|
Marienbad (video Game)
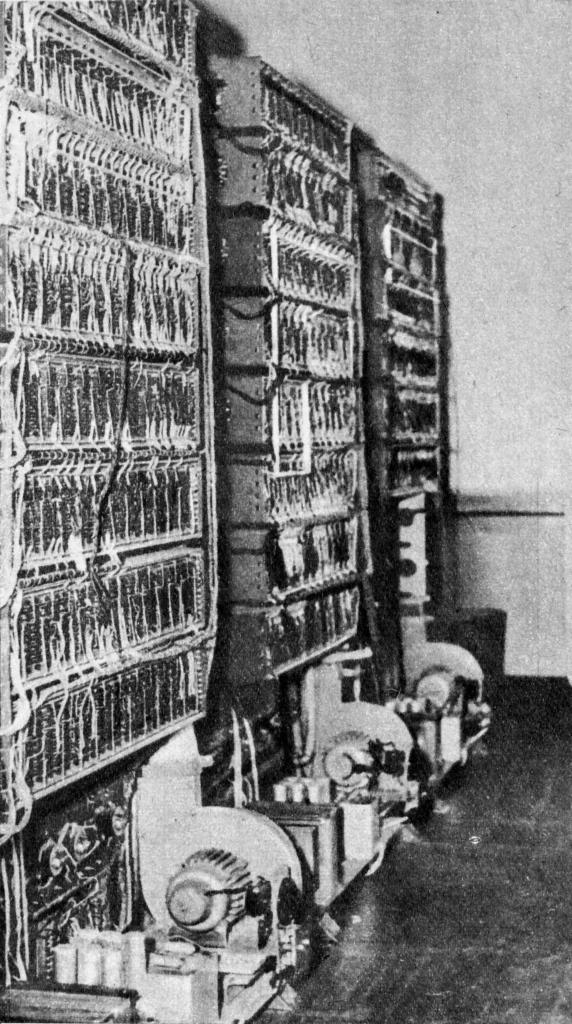
''Marienbad'' was a 1962 Polish puzzle mainframe game created by Elwro engineer Witold Podgórski in Wrocław, Poland for its Odra 1003. It was an adaption of the logic game nim. Inspired by the discussion in the magazine ''Przekrój'' of a variant of nim in the 1961 film ''Last Year at Marienbad'' (''L'Année dernière à Marienbad''), named "Marienbad" by the magazine, Podgórski programmed the game for the in-development 1003 mainframe, released in 1963. The game had players opposing the computer in alternating rounds of removing matches from a set, with the last player to take a match the loser. As the computer always played the optimal moves, it was essentially unbeatable. ''Marienbad'' did not spread far beyond its initial location. Elwro did not produce or advertise the game, though Podgórski recreated it at the Wojskowa Akademia Techniczna (Military University of Technology in Warsaw). The game fell into obscurity, with no pictures or documentation surviving to recrea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odra (computer)
Odra was a line of computers manufactured in Wrocław, Poland. The name comes from the Odra river that flows through the city of Wrocław. Overview The production started in 1959–1960. Models 1001, 1002, 1003, 1013, 1103, 1204 were of original Polish construction. Models 1304 and 1305 were functional counterparts of ICL 1905 and 1906 due to software agreement. The last model was 1325 based on two models by ICL. The computers were built at the Elwro manufacturing plant, which was closed in 1989. Odra 1002 was capable of only 100–400 operations per second. In 1962, Witold Podgórski, an employee of Elwro, managed to create a computer game on a prototype of Odra 1003; it was an adaptation of a variant of Nim, as depicted in the film ''Last Year at Marienbad''. The computer could play a perfect game and was guaranteed to win. The game was never distributed outside of the Elwro company, but its versions appeared elsewhere. It was probably the first Polish computer game in his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museum Of Technology, Warsaw
Muzeum Techniki w Warszawie is a museum in Warsaw, Poland. It was established in 1955. It is located in the Palace of Culture & Science. Exhibits include motorbikes, aeroplanes, 19th century musical boxes, and historic cars. References External links * * Technology Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, science, ... Museums established in 1955 Technology museums Science museums in Poland 1955 establishments in Poland {{Warsaw-struct-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The History Of Video Games
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with pronouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of pronoun ''thee'') when followed by a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FIMALAC
FIMALAC (known as Financière Marc de Lacharrière) is a French holding company focusing on credit rating and risk management companies. It manages commercial real estate through North Colonnade Ltd, and private equity funds through its subsidiary Fimalac Développement. History FIMALAC was created by Marc Ladreit de Lacharrière in 1991.Lacharrière : «Finance et culture sont complémentaires», in ''L'Express'', 05/10/200/ref> He serves as the CEO, and holds 100% of the shares of the FIMALAC Group, that holds ~80% of FIMALAC. It is headquartered in Paris. It operates in the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, France and other members of the European Union, Asia, and South America. In 2005, FIMALAC acquired Algorithmics Inc., which it sold to IBM in October 2011. That year, it acquired 40% of Groupe Lucien Barrière. In 2018, FIMALAC sold its last 20% of Fitch Ratings to Hearst Communications. Divisions FIMALAC operates in the real estate sector, mainly through Nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early History Of Video Games
The history of video games spans a period of time between the invention of the first electronic games and today, covering many inventions and developments. Video gaming reached mainstream popularity in the 1970s and 1980s, when arcade video games, gaming consoles and home computer games were introduced to the general public. Since then, video gaming has become a popular form of entertainment and a part of modern culture in most parts of the world. The early history of video games, therefore, covers the period of time between the first interactive electronic game with an electronic display in 1947, the first true video games in the early 1950s, and the rise of early arcade video games in the 1970s (''Pong'' and the beginning of the first generation of video game consoles with the Magnavox Odyssey, both in 1972). During this time there was a wide range of devices and inventions corresponding with large advances in computing technology, and the actual first video game is dependent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nimrod (computer)
The Nimrod, built in the United Kingdom by Ferranti for the 1951 Festival of Britain, was an early computer custom-built to play Nim, inspired by the earlier Nimatron. The twelve-by-nine-by-five-foot (3.7-by-2.7-by-1.5-meter) computer, designed by John Makepeace Bennett and built by engineer Raymond Stuart-Williams, allowed exhibition attendees to play a game of Nim against an artificial intelligence. The player pressed buttons on a raised panel corresponding with lights on the machine to select their moves, and the Nimrod moved afterward, with its calculations represented by more lights. The speed of the Nimrod's calculations could be reduced to allow the presenter to demonstrate exactly what the computer was doing, with more lights showing the state of the calculations. The Nimrod was intended to demonstrate Ferranti's computer design and programming skills rather than to entertain, though Festival attendees were more interested in playing the game than the logic behind it. Af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wild Hunt
The Wild Hunt is a folklore motif (Motif E501 in Stith Thompson's Motif-Index of Folk-Literature) that occurs in the folklore of various northern European cultures. Wild Hunts typically involve a chase led by a mythological figure escorted by a ghostly or supernatural group of hunters engaged in pursuit. The leader of the hunt is often a named figure associated with Odin in Germanic legends, but may variously be a historical or legendary figure like Theodoric the Great, the Danish king , the Welsh psychopomp , biblical figures such as Herod, Cain, Gabriel, or the Devil, or an unidentified lost soul or spirit either male or female. The hunters are generally the souls of the dead or ghostly dogs, sometimes fairies, Valkyries, or elves. Seeing the Wild Hunt was thought to presage some catastrophe such as war or plague, or at best the death of the one who witnessed it. People encountering the Hunt might also be abducted to the underworld or the fairy kingdom. In some instances, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gry Online
''Gry-Online'' is a group of Polish websites devoted to computer games and electronic entertainment. Founded by Mariusz Klamra, Wojciech Antonowicz and Rafał Swaczyna, the group has grown to include Gry-Online, TVGry.pl, Gameplay.pl, and Gamepressure. In 2017, the German branch of the French publisher Webedia Group bought Gry-OnLine from Empik, thereby entering the Polish market. The group won the 2010 Wings of Business award in the category of "Micro-reliable and dynamic company". Gry-Online.pl The paramount member of the group is the website Gry-Online.pl, which was launched January 1, 2001, and has undergone numerous overhauls and redesigns since. Its editor-in-chief is currently Krystian "U.V. Impaler" Smoszna. The position was formerly occupied by Borys "Shuck" Zajączkowski and Łukasz "Verminus" Malik. Gry-Online.pl publishes information and articles about video games for PC, Xbox ( 360 and Xbox One), PlayStation (PlayStation Vita, PlayStation Portable, PlayStation 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XYZ (computer)
XYZ was the first UMC (computer), Universal Digital Machine from the family of early computers built and launched in Poland in 1958. It was ahead of by a few months, while the earlier was not fully launched.Konstrukcje polskie: XYZ, Empacher A.B.Maszyny liczą same?/ Adam B. Empacher / Katalog HINT, Wiedza Powszechna, 1960, s. 114-122 (in Polish) Construction XYZ computer was built and launched in Warsaw at ul. Śniadeckich 8, at the premises of the Bureau of Calculations and Programs of the Mathematical Apparatus Department of the Polish Academy of Sciences (later the Institute of Mathematical Machines). The team was led by professor . XYZ was a laboratory model of a utility machine; the series was created on the basis of this computer. The logical organization was modeled on the simplified IBM 701, but the electronics were based on the Flip-flop (electronics), dynamic flip-flops of the M-20 machine, requiring twice as few lamps. The design of the flip-flops and gates was der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Łódź
Łódź, also rendered in English as Lodz, is a city in central Poland and a former industrial centre. It is the capital of Łódź Voivodeship, and is located approximately south-west of Warsaw. The city's coat of arms is an example of canting arms, canting, as it depicts a boat ( in Polish language, Polish), which alludes to the city's name. As of 2022, Łódź has a population of 670,642 making it the country's List of cities and towns in Poland, fourth largest city. Łódź was once a small settlement that first appeared in 14th-century records. It was granted city rights, town rights in 1423 by Polish King Władysław II Jagiełło and it remained a private town of the Kuyavian bishops and clergy until the late 18th century. In the Second Partition of Poland in 1793, Łódź was annexed to Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia before becoming part of the Napoleonic Duchy of Warsaw; the city joined Congress Poland, a Russian Empire, Russian client state, at the 1815 Congress of Vien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tajemnica Statuetki
''Tajemnica Statuetki'' is a Polish-language adventure game developed and published by Metropolis Software House for DOS-based computers in 1993. While it was never released in English, it is known in the English-speaking world as ''The Mystery of the Statuette''. The game was conceived by a team led by Adrian Chmielarz, who used photographs taken in France as static screens within the game. The first title in the adventure game genre that was produced in Poland, its plot revolves around a fictional Interpol agent named John Pollack trying to solve a mystery associated with the thefts of ancient artifacts around the world. At the time of the game's release, software piracy was rampant in Poland; the game, however, sold between 4,000 and 6,000 copies, becoming very popular there. ''Tajemnica Statuetki'' was praised for its plot and for being a cultural milestone that helped advance and legitimise the Polish gaming industry despite attracting minor criticism for its game mechanics a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)