing disease **Oral medication **Oral rehydration therapy, a simple treatment for dehydration associated with diarrhea **Oral sex, sexual activity involving the stimulation of genitalia by use of the mouth, tongue, teeth or throat. **Oral stage, a human development phase in Freudian developmental psychology **Oral tradition, cultural material and tradition transmitted orally from one generation to another **Oralism, the education of deaf students through oral language by using lip reading, and mimicking of mouth shapes and breathing patterns **Speech commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)