|
MV Agusta RVS 1
The MV Agusta RVS#1 is a limited-edition motorcycle produced by the Italians, Italian manufacturer MV Agusta. This machine is the first product of MV Agusta's “Reparto Veicoli Speciali” (RVS) (Special Vehicles Operations) department, and a reinterpretation of the ''MV Agusta Dragster series, MV Agusta Dragster''. It is powered by a 150 bhp (110 kW) version of the company's 800 cc three-cylinder engine. The machines are all hand assembled and went on sale in 2019. Background MV Agusta's CEO, Giovanni Castiglioni, set up a new division, the RVS, to design special and premium models. The first project was a reinterpretation of the ''Dragster''. The machine was designed in conjunction with the C.R.C. (Castiglioni Research Centre) who provided the engineering expertise. Technical details Engine The 799 cc engine, originally designed by Ezio Mascheroni and first fitted to the F3, uses a DOHC Straight-three engine, inline three-cylinder layout with Multi-valve#Four valves, four va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MV Agusta
MV Agusta (, full name: MV AGUSTA Motor S.p.A., original name: Meccanica Verghera Agusta or MV) is a motorcycle manufacturer founded by Count Domenico Agusta on 19 January 1945 as one of the branches of the Agusta aircraft company near Milan in Cascina Costa, Italy. The abbreviation MV stands for ''Meccanica'' (mechanics) ''Verghera'', the hamlet where the first MVs were made. The modern headquarters and main production facilities are located in Varese, Italy on the shore of Lake Varese. History 1943–1945: From idea to mass production It all began in the early years of the 20th century, when Count Giovanni Agusta left Sicily for northern Italy, where he built his first aircraft, the AG.1, four years after the Wright brothers had made history in the US. The First World War, which demonstrated the prospects of aviation, prompted the count to act decisively – and in 1923, in the town of Samarate, he founded the Costruzioni Aeronautiche Giovanni Agusta S.A. (usually shorte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italians
, flag = , flag_caption = The national flag of Italy , population = , regions = Italy 55,551,000 , region1 = Brazil , pop1 = 25–33 million , ref1 = , region2 = Argentina , pop2 = 20–25 million , ref2 = , region3 = United States , pop3 = 17-20 million , ref3 = , region4 = France , pop4 = 1-5 million , ref4 = , region5 = Venezuela , pop5 = 1-5 million , ref5 = , region6 = Paraguay , pop6 = 2.5 million , region7 = Colombia , pop7 = 2 million , ref7 = , region8 = Canada , pop8 = 1.5 million , ref8 = , region9 = Australia , pop9 = 1.0 million , ref9 = , region10 = Uruguay , pop10 = 1.0 million , r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine Control Unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by reading values from a multitude of sensors within the engine bay, interpreting the data using multidimensional performance maps (called lookup tables), and adjusting the engine actuators. Before ECUs, air–fuel mixture, ignition timing, and idle speed were mechanically set and dynamically controlled by mechanical and pneumatic means. If the ECU has control over the fuel lines, then it is referred to as an electronic engine management system (EEMS). The fuel injection system has the major role of controlling the engine's fuel supply. The whole mechanism of the EEMS is controlled by a stack of sensors and actuators. Workings Control of air–fuel ratio Most modern engines use some type of fuel injection to deliver fuel to the cylinders. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headlight
A headlamp is a lamp (electrical component), lamp attached to the front of a vehicle to illuminate the road ahead. Headlamps are also often called headlights, but in the most precise usage (language), usage, ''headlamp'' is the term for the device itself and ''headlight'' is the term for the light beam, beam of light produced and distributed by the device. Headlamp performance has steadily improved throughout the automobile age, spurred by the great disparity between daytime and nighttime traffic fatalities: the US National Highway Traffic Safety Administration states that nearly half of all traffic-related fatalities occur in the dark, despite only 25% of traffic travelling during darkness. Other vehicles, such as trains and aircraft, are required to have headlamps. Bicycle lighting, Bicycle headlamps are often used on bicycles, and are required in some jurisdictions. They can be powered by a battery (electricity), battery or a small generator like a bottle dynamo, bottle o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Fibre
Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (American English), carbon-fibre-reinforced polymers (Commonwealth English), carbon-fiber-reinforced plastics, carbon-fiber reinforced-thermoplastic (CFRP, CRP, CFRTP), also known as carbon fiber, carbon composite, or just carbon, are extremely strong and light fiber-reinforced plastics that contain carbon fibers. CFRPs can be expensive to produce, but are commonly used wherever high strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness (rigidity) are required, such as aerospace, superstructures of ships, automotive, civil engineering, sports equipment, and an increasing number of consumer and technical applications. The binding polymer is often a thermoset resin such as epoxy, but other thermoset or thermoplastic polymers, such as polyester, vinyl ester, or nylon, are sometimes used. The properties of the final CFRP product can be affected by the type of additives introduced to the binding matrix (resin). The most common additive is silica, but other addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZF Sachs
ZF Sachs AG, also known as Fichtel & Sachs, was founded in Schweinfurt in 1895 and was a well-known German family business. At its last point as an independent company, the company name was Fichtel & Sachs AG. In 1997, the automotive supplier was taken over by Mannesmann and renamed Mannesmann Sachs AG. As of 2001, Sachs belonged to ZF Friedrichshafen as a subsidiary company ZF Sachs AG. In 2011, ZF Sachs, like other Group subsidiaries, was legally merged with ZF Friedrichshafen AG and the independent business units integrated into the ZF divisions. Sachs has since become a brand of ZF Friedrichshafen AG. The head office for development, production and sales of products of the brand Sachs remained in Schweinfurt. The Schweinfurt plant is today (2017) the largest location of the automotive supplier ZF Friedrichshafen. Today, Fichtel & Sachs is a German manufacturer of automotive parts, producing powertrain and suspension components. In the past the company also having produced bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marzocchi
Marzocchi is an Italian manufacturer founded in 1949 by brothers Stefano and Guglielmo Marzocchi. The company profile doesn't include hydraulic industrial pumps anymore but only suspension components for motorcycles and bicycles. The Marzocchi Pompe is still in the hands of the Marzocchi Family and produces gear pumps and motors in Bologna. In 2008 the company was acquired by American automotive parts manufacturer Tenneco. Until 2007, Marzocchi manufactured the mountain bike suspension forks in Italy. In order to remain competitive, Marzocchi, like RockShox before it, moved the production of the forks to Taiwan. In the 4th quarter of 2015, Fox Factory acquired certain assets of Marzocchi's mountain bike product lines. Motorcycle suspension Up until the 1980s, Marzocchi were original equipment manufacturers ('OEM') for a number of Italian motorcycle marques including Moto Morini and Ducati, their oil shock absorbers also being OEM for Triumph Motorcycles in the latter stages of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stressed Member Engine
A stressed member engine is a vehicle engine used as an active structural element of the chassis to transmit forces and torques, rather than being passively contained by the chassis with anti-vibration mounts. Automotive engineers use the method for weight reduction and mass centralization in vehicles. Applications are found in several vehicles where mass reduction is critical for performance reasons, usually after several iterations of conventional frame/chassis designs have been employed. Applications Motorcycles Stressed member engines was patented in 1900 by Joah ("John") Carver Phelon and his nephew Harry Rayner. and were pioneered at least as early as the 1916 Harley-Davidson 8-valve racer, and incorporated in the production Harley-Davidson Model W by 1919. The technique was developed in the 20th century by Vincent and others, and by the end of the century was common feature of chassis built by Ducati, BMW and others. In 2019, KTM Duke 790's engine is used as a stres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrome-molybdenum Steel
41xx steel is a family of SAE steel grades, as specified by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE). Alloying elements include chromium and molybdenum, and as a result these materials are often informally referred to as chromoly steel (common variant stylings include ''chrome-moly'', ''cro-moly'', ''CrMo'', ''CRMO'', ''CR-MOLY'', and similar). They have an excellent strength to weight ratio and are considerably stronger and harder than standard 1020 steel, but are not easily welded, requiring thermal treatment both before and after welding to avoid cold cracking. While these grades of steel do contain chromium, it is not in great enough quantities to provide the corrosion resistance found in stainless steel. Examples of applications for 4130, 4140 and 4145 include structural tubing, bicycle frames, gas bottles for transportation of pressurized gases, firearm parts, clutch and flywheel components, and roll cages. 4150 stands out as being one of the steels accepted for use in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
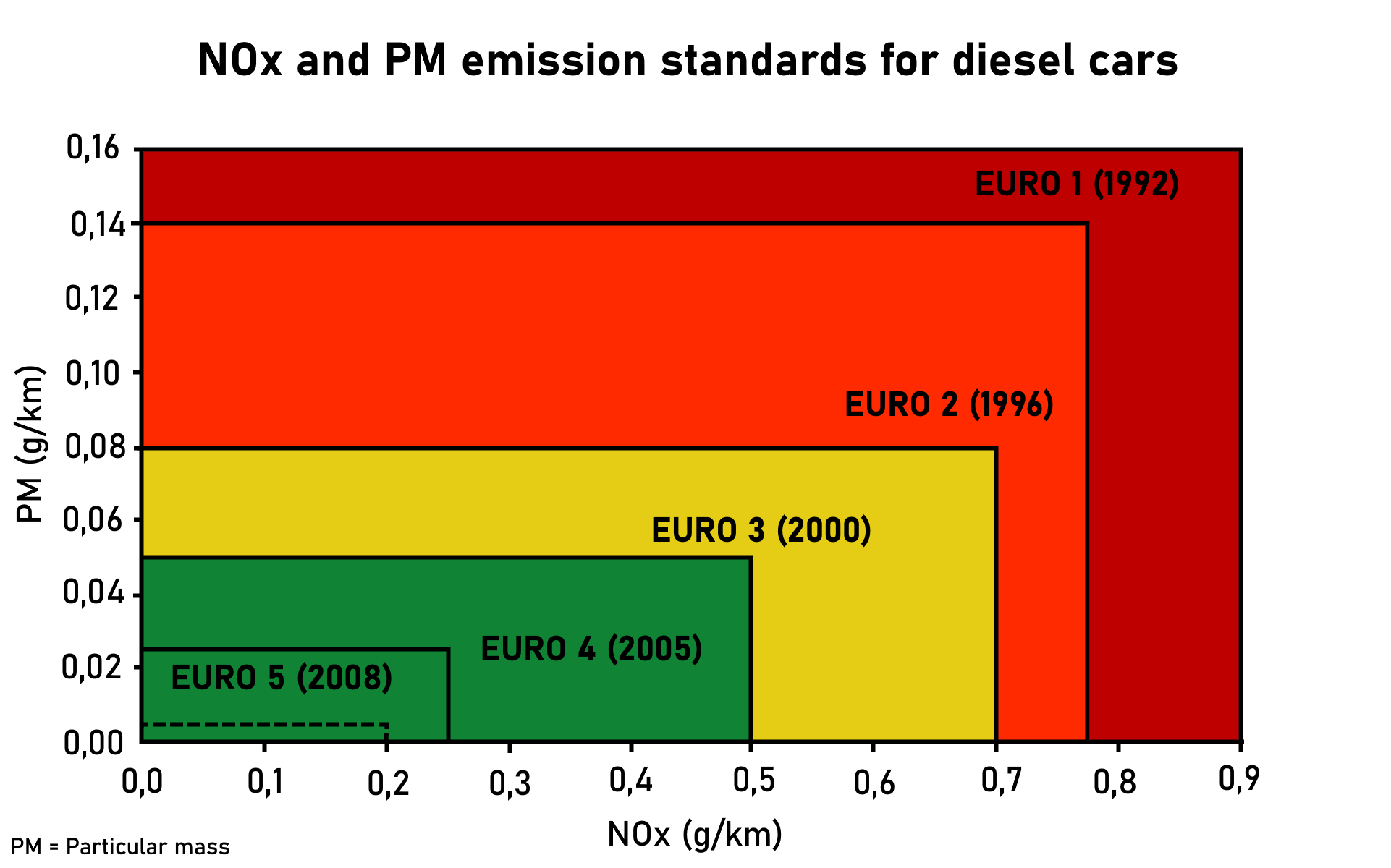
Euro4
The European emission standards are vehicle emission standards for pollution from the use of new land surface vehicles sold in the European Union and EEA member states and the UK, and ships in EU waters. The standards are defined in a series of European Union directives staging the progressive introduction of increasingly stringent standards. , the standards do not include non-exhaust emissions such as particulates from tyres and brakes. Details of Euro 7 have been postponed to 12 October 2022. Background In the European Union, emissions of nitrogen oxides (), total hydrocarbon (THC), non-methane hydrocarbons (NMHC), carbon monoxide (CO) and particulate matter (PM) are regulated for most vehicle types, including cars, trucks (lorries), locomotives, tractors and similar machinery, barges, but excluding seagoing ships and aeroplanes. For each vehicle type, different standards apply. Compliance is determined by running the engine at a standardised test cycle. Non-compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroke (engine)
In the context of an internal combustion engine, the term stroke has the following related meanings: * A phase of the engine's cycle (e.g. compression stroke, exhaust stroke), during which the piston travels from top to bottom or vice versa. * The type of power cycle used by a piston engine (e.g. two-stroke engine, four-stroke engine). * "Stroke length", the distance travelled by the piston during each cycle. The stroke length––along with bore diameter––determines the engine's displacement. Phases in the power cycle Commonly used engine phases or strokes (i.e. those used in a four-stroke engine) are described below. Other types of engines can have very different phases. Induction-intake stroke The induction stroke is the first phase in a four-stroke (e.g. Otto cycle or Diesel cycle) engine. It involves the downward movement of the piston, creating a partial vacuum that draws a air-fuel mixture (or air alone, in the case of a direct injection engine) into the combus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bore (engine)
In a piston engine, the bore (or cylinder bore) is the diameter of each cylinder. Engine displacement is calculated based on bore, stroke length and the number of cylinders: displacement = The stroke ratio, determined by dividing the bore by the stroke, traditionally indicated whether an engine was designed for power at high engine speeds (rpm) or torque at lower engine speeds. The term "bore" can also be applied to the bore of a locomotive cylinder or steam engine pistons. Steam locomotive The term bore also applies to the cylinder of a steam locomotive or steam engine. See also * Bore pitch * Compression ratio * Engine displacement Engine displacement is the measure of the cylinder volume swept by all of the pistons of a piston engine, excluding the combustion chambers. It is commonly used as an expression of an engine's size, and by extension as a loose indicator of the ... References {{Steam engine configurations Engine technology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |