|
Marcus Appius Bradua
Marcus Appius Bradua, also known by his full name Marcus Atilius Metilius BraduaBirley, ''Roman government'', p. 112 (Greek: ''╬£╬▒Žü╬║Žī╬Į ╬åŽĆŽĆ╬╣╬┐╬Į ╬ÆŽü╬▒╬┤╬┐ŽŹ╬▒╬Į'' This version of his name is known from an honorific Greek stone inscription dedicated to Bradua at Olympia, Greece. Birley, ''Roman government'', p. 112) was a Roman politician who lived in the second half of the 1st century and the first half of the 2nd century in the Roman Empire. Biography Bradua was a member of the gens Atilia. He was born and raised in a Roman family of consular rank, possibly of Patrician rank. Bradua originated in Cisalpina (northern Italy). His father, Marcus Atilius Postumus Bradua, served as a proconsul of the Asia Province under the Emperor Domitian (81ŌĆō96). His second nomen, ''Metilius'', suggests that his mother may have been a Metilia. If so, his uncle could be the governor Publius Metilius Nepos. Probably due to his patrician rank, Bradua went from the quaestorship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koine. Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praetor
Praetor ( , ), also pretor, was the title granted by the government of Ancient Rome to a man acting in one of two official capacities: (i) the commander of an army, and (ii) as an elected '' magistratus'' (magistrate), assigned to discharge various duties. The functions of the magistracy, the ''praetura'' (praetorship), are described by the adjective: the ''praetoria potestas'' (praetorian power), the ''praetorium imperium'' (praetorian authority), and the ''praetorium ius'' (praetorian law), the legal precedents established by the ''praetores'' (praetors). ''Praetorium'', as a substantive, denoted the location from which the praetor exercised his authority, either the headquarters of his '' castra'', the courthouse (tribunal) of his judiciary, or the city hall of his provincial governorship. History of the title The status of the ''praetor'' in the early republic is unclear. The traditional account from Livy claims that the praetorship was created by the Sextian-Licinian Rogatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa (Roman Province)
Africa Proconsularis was a Roman province on the northern African coast that was established in 146 BC following the defeat of Carthage in the Third Punic War. It roughly comprised the territory of present-day Tunisia, the northeast of Algeria, and the coast of western Libya along the Gulf of Sirte. The territory was originally inhabited by Berber people, known in Latin as ''Mauri'' indigenous to all of North Africa west of Egypt; in the 9th century BC, Phoenicians built settlements along the Mediterranean Sea to facilitate shipping, of which Carthage rose to dominance in the 8th century BC until its conquest by the Roman Republic. It was one of the wealthiest provinces in the western part of the Roman Empire, second only to Italy. Apart from the city of Carthage, other large settlements in the province were Hadrumetum (modern Sousse, Tunisia), capital of Byzacena, and Hippo Regius (modern Annaba, Algeria). History Rome's first province in northern Africa was established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appius Annius Trebonius Gallus (consul 139)
The gens Annia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Livy mentions a Lucius Annius, praetor of the Roman colony of Setia, in 340 BC, and other Annii are mentioned at Rome during this period. Members of this gens held various positions of authority from the time of the Second Punic War, and Titus Annius Luscus attained the consulship in 153 BC. In the second century AD, the Annii gained the Empire itself; Marcus Aurelius was descended from this family. Origin The Annii claimed a descent from the goddess Anna Perenna, the sister of Dido, portrayed on the coins of Gaius Annius Luscus. The nomen ''Annius'' was classified by Chase as one of Picentine origin, while the first of the Annii appearing in history (in 340 BC) was praetor of Setia, originally a Volscian town, captured by the Romans in 382 BC. Both the Picentes and the Volsci spoke Umbrian languages, so it may be that Annius was a member of an old Volscian family, rather than one of the Latin colonists, on whose behal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atilia Caucidia Tertulla
Atilia Caucidia TertullaPomeroy, ''The murder of Regilla: a case of domestic violence of antiquity'' p. 15 (flourished 2nd century) was an aristocratic woman from Ancient Rome, Ancient Roman society. Atilia was a member of the Atilia gens and was born into a family of consular rank, probably of Patrician (ancient Rome), Patrician rank.Birley, ''The Roman government of Britain'' p. 112 Atilia was the daughter of the Roman Senate, Roman Senator, Consul and Governor Marcus Appius Bradua and Caucidia Tertulla. Her brother was Marcus Atilius Metilius Bradua Caucidius Tertullus...Bassus.Birley, ''The Roman government of Britain'' p. 113-114 He served as a polyonymous Proconsul of the Africa Province under Roman Emperor Antoninus Pius (138-161). Atilia was an aristocratic, wealthy woman, little is known about her life. She married the distinguished Roman Senator Appius Annius Trebonius Gallus (consul 139), Appius Annius Trebonius Gallus. The father of Atilia and the father of Annius Gallu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etruscan Civilization
The Etruscan civilization () was developed by a people of Etruria in ancient Italy with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, roughly what is now Tuscany, western Umbria, and northern Lazio, as well as what are now the Po Valley, Emilia-Romagna, south-eastern Lombardy, southern Veneto, and western Campania. The earliest evidence of a culture that is identifiably Etruscan dates from about 900BC. This is the period of the Iron Age Villanovan culture, considered to be the earliest phase of Etruscan civilization, which itself developed from the previous late Bronze Age Proto-Villanovan culture in the same region. Etruscan civilization endured until it was assimilated into Roman society. Assimilation began in the late 4thcenturyBC as a result of the RomanŌĆōEtruscan Wars; it accelerated with the grant of Roman citizenship in 90 BC, and became complete in 27 BC, when the Etr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoninus Pius
Antoninus Pius (Latin: ''Titus Aelius Hadrianus Antoninus Pius''; 19 September 86 ŌĆō 7 March 161) was Roman emperor from 138 to 161. He was the fourth of the Five Good Emperors from the NervaŌĆōAntonine dynasty. Born into a senatorial family, Antoninus held various offices during the reign of Emperor Hadrian. He married Hadrian's niece Faustina, and Hadrian adopted him as his son and successor shortly before his death. Antoninus acquired the cognomen Pius after his accession to the throne, either because he compelled the Senate to deify his adoptive father, or because he had saved senators sentenced to death by Hadrian in his later years. His reign is notable for the peaceful state of the Empire, with no major revolts or military incursions during this time. A successful military campaign in southern Scotland early in his reign resulted in the construction of the Antonine Wall. Antoninus was an effective administrator, leaving his successors a large surplus in the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadrian
Hadrian (; la, Caesar Tr├ói─ünus Hadri─ünus ; 24 January 76 ŌĆō 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica (close to modern Santiponce in Spain), a Roman ''municipium'' founded by Italic settlers in Hispania Baetica and he came from a branch of the gens Aelia that originated in the Picenean town of Hadria, the ''Aeli Hadriani''. His father was of senatorial rank and was a first cousin of Emperor Trajan. Hadrian married Trajan's grand-niece Vibia Sabina early in his career before Trajan became emperor and possibly at the behest of Trajan's wife Pompeia Plotina. Plotina and Trajan's close friend and adviser Lucius Licinius Sura were well disposed towards Hadrian. When Trajan died, his widow claimed that he had nominated Hadrian as emperor immediately before his death. Rome's military and Senate approved Hadrian's succession, but four leading senators were unlawfully put to death soon after. They had opposed Hadrian or seemed to threaten his s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa Province
Africa Proconsularis was a Roman province on the northern African coast that was established in 146 BC following the defeat of Carthage in the Third Punic War. It roughly comprised the territory of present-day Tunisia, the northeast of Algeria, and the coast of western Libya along the Gulf of Sirte. The territory was originally inhabited by Berber people, known in Latin as ''Mauri'' indigenous to all of North Africa west of Egypt; in the 9th century BC, Phoenicians built settlements along the Mediterranean Sea to facilitate shipping, of which Carthage rose to dominance in the 8th century BC until its conquest by the Roman Republic. It was one of the wealthiest provinces in the western part of the Roman Empire, second only to Italy. Apart from the city of Carthage, other large settlements in the province were Hadrumetum (modern Sousse, Tunisia), capital of Byzacena, and Hippo Regius (modern Annaba, Algeria). History Rome's first province in northern Africa was established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
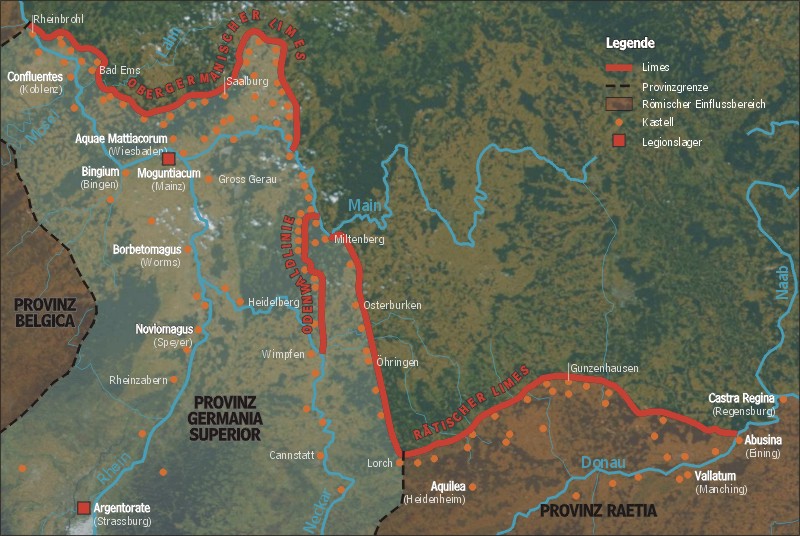
Germania Superior
Germania Superior ("Upper Germania") was an imperial province of the Roman Empire. It comprised an area of today's western Switzerland, the French Jura and Alsace regions, and southwestern Germany. Important cities were Besan├¦on ('' Vesontio''), Strasbourg (''Argentoratum''), Wiesbaden ('' Aquae Mattiacae''), and Germania Superior's capital, Mainz (''Mogontiacum''). It comprised the Middle Rhine, bordering on the ''Limes Germanicus'', and on the Alpine province of Raetia to the south-east. Although it had been occupied militarily since the reign of Augustus, Germania Superior (along with Germania Inferior) was not made into an official province until c. 85 AD. Origin Initial Roman involvement The terms, "Upper Germania" and "Lower Germania" do not appear in the ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico'' of Julius Caesar, yet he writes about reports that the people who lived in those regions were referred to as "Germani" locally, a term used for a tribe that the Romans called the Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germania Inferior
Germania Inferior ("Lower Germania") was a Roman province from AD 85 until the province was renamed Germania Secunda in the fourth century, on the west bank of the Rhine bordering the North Sea. The capital of the province was Colonia Agrippinensis (modern-day Cologne). Geography According to Ptolemy (2.9), Germania Inferior included the Rhine from its mouth up to the mouth of the ''Obringa'', a river identified with either the Aar or the Moselle. The territory included modern-day Luxembourg, the southern Netherlands, part of Belgium, and part of North Rhine-Westphalia in Germany, west of the Rhine. The principal settlements of the province were Castra Vetera and Colonia Ulpia Traiana (both near Xanten), Coriovallum (Heerlen), Albaniana ( Alphen aan den Rijn), Lugdunum Batavorum (Katwijk), Forum Hadriani (Voorburg), Ulpia Noviomagus Batavorum (Nijmegen), Traiectum (Utrecht), Atuatuca Tungrorum (Tongeren), Bona (Bonn), and Colonia Agrippinensis (Cologne), the capital of Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered was raised to the status of a Roman province. Julius Caesar invaded Britain in 55 and 54 BC as part of his Gallic Wars. According to Caesar, the Britons had been overrun or culturally assimilated by other Celtic tribes during the British Iron Age and had been aiding Caesar's enemies. He received tribute, installed the friendly king Mandubracius over the Trinovantes, and returned to Gaul. Planned invasions under Augustus were called off in 34, 27, and 25 BC. In 40 AD, Caligula assembled 200,000 men at the Channel on the continent, only to have them gather seashells ('' musculi'') according to Suetonius, perhaps as a symbolic gesture to proclaim Caligula's victory over the sea. Three years later, Claudius directed four legi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |