|
Maresin
Maresin 1 (MaR1 or 7''R'',14''S''-dihydroxy-4''Z'',8''E'',10''E'',12''Z'',16''Z'',19''Z''-docosahexaenoic acid) is a macrophage-derived mediator of inflammation resolution coined from macrophage mediator in resolving inflammation. Maresin 1, and more recently defined maresins, are 12-lipoxygenase-derived metabolites of the omega-3 fatty acid, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), that possess potent anti-inflammatory, pro-resolving, protective, and pro-healing properties similar to a variety of other members of the specialized proresolving mediators (SPM) class of polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) metabolites. SPM are dihydroxy, trihydroxy, and epoxy-hydroxy metabolites of long chain PUFA made by certain dioxygenase enzymes viz., cyclooxygenases and lipoxygenases. In addition to the maresins, this class of mediators includes: the 15-lipoxygenase (i.e. ALOX15 and/or possibly ALOX15B)-derived Lipoxin A4 and B4 metabolites of the omega 6 fatty acid, arachidonic acid; the cyclooxygenase 2- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specialized Proresolving Mediators
Specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPM, also termed specialized proresolving mediators) are a large and growing class of cell signaling molecules formed in cells by the metabolism of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) by one or a combination of lipoxygenase, cyclooxygenase, and cytochrome P450 monooxygenase enzymes. Pre-clinical studies, primarily in animal models and human tissues, implicate SPM in orchestrating the resolution of inflammation. Prominent members include the resolvins and Protectin D1, protectins. SPM join the long list of other physiological agents which tend to limit inflammation (see ) including glucocorticoids, interleukin 10 (an anti-inflammatory cytokine), interleukin 1 receptor antagonist (an inhibitor of the action of pro-inflammatory cytokine, interleukin 1), annexin A1 (an inhibitor of formation of pro-inflammatory metabolites of polyunsaturated fatty acids), and the gaseous resolvins, carbon monoxide (see ), nitric oxide (see ), and hydrogen sulfide (se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12-lipoxygenase
ALOX12 (), also known as arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase, 12-lipoxygenase, 12''S''-Lipoxygenase, 12-LOX, and 12''S''-LOX is a lipoxygenase-type enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''ALOX12'' gene which is located along with other lipoyxgenases on chromosome 17p13.3. ALOX12 is 75 kilodalton protein composed of 663 amino acids. Nomenclature Other systematic names for ALOX12 include 12S-Lipoxygenase, platelet-type 12-lipoxygenase, arachidonate:oxygen 12-oxidoreductase, Delta12-lipoxygenase, 12Delta-lipoxygenase, and C-12 lipoxygenase. ALOX12, often termed plate platelet-type 12-lipoxygenase, is distinguished from leukocyte-type 12-lipoxygenase which is found in mice, rats, cows, and pigs but not humans. Leukocyte-type 12-lipoxygenase in these animal species shares 73-86% amino acid identity with human ALOX15 but only 57-66% identity with human platelet-type 12-lipoxygenase and, like ALOX15, metabolizes arachidonic acid primarily to 15(''S'')-hydroperoxy-5''Z'',8''Z'',11''Z'',13' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris, and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. The process is called phagocytosis, which acts to defend the host against infection and injury. These large phagocytes are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting other immune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulatory T Cells
The regulatory T cells (Tregs or Treg cells), formerly known as suppressor T cells, are a subpopulation of T cells that modulate the immune system, maintain tolerance to self-antigens, and prevent autoimmune disease. Treg cells are immunosuppressive and generally suppress or downregulate induction and proliferation of effector T cells. Treg cells express the biomarkers CD4, FOXP3, and CD25 and are thought to be derived from the same lineage as naïve CD4+ cells. Because effector T cells also express CD4 and CD25, Treg cells are very difficult to effectively discern from effector CD4+, making them difficult to study. Research has found that the cytokine transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is essential for Treg cells to differentiate from naïve CD4+ cells and is important in maintaining Treg cell homeostasis. Mouse models have suggested that modulation of Treg cells can treat autoimmune disease and cancer and can facilitate orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is called a phagocyte. In a multicellular organism's immune system, phagocytosis is a major mechanism used to remove pathogens and cell debris. The ingested material is then digested in the phagosome. Bacteria, dead tissue cells, and small mineral particles are all examples of objects that may be phagocytized. Some protozoa use phagocytosis as means to obtain nutrients. History Phagocytosis was first noted by Canadian physician William Osler (1876), and later studied and named by Élie Metchnikoff (1880, 1883). In immune system Phagocytosis is one main mechanisms of the innate immune defense. It is one of the first processes responding to infection, and is also one of the initiating branches of an adaptive immune response. Although mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptotic
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For an average human child between eight and fourteen years old, approximately twenty to thirty billion cells die per day. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic bod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efferocytosis
In cell biology, efferocytosis (from ''efferre'', Latin for 'to take to the grave', 'to bury') is the process by which apoptotic cells are removed by phagocytic cells. It can be regarded as the 'burying of dead cells'. During efferocytosis, the cell membrane of phagocytic cells engulfs the apoptotic cell, forming a large fluid-filled vesicle containing the dead cell. This ingested vesicle is called an efferosome (in analogy to the term phagosome). This process is similar to macropinocytosis. For apoptosis, the effect of efferocytosis is that dead cells are removed before their membrane integrity is breached and their contents leak into the surrounding tissue. This prevents exposure of tissue to toxic enzymes, oxidants and other intracellular components such as proteases and caspases. Efferocytosis can be performed not only by 'professional' phagocytic cells such as macrophages or dendritic cells, but also by many other cell types including epithelial cells and fibroblasts. To disti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planaria
''Planaria'' is a genus of planarians in the family Planariidae. When an individual is cut into pieces, each piece has the ability to regenerate into a fully formed individual. Description Currently the genus ''Planaria'' is defined as freshwater triclads with oviducts that unite to form a common oviduct without embracing the bursa copulatrix and with an adenodactyl present in the male atrium. The testes occur along the whole body. Planaria originally have habitats in dark, murky water which results in such sensitivity (Paskin et al., 2014). They are also sensitive to other stimuli such as chemical gradients, vibration, magnetic and electric fields (Deochand et al., 2018). Their central nervous system includes the anterior (head, brain and eyes) and middle (abdominal trunk and pharynx) (Deochand et al., 2018). Diet The food of ''Planaria'' species includes freshwater gastropods, tubificid worms, and freshwater arthropods, such as isopods of the genus ''Asellus'' and chiro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platelets
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby initiating a blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments of cytoplasm that are derived from the megakaryocytes of the bone marrow or lung, which then enter the circulation. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other vertebrates (e.g. birds, amphibians), thrombocytes circulate as intact mononuclear cells. One major function of platelets is to contribute to hemostasis: the process of stopping bleeding at the site of interrupted endothelium. They gather at the site and, unless the interruption is physically too large, they plug the hole. First, platelets attach to substances outside the interrupted endothelium: ''adhesion''. Second, they change shape, turn on receptors and secrete chemical messengers: ''activatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
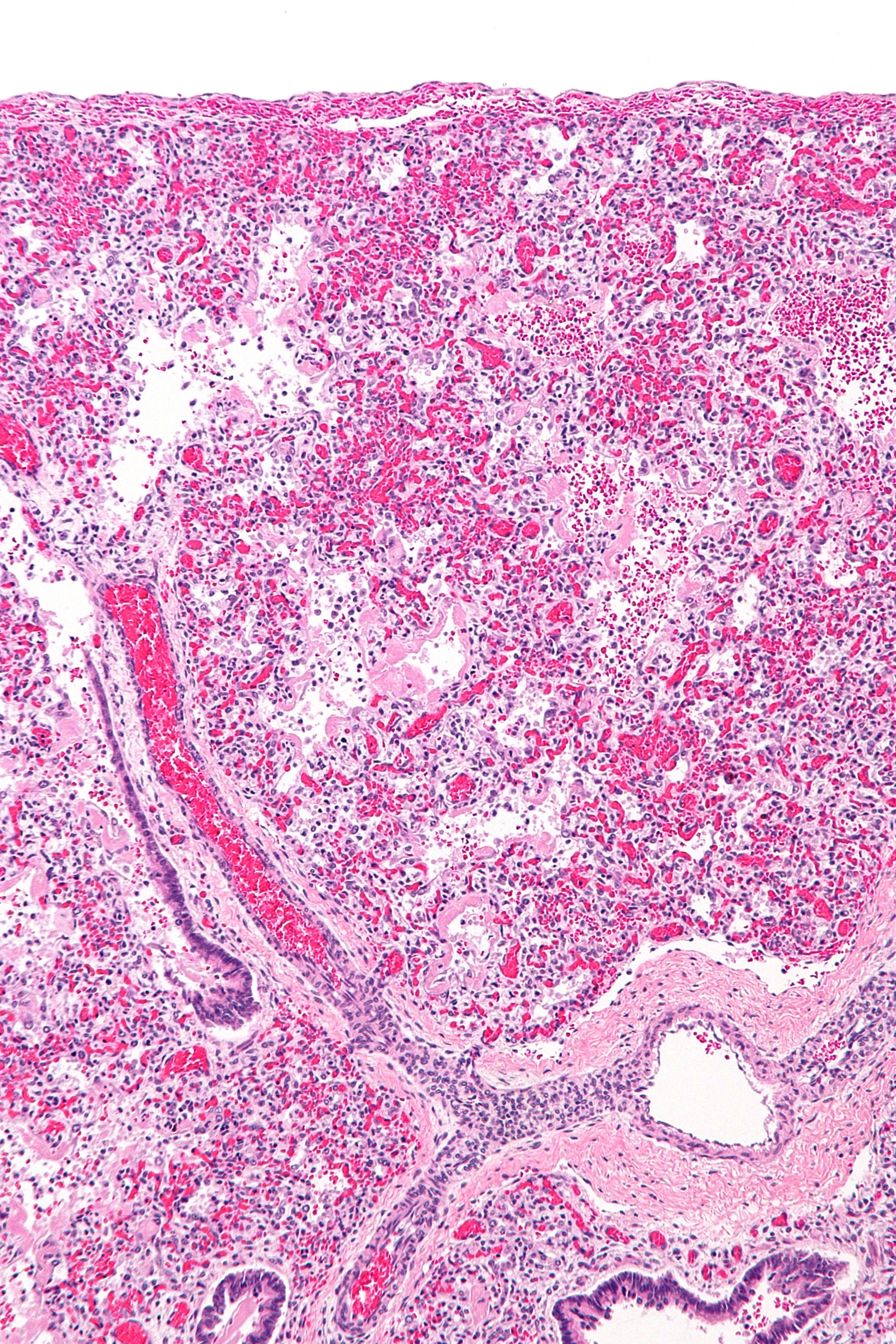
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a type of respiratory failure characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath (dyspnea), rapid breathing (tachypnea), and bluish skin coloration (cyanosis). For those who survive, a decreased quality of life is common. Causes may include sepsis, pancreatitis, trauma, pneumonia, and aspiration. The underlying mechanism involves diffuse injury to cells which form the barrier of the microscopic air sacs of the lungs, surfactant dysfunction, activation of the immune system, and dysfunction of the body's regulation of blood clotting. In effect, ARDS impairs the lungs' ability to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide. Adult diagnosis is based on a PaO2/FiO2 ratio (ratio of partial pressure arterial oxygen and fraction of inspired oxygen) of less than 300 mm Hg despite a positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) of more than 5 cm H2O. Cardiogenic pulmonary edema, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involved, with the same joints typically involved on both sides of the body. The disease may also affect other parts of the body, including skin, eyes, lungs, heart, nerves and blood. This may result in a low red blood cell count, inflammation around the lungs, and inflammation around the heart. Fever and low energy may also be present. Often, symptoms come on gradually over weeks to months. While the cause of rheumatoid arthritis is not clear, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves the body's immune system attacking the joints. This results in inflammation and thickening of the joint capsule. It also affects the underlying bone and cartilage. The diagnosis is made mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-lipoxygenase
Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase, also known as ALOX5, 5-lipoxygenase, 5-LOX, or 5-LO, is a non-heme iron-containing enzyme (EC 1.13.11.34) that in humans is encoded by the ''ALOX5'' gene. Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase is a member of the lipoxygenase family of enzymes. It transforms essential fatty acids (EFA) substrates into leukotrienes as well as a wide range of other biologically active products. ALOX5 is a current target for pharmaceutical intervention in a number of diseases. Gene The ''ALOX5'' gene, which occupies 71.9 kilobase pairs (kb) on chromosome 10 (all other human lipoxygenases are clustered together on chromosome 17), is composed of 14 exons divided by 13 introns encoding the mature 78 kilodalton (kD) ALOX5 protein consisting of 673 amino acids. The gene promoter region of ALOX5 contains 8 GC boxes but lacks TATA boxes or CAT boxes and thus resembles the gene promoters of typical housekeeping genes. Five of the 8 GC boxes are arranged in tandem and are recognized by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |