|
Mayna Language
Omurano is an unclassified language from Peru. It is also known as Humurana, Roamaina, Numurana, Umurano, and Mayna. The language was presumed to have become extinct by 1958, but in 2011 a rememberer was found who knew some 20 words in Omurano; he claimed that there were still people who could speak it. It was spoken near the Urituyacu River (a tributary of the Marañón River), or on the Nucuray River according to Loukotka (1968). Classification Tovar (1961) linked Omurano to Taushiro (and later Taushiro with Kandoshi); Kaufman (1994) finds the links reasonable, and in 2007 he classified Omurano and Taushiro (but not Kandoshi) as Saparo–Yawan languages. Maynas, once mistaken for a synonym, is a separate language. Despite there being previous proposals linking Omurano with Zaparoan, de Carvalho (2013) finds no evidence that Omurano is related to Zaparoan.de Carvalho. 2013. On Záparoan as a valid genetic unity: Preliminary correspondences and the status of Omurano. ''Rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg , image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg , other_symbol = Great Seal of the State , other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal , national_motto = "Firm and Happy for the Union" , national_anthem = "National Anthem of Peru" , march = "March of Flags" , image_map = PER orthographic.svg , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Lima , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = Peruvian Spanish, Spanish , languages_type = Co-official languages , languages = , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2017 , demonym = Peruvians, Peruvian , government_type = Unitary state, Unitary Semi-presidential system, semi-presidential republic , leader_title1 = President of Peru, President ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
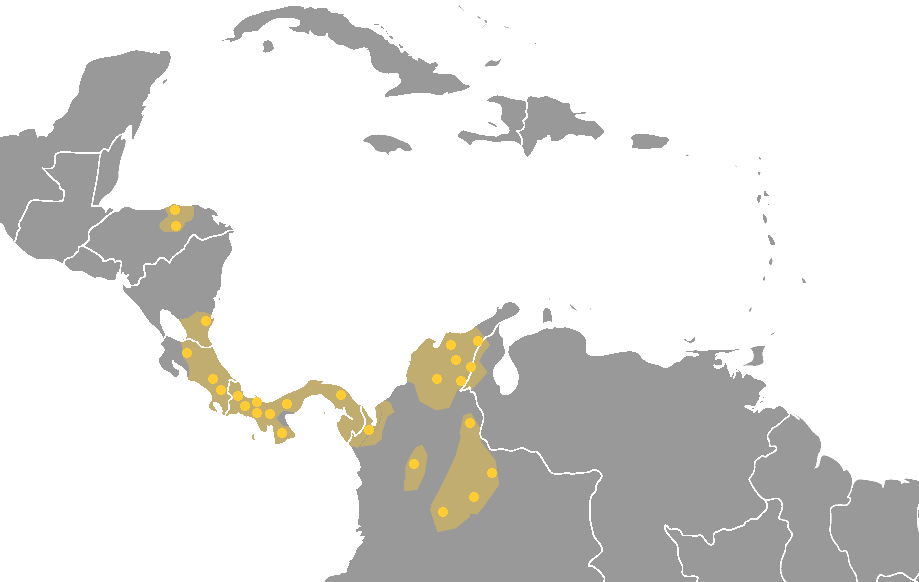
Arawak Languages
Arawakan (''Arahuacan, Maipuran Arawakan, "mainstream" Arawakan, Arawakan proper''), also known as Maipurean (also ''Maipuran, Maipureano, Maipúre''), is a language family that developed among ancient indigenous peoples in South America. Branches migrated to Central America and the Greater Antilles in the Caribbean and the Atlantic, including what is now the Bahamas. Almost all present-day South American countries are known to have been home to speakers of Arawakan languages, the exceptions being Ecuador, Uruguay, and Chile. Maipurean may be related to other language families in a hypothetical Macro-Arawakan stock. Name The name ''Maipure'' was given to the family by Filippo S. Gilij in 1782, after the Maipure language of Venezuela, which he used as a basis of his comparisons. It was renamed after the culturally more important Arawak language a century later. The term ''Arawak'' took over, until its use was extended by North American scholars to the broader Macro-Arawakan propo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of Peru
Peru has many languages in use. One of its official languages, Peruvian Spanish, Spanish, has been in the country since it began being taught in the time of José Pardo y Barreda, José Pardo instead of the country's Native languages, especially the languages in the Andes. In the beginning of the 21st century, it was estimated that in this multilingual country, about 50 very different and popular languages are spoken: which reduces to 44 languages if dialects are considered variants of the same language. The majority of these languages are indigenous peoples, Indigenous, but the most common language is Spanish, the main language that about 94.4% of the population speaks. Spanish is followed by the country's Indigenous languages, especially all types of Quechuan languages, Quechua (11.1% combined) and Aymara languages, Aymara (1.4%), who also have co-official status according to Article 48 of the Constitution of Peru, as well as the languages of the Amazon Basin, Amazon and the Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Languages Of The Andes
*
*
{{disambiguation ...
Indigenous may refer to: *Indigenous peoples *Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention * Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band * Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse * ''Indigenous'' (film), Australian, 2016 See also * Disappeared indigenous women *Indigenous Australians *Indigenous language * Indigenous religion * Indigenous peoples in Canada *Native (other) Native may refer to: People * Jus soli, citizenship by right of birth * Indigenous peoples, peoples with a set of specific rights based on their historical ties to a particular territory ** Native Americans (other) In arts and enterta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiktionary
Wiktionary ( , , rhyming with "dictionary") is a multilingual, web-based project to create a free content dictionary of terms (including words, phrases, proverbs, linguistic reconstructions, etc.) in all natural languages and in a number of artificial languages. These entries may contain definitions, images for illustration, pronunciations, etymologies, inflections, usage examples, quotations, related terms, and translations of terms into other languages, among other features. It is collaboratively edited via a wiki. Its name is a portmanteau of the words ''wiki'' and ''dictionary''. It is available in languages and in Simple English. Like its sister project Wikipedia, Wiktionary is run by the Wikimedia Foundation, and is written collaboratively by volunteers, dubbed "Wiktionarians". Its wiki software, MediaWiki, allows almost anyone with access to the website to create and edit entries. Because Wiktionary is not limited by print space considerations, most of Wiktio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classification Of Indigenous Languages Of The Americas
This is a list of different language classification proposals developed for the indigenous languages of the Americas. The article is divided into North, Central, and South America sections; however, the classifications do not correspond to these divisions. North America ''Glottolog'' 4.1 (2019) ''Glottolog'' 4.1 (2019) recognizes 42 independent families and 31 isolates in North America (73 total). The vast majority are (or were) spoken in the United States, with 26 families and 26 isolates (52 total). ;North American languages families proposed in ''Glottolog'' 4.1 ;Families (42) #Otomanguean (180) #Arawakan (78) # Uto-Aztecan (69) #Algic (46) # Athabaskan-Eyak-Tlingit (45) #Mayan (33) #Chibchan (27) #Salishan (25) # Mixe-Zoque (19) #Siouan (18) #Eskimo–Aleut (12) # Totonacan (12) # Cochimi-Yuman (11) #Iroquoian (11) # Miwok-Costanoan (11) #Kiowa-Tanoan (8) #Muskogean (7) # Pomoan (7) # Chumashan (6) #Wakashan (6) #Caddoan (5) #Misumalpan (5) #Sahaptian (5) # Xincan (5) #C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
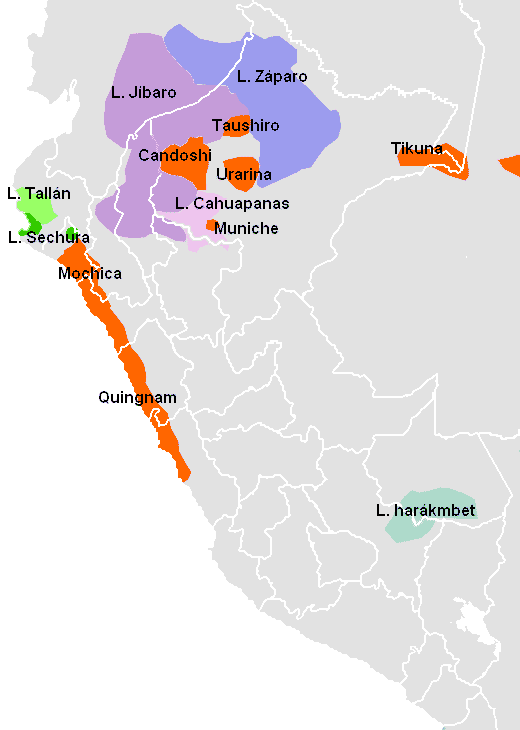
Extinct Languages Of The Marañón River Basin
The Marañón River basin, at a low point in the Andes which made it an attractive location for trade between the Inca Empire and the Amazon basin, once harbored numerous languages which have been poorly attested or not attested at all. Those of the middle reaches of the river, above the Amazon basin, were replaced in historical times by Aguaruna, a Jivaroan language from the Amazon which is still spoken there. The languages further upriver are difficult to identify, due to lack of data. The region was multilingual at the time of the Conquest, and the people largely switched to Spanish rather than to Quechua, though Quechua also expanded during Colonial times. In Ecuador, at the province of Loja, were Palta, Malacato, Rabona, Bolona, and Xiroa. Historical sources suggest these were closely related, and there is some evidence that Palta (see) was a Jivaroan language. The name ''Xiroa'' may be a variant of ''Jivaro''. Rabona is attested by a few words, some of which seem to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Čestmír Loukotka
Čestmír Loukotka (12 November 1895 – 13 April 1966) was a Czechoslovak linguist. His daughter was Jarmila Loukotková. Career Loukotka proposed a Classification of indigenous languages of the Americas#Loukotka (1968), classification for the languages of South America based on several previous works. This classification contained a lot of unpublished material and was therefore superior to all previous classifications. He divided the languages of South America and the Caribbean into 77 different families, based upon similarities of vocabulary and available lists. His classification of 1968 is the most influential and was based upon two previous schemes (1935, 1944), which were similar to those proposed by Paul Rivet (whom he was a student of), although the number of families was increased to 94 and 114. References 1895 births 1958 deaths Linguists from the Czech Republic Paleolinguists Linguists of indigenous languages of the Americas 20th-century linguists { ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leco Language
LECO Corporation, founded in 1936 by Carl Schultz and George Krasl, operates its analytical instrumentation research and development, and manufacturing from its headquarters located in St. Joseph, Michigan. LECO develops and manufactures elemental measurement and molecular Time-of-flight mass spectrometry instrumentation, following ISO 9000 standards. The LECO trademark is an acronym of the original name, Laboratory Equipment Corporation. One of LECO's early products was a combustion analyzer invented by Krasl in 1957 that used crucibles invented by his employee Eugene Bennet., LECO carries out research in many fields of analytical chemistry including protein measurement in foods, sulfur in coal emissions, glow discharge emission in metals, multi-dimensional gas chromatograph mass spectrometry, environmental monitoring, air quality, Metabolomics, and diverse medical and pharmaceutical applications. LECO has been a manufacturer and distributor of metallographic equipment since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaparo Languages
Zaparoan (also Sáparoan, Záparo, Zaparoano, Zaparoana) is an endangered language family of Peru and Ecuador with fewer than 100 speakers. Zaparoan speakers seem to have been very numerous before the arrival of the Europeans. However, their groups have been decimated by imported diseases and warfare, and only a handful of them have survived. Languages There were 39 Zaparoan-speaking tribes at the beginning of the 20th century, every one of them presumably using its own distinctive language or dialect. Most of them have become extinct before being recorded, however, and we have information only about nine of them. * Zaparo group ** Záparo–Conambo *** Záparo (a few speakers left) *** Conambo † ** Arabela–Andoa *** Arabela (50 speakers) *** Andoa † * Iquito–Cahuarano ** Iquito (35 speakers) ** Cahuarano † * Unclassified ** Aushiri † ** ? Omurano † Aushiri and Omurano are included by Stark (1985). Aushiri is generally accepted as Zaparoan, but Omurano rema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urarina Language
Urarina is an isolated language spoken in Peru, specifically in the Loreto Region of Northwest Peru, by the Urarina people. There are around 3,000 speakers in Urarinas District (along the Chambira River). It uses a Latin script. It is also known as Itucali, Simacu or Shimacu. It has a canonical word order of object–verb–subject. Classification The classification of Urarina remains contentious: academics have placed the language in at least four different language families including Panoan, Tupian, Macro-Tucanoan, and Amerind. However, the proposed language families share few similarities with Urarina, meaning it is likely best described as either “unclassified” or as a language isolate. It is usually assumed that it is a language isolate given Urarina’s complete lack of lexical overlap with any languages surrounding Urarina territory. Language contact Jolkesky (2016) notes that there are lexical similarities with the Arawak, Leko Leko may refer to: * Leko (su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |