|
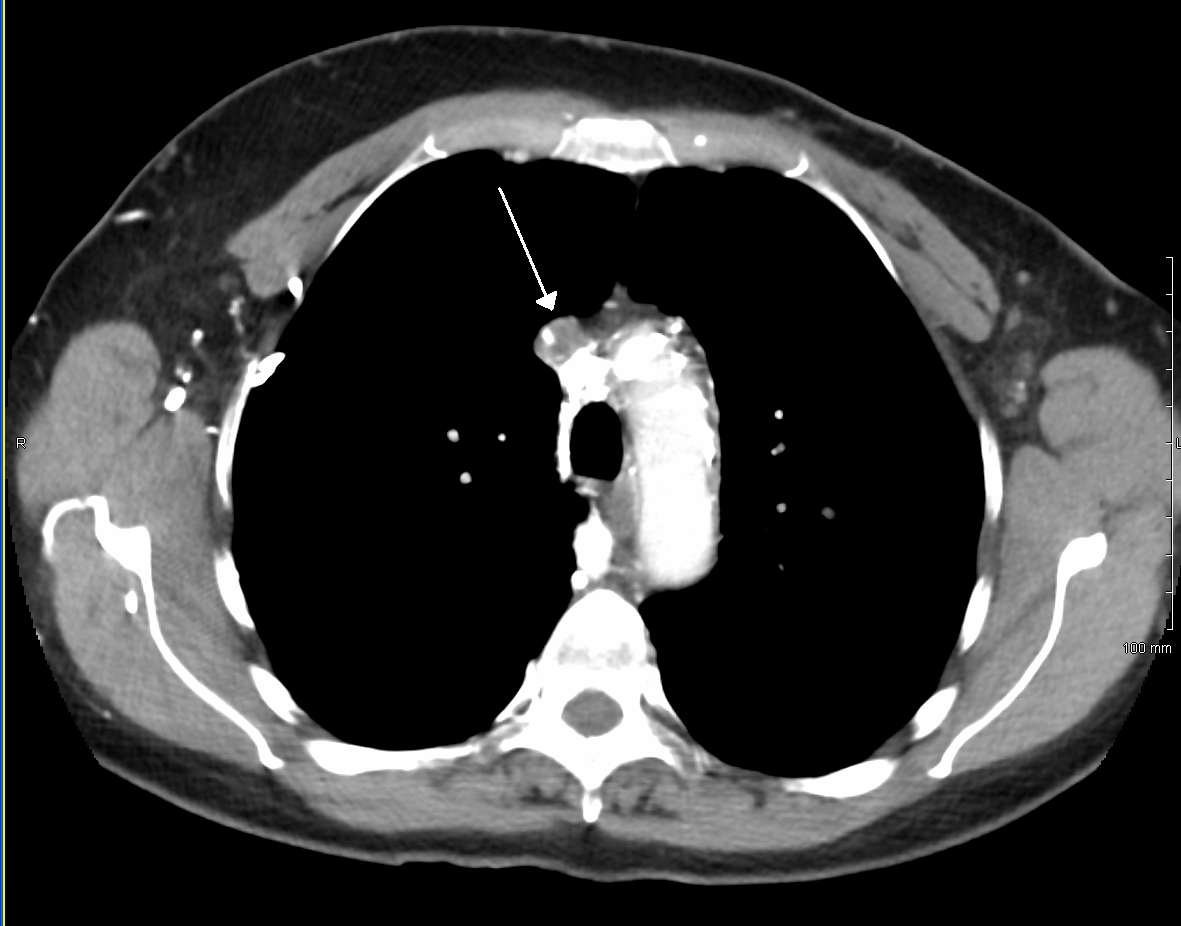
Mediastinal Tumors
A mediastinal tumor is a tumor in the mediastinum, the cavity that separates the lungs from the rest of the chest. It contains the heart, esophagus, trachea, thymus, and aorta. The most common mediastinal masses are neurogenic tumors (20% of mediastinal tumors), usually found in the posterior mediastinum, followed by thymoma (15–20%) located in the anterior mediastinum. Lung cancer typically spreads to the lymph nodes in the mediastinum. The mediastinum has three main parts: the anterior mediastinum (front), the middle mediastinum, and the posterior mediastinum (back). Masses in the anterior portion of the mediastinum can include thymoma, lymphoma, pheochromocytoma, germ cell tumors including teratoma, thyroid tissue, and parathyroid lesions. Masses in this area are more likely to be malignant than those in other compartments. Masses in the posterior portion of the mediastinum tend to be neurogenic in origin, and in adults tend to be of neural sheath origin including neurilemoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to as ''photomicroscopy''. At a basic level, photomicroscopy may be performed simply by connecting a camera to a microscope, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teratoma
A teratoma is a tumor made up of several different types of tissue, such as hair, muscle, teeth, or bone. Teratomata typically form in the ovary, testicle, or coccyx. Symptoms Symptoms may be minimal if the tumor is small. A testicular teratoma may present as a painless lump. Complications may include ovarian torsion, testicular torsion, or hydrops fetalis. They are a type of germ cell tumor (a tumor that begins in the cells that give rise to sperm or eggs). They are divided into two types: mature and immature. Mature teratomas include dermoid cysts and are generally benign. Immature teratomas may be cancerous. Most ovarian teratomas are mature. In adults, testicular teratomas are generally cancerous. Definitive diagnosis is based on a tissue biopsy. Treatment of coccyx, testicular, and ovarian teratomas is generally by surgery. Testicular and immature ovarian teratomas are also frequently treated with chemotherapy. Teratomas occur in the coccyx in about one in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
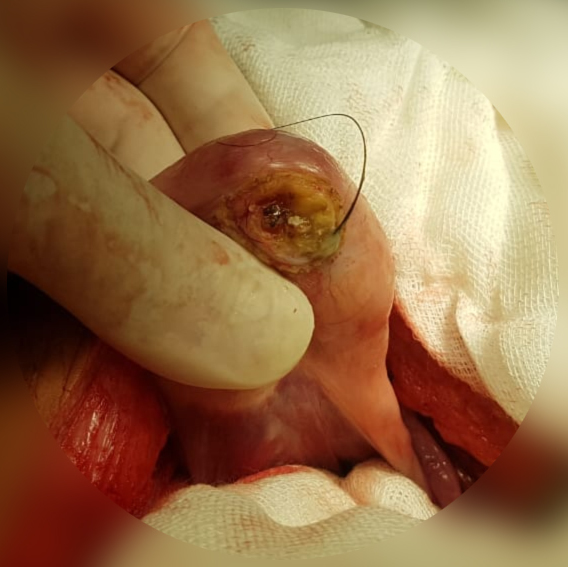
Mediastinotomy
Mediastinoscopy is a procedure that enables visualization of the contents of the mediastinum, usually for the purpose of obtaining a biopsy. Mediastinoscopy is often used for staging of lymph nodes of lung cancer or for diagnosing other conditions affecting structures in the mediastinum such as sarcoidosis or lymphoma. Mediastinoscopy involves making an incision approximately 1 cm above the suprasternal notch of the sternum, or breast bone. Dissection is carried out down to the pretracheal space and down to the carina. A scope (mediastinoscope) is then advanced into the created tunnel which provides a view of the mediastinum. The scope may provide direct visualization or may be attached to a video monitor. Mediastinoscopy provides access to mediastinal lymph node levels 2, 4, and 7. Current use Historically, mediastinoscopy has been the gold standard for the staging of lung cancer. However, with advances in minimally invasive procedures and imaging, mediastinoscopy usage has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediastinoscopy
Mediastinoscopy is a procedure that enables visualization of the contents of the mediastinum, usually for the purpose of obtaining a biopsy. Mediastinoscopy is often used for staging of lymph nodes of lung cancer or for diagnosing other conditions affecting structures in the mediastinum such as sarcoidosis or lymphoma. Mediastinoscopy involves making an incision approximately 1 cm above the suprasternal notch of the sternum, or breast bone. Dissection is carried out down to the pretracheal space and down to the carina. A scope (mediastinoscope A mediastinoscope is a thin, tube-like instrument used to examine the tissues and lymph nodes in the area between the lungs (mediastinum) in a procedure known as mediastinoscopy. These tissues include the heart and its large blood vessels, trachea, ...) is then advanced into the created tunnel which provides a view of the mediastinum. The scope may provide direct visualization or may be attached to a video monitor. Mediastinoscopy prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleural Effusion
A pleural effusion is accumulation of excessive fluid in the pleural space, the potential space that surrounds each lung. Under normal conditions, pleural fluid is secreted by the parietal pleural capillaries at a rate of 0.6 millilitre per kilogram weight per hour, and is cleared by lymphatic absorption leaving behind only 5–15 millilitres of fluid, which helps to maintain a functional vacuum between the parietal and visceral pleurae. Excess fluid within the pleural space can impair inspiration by upsetting the functional vacuum and hydrostatically increasing the resistance against lung expansion, resulting in a fully or partially collapsed lung. Various kinds of fluid can accumulate in the pleural space, such as serous fluid ( hydrothorax), blood ( hemothorax), pus (pyothorax, more commonly known as pleural empyema), chyle (chylothorax), or very rarely urine (urinothorax). When unspecified, the term "pleural effusion" normally refers to hydrothorax. A pleural effu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Vena Cava Syndrome
Superior vena cava syndrome (SVCS), is a group of symptoms caused by obstruction of the superior vena cava ("SVC"), a short, wide vessel carrying circulating blood into the heart. The majority of cases are caused by malignant tumors within the mediastinum, most commonly lung cancer and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, directly compressing or invading the SVC wall. Non-malignant causes are increasing in prevalence due to expanding use of intravascular devices (such as permanent central venous catheters and leads for pacemakers and defibrillators), which can result in thrombosis. Other non-malignant causes include benign mediastinal tumors, aortic aneurysm, infections, and fibrosing mediastinitis. Characteristic features are edema (swelling due to excess fluid) of the face and arms and development of swollen collateral veins on the front of the chest wall. Shortness of breath and coughing are quite common symptoms; difficulty swallowing is reported in 11% of cases, headache in 6% a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Night Sweats
Night sweats, also referred to as nocturnal hyperhidrosis (Hyperhidrosis - a medical term for excessive sweating + nocturnal - night), is the repeated occurrence of excessive sweating during sleep Sleep is a sedentary state of mind and body. It is characterized by altered consciousness, relatively inhibited Perception, sensory activity, reduced muscle activity and reduced interactions with surroundings. It is distinguished from wakefuln .... The person may or may not also perspiration, perspire excessively while awake. One of the most common causes of night sweats in women over 40 is the hormonal changes related to menopause and perimenopause. This is a very common occurrence during the menopausal transition years. Over 80% of women experience hot flashes, which may include excessive sweating, during menopause. Night sweats range from being relatively harmless to a sign of underlying disease. Night sweats may happen because the sleep environment is too warm, either becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weight Loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat ( adipose tissue), or lean mass (namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other connective tissue). Weight loss can either occur unintentionally because of malnourishment or an underlying disease, or from a conscious effort to improve an actual or perceived overweight or obese state. "Unexplained" weight loss that is not caused by reduction in calorific intake or exercise is called cachexia and may be a symptom of a serious medical condition. Intentional Intentional weight loss is the loss of total body mass as a result of efforts to improve fitness and health, or to change appearance through slimming. Weight loss is the main treatment for obesity, and there is substantial evidence this can prevent progression from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes with a 7-10% weight loss and manage cardiometabolic health for dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using values between in humans. The increase in set point triggers increased muscle contractions and causes a feeling of cold or chills. This results in greater heat production and efforts to conserve heat. When the set point temperature returns to normal, a person feels hot, becomes flushed, and may begin to sweat. Rarely a fever may trigger a febrile seizure, with this being more common in young children. Fevers do not typically go higher than . A fever can be caused by many medical conditions ranging from non-serious to life-threatening. This includes viral, bacterial, and parasitic infections—such as influenza, the common cold, meningitis, urinary tract infections, appendicitis, Lassa, COVID-19, and malaria. Non-infectious cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Mediastinal B-cell Lymphoma
Primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma, abbreviated PMBL, is a rare type of lymphoma that forms in the mediastinum (the space in between the lungs) and predominantly affects young adults. It is a subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; however, it generally has a significantly better prognosis. Diagnosis Diagnosis requires a biopsy, so that the exact type of tissue can be determined by examination under a microscope. PMBL is generally considered a sub-type of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, although it is also closely related to nodular sclerosing Hodgkin lymphoma (NSHL). Tumors that are even more closely related to NSHL than typical for PMBL are called gray zone lymphoma. Treatment Treatment commonly begins with months of multi-drug chemotherapy regimen. Either R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisolone) or DA-EPOCH-R (dose-adjusted etoposide, prednisolone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, rituximab) has been typical. Other, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), also known as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a group of blood cancers that includes all types of lymphomas except Hodgkin lymphomas. Symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and tiredness. Other symptoms may include bone pain, chest pain, or itchiness. Some forms are slow-growing while others are fast-growing. Lymphomas are types of cancer that develop from lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell. Risk factors include poor immune function, autoimmune diseases, ''Helicobacter pylori'' infection, hepatitis C, obesity, and Epstein–Barr virus infection. The World Health Organization classifies lymphomas into five major groups, including one for Hodgkin lymphoma. Within the four groups for NHL are over 60 specific types of lymphoma. Diagnosis is by examination of a bone marrow or lymph node biopsy. Medical imaging is done to help with cancer staging. Treatment depends on whether the lymphoma is slow- or fas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |