|
Mazu Daoyi
Mazu Daoyi (709–788) (, Japanese: Baso Dōitsu) was an influential abbot of Chan Buddhism during the Tang dynasty. The earliest recorded use of the term "Chan school" is from his ''Extensive Records''. Master Ma's teaching style of "strange words and extraordinary actions" became paradigmatic Zen lore. Biography His family name was Ma – Mazu meaning ''Ancestor Ma'' or ''Master Ma''. He was born in 709 northwest of Chengdu in Sichuan. During his years as master, Mazu lived in Jiangxi, from which he took the name "Jiangxi Daoyi". In the ''Transmission of the Lamp'', compiled in 1004, Mazu is described as follows: According to the ''Transmission of the Lamp'', Mazu was a student of Nanyue Huairang (677-744) at Mount Heng in Hunan A story in the entry on Nanyue Huairang in the ''Transmission of the Lamp'' is regarded as Mazu's enlightenment-account, though the text does not claim it as such. An earlier and more primitive version of this story appears in the '' Anthology of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; " taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dharma
Dharma (; sa, धर्म, dharma, ; pi, dhamma, italic=yes) is a key concept with multiple meanings in Indian religions, such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism and others. Although there is no direct single-word translation for ''dharma'' in European languages, it is commonly translated as "righteousness", "merit" or "religious and moral duties" governing individual conduct.Britannica, The Editors of Encyclopaedia. (9 April 2019)Dharma. ''Encyclopedia Britannica''. Accessed 14 September 2021. In Hinduism, dharma is one of the four components of the ''Puruṣārtha'', the aims of life, and signifies behaviours that are considered to be in accord with '' Ṛta'', the order that makes life and universe possible. It includes duties, rights, laws, conduct, virtues and "right way of living".see: *"Dharma", ''The Columbia Encyclopedia'', 6th Ed. (2013), Columbia University Press, Gale, ; *Steven Rosen (2006), Essential Hinduism, Praeger, , Chapter 3. It had a transtempor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Cliff Record
The ''Blue Cliff Record'' () is a collection of Chan Buddhist kōans originally compiled in Song China in 1125, during the reign of Emperor Huizong, and then expanded into its present form by Chan master Yuanwu Keqin (1063–1135; ).K. Sekida, ''Two Zen Classics'' (1977) p. 18-20 The book includes Yuanwu's annotations and commentary on ''100 Verses on Old Cases'' (), a compilation of 100 kōans collected by Xuedou Chongxian (980–1052; , '). Xuedou selected 82 of these from '' The Jingde Record of the Transmission of the Lamp'', with the remainder selected from the ''Yunmen Guanglu'' (, ''Extensive Record of Yunmen Wenyan'', 864–949). Name and origin The ''Blue Cliff Record'' derives its name from the temple where Yuanwu Keqin wrote most of his commentaries, the Blue Cliff Cloister (碧巖院, ''Bìyán Yuàn'') in Hunan. The work was originally called Xuedou's ''Juko'' (''ju'', verse; ''ko'', old koans) before its ''Blue Cliff Record'' title was attributed. Yuanwu f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zazen
''Zazen'' (literally " seated meditation"; ja, 座禅; , pronounced ) is a meditative discipline that is typically the primary practice of the Zen Buddhist tradition. However, the term is a general one not unique to Zen, and thus technically any Buddhist tradition's seated meditation is "zazen". The term ''zuòchán'' can be found in early Chinese Buddhist sources, such as the Dhyāna sutras. For example, the famous translator Kumārajīva (344-413) translated a work termed ''Zuòchán sān mēi jīng'' (''A'' ''Manual on the Samādhi of Sitting Meditation'') and the Chinese Tiantai master Zhiyi (538–597 CE) wrote some very influential works on sitting meditation.Swanson, Paul L. (2002). ''Ch'an and Chih-kuan: T'ien-t’ai Chih-i's View of "Zen" and the Practice of the Lotus Sutra''. Presented at the International Lotus Sutra Conference on the theme "The Lotus Sutra and Zen", 11–16 July 2002. Source: (accessed: 6 August 2008). p.4 The earliest manual on sitting medit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keisaku
In Zen Buddhism, the ''keisaku'' (Japanese: 警策, Chinese: 香板, ''xiāng bǎn''; ''kyōsaku'' in the Soto school) is a flat wooden stick or slat used during periods of meditation to remedy sleepiness or lapses of concentration. This is accomplished through a strike or series of strikes, usually administered on the meditator's back and shoulders in the muscular area between the shoulder and the spine. The keisaku itself is thin and somewhat flexible; strikes with it, though they may cause momentary sting if performed vigorously, are not injurious. Purpose The word "keisaku" may be translated as "warning stick", or "awakening stick", and is wielded by the jikijitsu. "Encouragement stick" is a common translation for "kyōsaku". In Soto Zen, the kyōsaku is always administered at the request of the meditator, by way of bowing one's head and putting the palms together in gassho, and then exposing each shoulder to be struck in turn. The kyōsaku may also be administered as a me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katsu (Zen)
''Katsu'' ( Chinese: 喝; Pinyin: ''hè'', Wade-Giles: ''ho''; Cantonese: ', rōmaji: ''katsu'') is a shout that is described in Chan and Zen Buddhism encounter-stories, to expose the enlightened state (Japanese: ''satori'') of the Zen-master, and/or to induce initial enlightenment experience in a student. The shout is also sometimes used in the East Asian martial arts for a variety of purposes; in this context, ''katsu'' is very similar to the shout '' kiai''. Etymology The word in Chinese means literally "to yell" or "to shout". In Japanese it has also developed the meaning of " to browbeat", "to scold", and "hoarse". In the context of Chan and Zen practice, the word is not generally used in its literal meaning(s), but rather—much as with the martial arts shout of ''kiai''—as fundamentally a means of focusing energy. When the Chan and Zen practice of the ''katsu'' first emerged in Jiangxi province in the south of Tang dynasty China in the 8th century CE, the word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is a trans-boundary river of Asia which flows through India and Bangladesh. The river rises in the western Himalayas in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It flows south and east through the Gangetic plain of North India, receiving the right-bank tributary, the Yamuna, which also rises in the western Indian Himalayas, and several left-bank tributaries from Nepal that account for the bulk of its flow. In West Bengal state, India, a feeder canal taking off from its right bank diverts 50% of its flow southwards, artificially connecting it to the Hooghly river. The Ganges continues into Bangladesh, its name changing to the Padma. It is then joined by the Jamuna, the lower stream of the Brahmaputra, and eventually the Meghna, forming the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nestorian Church
The Church of the East ( syc, ܥܕܬܐ ܕܡܕܢܚܐ, ''ʿĒḏtā d-Maḏenḥā'') or the East Syriac Church, also called the Church of Seleucia-Ctesiphon, the Persian Church, the Assyrian Church, the Babylonian Church or the Nestorian Church, was an Eastern Christian church of the East Syriac Rite, based in Mesopotamia. It was one of three major branches of Eastern Christianity that arose from the Christological controversies of the 5th and 6th centuries, alongside the Oriental Orthodox Churches and the Chalcedonian Church. During the early modern period, a series of schisms gave rise to rival patriarchates, sometimes two, sometimes three. Since the latter half of the 20th century, three churches in Iraq claim the heritage of the Church of the East. Meanwhile, the East Syriac churches in India claim the heritage of the Church of the East in India. The Church of the East organized itself in 410 as the national church of the Sasanian Empire through the Council of Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Wuzong Of Tang
Emperor Wuzong of Tang (July 2, 814 – April 22, 846), né Li Chan, later changed to Li Yan just before his death, was an emperor of the Tang Dynasty of China, reigning from 840 to 846. Emperor Wuzong is mainly known in modern times for the religious persecution that occurred during his reign. However, he was also known for his successful reactions against incursions by remnants of the Uyghur Khanate and the rebellion by Liu Zhen, as well as his deep trust and support for chancellor Li Deyu. Background Li Chan was born in 814, as the ninth son of Li Heng at least, who was then Crown Prince under Li Chan's grandfather Emperor Xianzong. He was born at the Eastern Palace (i.e., the Crown Prince's palace). His mother was Consort Wei, whose rank was lost to history. After Li Heng became Emperor Muzong in 820, he made many of his brothers and sons princes in 821, and Li Chan was made the Prince of Ying. Little is known about Li Chan's activities during the reigns of Empe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taoist
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the '' Tao'' (, 'Thoroughfare'); the ''Tao'' is generally defined as the source of everything and the ultimate principle underlying reality. The ''Tao Te Ching'', a book containing teachings attributed to Laozi (), together with the later writings of Zhuangzi, are both widely considered the keystone works of Taoism. Taoism teaches about the various disciplines for achieving perfection through self-cultivation. This can be done through the use of Taoist techniques and by becoming one with the unplanned rhythms of the all, called "the way" or "Tao". Taoist ethics vary depending on the particular school, but in general tend to emphasize ''wu wei'' (action without intention), naturalness, simplicity, spontaneity and the Three Treasures: , compassion, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
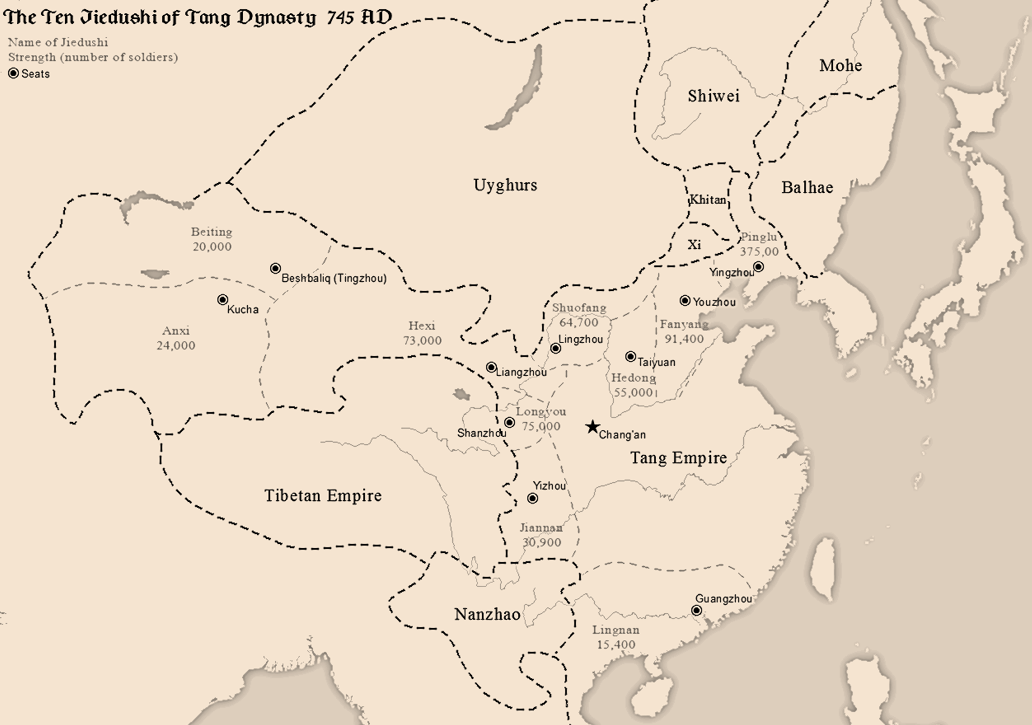
An Lushan Rebellion
The An Lushan Rebellion was an uprising against the Tang dynasty of China towards the mid-point of the dynasty (from 755 to 763), with an attempt to replace it with the Yan dynasty. The rebellion was originally led by An Lushan, a general officer of the Tang military system. The event involved military activity and direct deaths from battle, but also significant associated population loss from famine, and population dislocations. The event is also known, especially in Chinese historiography, either as the An–Shi Rebellion or as the An–Shi Disturbances (). The use of the term ''luàn'' ("chaos") indicates the extreme social instability and population loss which eventually resulted, far beyond the initial consequences of the rebellion. Traditionally, Chinese family names have begun with the family name first. In this case the family name of the initial rebel leader is An. The term ''Ān-Shǐ'' is used to recognize that the rebellion continued after An Lushan's death, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |