|
Materiality (auditing)
Materiality is a concept or convention within auditing and accounting relating to the importance/significance of an amount, transaction, or discrepancy. The objective of an audit of financial statements is to enable the auditor to express an opinion whether the financial statements are prepared, in all ''material'' respects, in conformity with an identified financial reporting framework such as Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). As a simple example, an expenditure of ten cents on paper is generally immaterial, and, if it were forgotten or recorded incorrectly, then no practical difference would result, even for a very small business. However, a transaction of many millions of dollars is almost always material, and if it were forgotten or recorded incorrectly, then financial managers, investors, and others would make different decisions as a result of this error than they would have had the error not been made. The assessment of what is material – where to draw t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auditing
An audit is an "independent examination of financial information of any entity, whether profit oriented or not, irrespective of its size or legal form when such an examination is conducted with a view to express an opinion thereon.” Auditing also attempts to ensure that the books of accounts are properly maintained by the concern as required by law. Auditors consider the propositions before them, obtain evidence, and evaluate the propositions in their auditing report. Audits provide third-party assurance to various stakeholders that the subject matter is free from material misstatement. The term is most frequently applied to audits of the financial information relating to a legal person. Other commonly audited areas include: secretarial and compliance, internal controls, quality management, project management, water management, and energy conservation. As a result of an audit, stakeholders may evaluate and improve the effectiveness of risk management, control, and governanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Auditing And Assurance Standards Board
The International Auditing and Assurance Standards Board (IAASB) is an independent standards body that issues standards, like the International Standards on Auditing, quality control guidelines, and other services, to support the international auditing of financial statements. It is a body supported by the International Federation of Accountants (IFAC). The Public Interest Oversight Board provides oversight of the IAASB, ensuring that the standards are in the public interest. To further ensure proposed standards are in the public interest the IAASB consults its Consultative Advisory Group, which is composed of standard setters, various international organizations from the private and public sectors, and regulators. Representatives include a balance of users and prepares of financial statements, and should to the extent practicable be balanced geographically. Founded in March 1978 as the International Auditing Practices Committee (IAPC), the IAASB's current strategic objectives inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
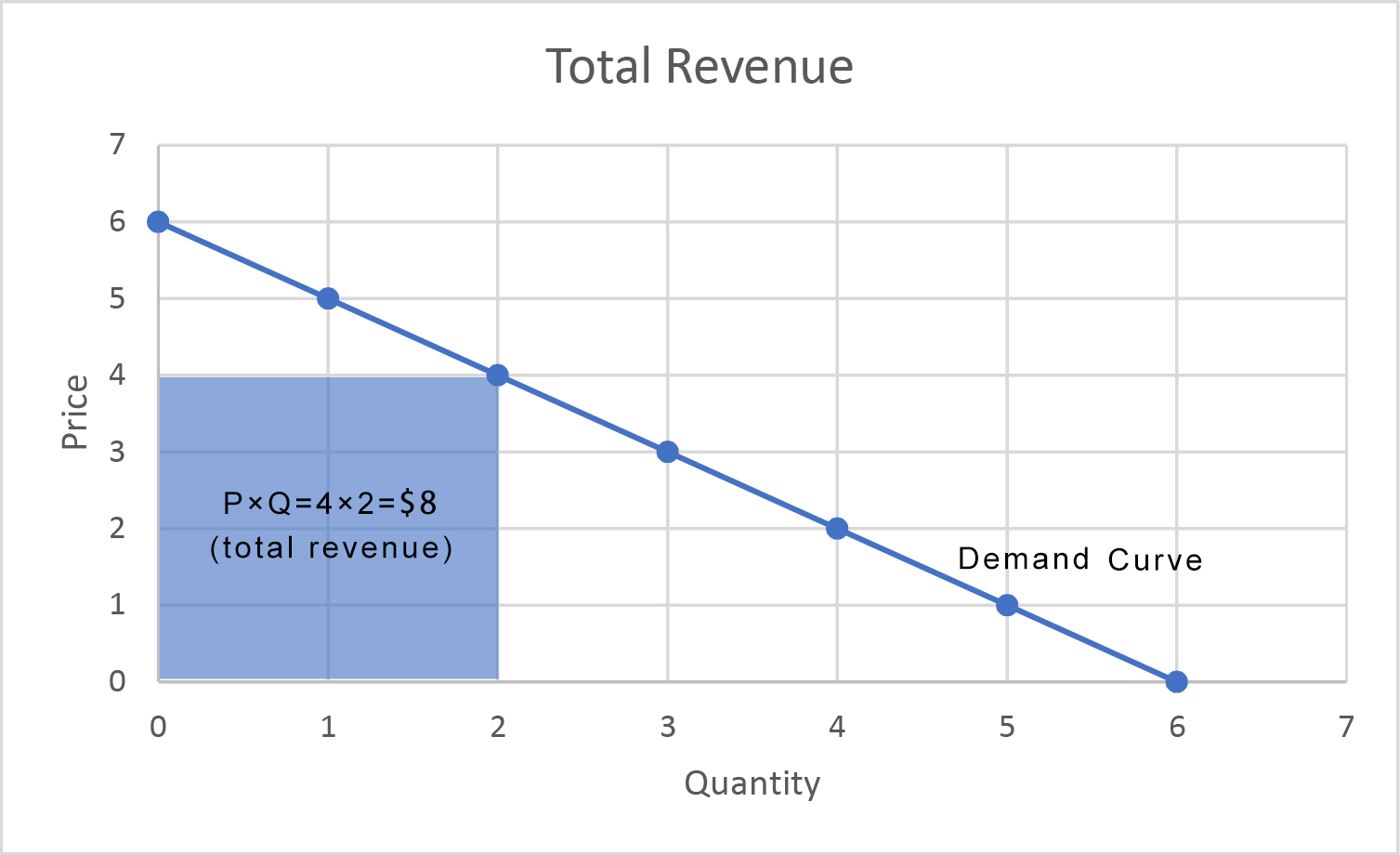
Total Revenue
Total revenue is the total receipts a seller can obtain from selling goods or services to buyers. It can be written as ''P × Q'', which is the price of the goods multiplied by the quantity of the sold goods. Perfect competitor A perfectly competitive firm faces a demand curve that is infinitely elastic. That is, there is exactly one price that it can sell at – the market price. At any lower price it could get more revenue by selling the same amount at the market price, while at any higher price no one would buy any quantity. Total revenue equals the market price times the quantity the firm chooses to produce and sell. Monopoly As with a perfect competitor, a monopolist’s total revenue is the total receipts it can obtain from selling goods or services to buyers. It can be written as P\times Q, which is the price of the goods multiplied by the quantity of the sold goods. A monopolist's total revenue can be graphed as in Figure 1, in which Price (P) is the height of the box ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equity (finance)
In finance, equity is ownership of assets that may have debts or other liabilities attached to them. Equity is measured for accounting purposes by subtracting liabilities from the value of the assets. For example, if someone owns a car worth $24,000 and owes $10,000 on the loan used to buy the car, the difference of $14,000 is equity. Equity can apply to a single asset, such as a car or house, or to an entire business. A business that needs to start up or expand its operations can sell its equity in order to raise cash that does not have to be repaid on a set schedule. In government finance or other non-profit settings, equity is known as "net position" or "net assets". Origins The term "equity" describes this type of ownership in English because it was regulated through the system of equity law that developed in England during the Late Middle Ages to meet the growing demands of commercial activity. While the older common law courts dealt with questions of property title, equi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Assets
In financial accounting, an asset is any resource owned or controlled by a business or an economic entity. It is anything (tangible or intangible) that can be used to produce positive economic value. Assets represent value of ownership that can be converted into cash (although cash itself is also considered an asset). The balance sheet of a firm records the monetaryThere are different methods of assessing the monetary value of the assets recorded on the Balance Sheet. In some cases, the ''Historical Cost'' is used; such that the value of the asset when it was bought in the past is used as the monetary value. In other instances, the present fair market value of the asset is used to determine the value shown on the balance sheet. value of the assets owned by that firm. It covers money and other valuables belonging to an individual or to a business. Assets can be grouped into two major classes: tangible assets and intangible assets. Tangible assets contain various subclasses, includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Income
Income is the consumption and saving opportunity gained by an entity within a specified timeframe, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. Income is difficult to define conceptually and the definition may be different across fields. For example, a person's income in an economic sense may be different from their income as defined by law. An extremely important definition of income is Haig–Simons income, which defines income as ''Consumption + Change in net worth'' and is widely used in economics. For households and individuals in the United States, income is defined by tax law as a sum that includes any wage, salary, profit, interest payment, rent, or other form of earnings received in a calendar year.Case, K. & Fair, R. (2007). ''Principles of Economics''. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. p. 54. Discretionary income is often defined as gross income minus taxes and other deductions (e.g., mandatory pension contributions), and is widely used as a basis to co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calculation
A calculation is a deliberate mathematical process that transforms one or more inputs into one or more outputs or ''results''. The term is used in a variety of senses, from the very definite arithmetical calculation of using an algorithm, to the vague heuristics of calculating a strategy in a competition, or calculating the chance of a successful relationship between two people. For example, multiplying 7 by 6 is a simple algorithmic calculation. Extracting the square root or the cube root of a number using mathematical models is a more complex algorithmic calculation. Statistical estimations of the likely election results from opinion polls also involve algorithmic calculations, but produces ranges of possibilities rather than exact answers. To ''calculate'' means to determine mathematically in the case of a number or amount, or in the case of an abstract problem to deduce the answer usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Securities Regulation
Financial regulation is a form of regulation or supervision, which subjects financial institutions to certain requirements, restrictions and guidelines, aiming to maintain the stability and integrity of the financial system. This may be handled by either a government or non-government organization. Financial regulation has also influenced the structure of banking sectors by increasing the variety of financial products available. Financial regulation forms one of three legal categories which constitutes the content of financial law, the other two being market practices and case law. History In the early modern period, the Dutch were the pioneers in financial regulation. The first recorded ban (regulation) on short selling was enacted by the Dutch authorities as early as 1610. Aims of regulation The objectives of financial regulators are usually: * market confidence – to maintain confidence in the financial system * financial stability – contributing to the protection and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proportionality (mathematics)
In mathematics, two sequences of numbers, often experimental data, are proportional or directly proportional if their corresponding elements have a constant ratio, which is called the coefficient of proportionality or proportionality constant. Two sequences are inversely proportional if corresponding elements have a constant product, also called the coefficient of proportionality. This definition is commonly extended to related varying quantities, which are often called ''variables''. This meaning of ''variable'' is not the common meaning of the term in mathematics (see variable (mathematics)); these two different concepts share the same name for historical reasons. Two functions f(x) and g(x) are ''proportional'' if their ratio \frac is a constant function. If several pairs of variables share the same direct proportionality constant, the equation expressing the equality of these ratios is called a proportion, e.g., (for details see Ratio). Proportionality is closely rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audit Risk
Audit risk (also referred to as residual risk) as per ISA 200 refers to the risk that the auditor expresses an inappropriate opinion when the financial statements are materiality misstated. This risk is composed of: * Inherent risk (IR), the risk involved in the nature of business or transaction. Example, transactions involving exchange of cash may have higher IR than transactions involving settlement by cheques. The term ''inherent risk'' may have other definitions in other contexts.; *Control risk (CR), the risk that a misstatement may not be prevented or detected and corrected due to weakness in the entity's internal control mechanism. Example, control risk assessment may be higher in an entity where separation of duties is not well defined; and * Detection risk (DR), the probability that the auditing procedures may fail to detect existence of a material error or fraud. Detection risk may be due to sampling error or non-sampling error. Audit risk can be calculated as: :AR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Standards On Auditing
International Standards on Auditing (ISA) are professional standards for the auditing of financial information. These standards are issued by the International Auditing and Assurance Standards Board (IAASB). According to Olung M (CAO - L), ISA guides the auditor to add value to the assignment hence building confidence of investors. The standards cover various areas of auditing, including respective responsibilities, audit planning, Internal Control, audit evidence, using the work of other experts, audit conclusions and audit reports, and standards for specialized areas. Use of the ISAs * European Union: The Audit Directive of 17 May 2006 enforces the use of the ''International Standards on Auditing'' for all Statutory audits to be performed in the European Union. The Audit Directive of 17 May 2006 is important in order to ensure a high quality for all statutory audits required by Community law requiring all statutory audits be carried out on the basis of all international audi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assurance Services
Assurance service is an independent professional service, typically provided by Chartered Accountant, Chartered or Certified Public Accountants or Chartered Certified Accountants, with the goal of improving information or the context of information so that decision makers can make more informed, and presumably better, decisions. Assurance services provide independent and professional opinions that reduce information risk (risk from incorrect information). Definition and distinction from other services The technical definition of assurance requires five components set out in theInternational Framework for Assurance Engagements # A three-party relationship – the responsible party who prepares the information to be assured; the independent practitioner who assures the information; and the users who are expected to rely on the information. In the case of an audit, the responsible party is the management of the company, the practitioner is the audit firm and the users are primarily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |