|
MEGA, Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis
Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) is computer software for conducting statistical analysis of molecular evolution and for constructing phylogenetic trees. It includes many sophisticated methods and tools for phylogenomics and phylomedicine. It is licensed as proprietary freeware. The project for developing this software was initiated by the leadership of Masatoshi Nei in his laboratory at the Pennsylvania State University in collaboration with his graduate student Sudhir Kumar and postdoctoral fellow Koichiro Tamura.Kumar, S., K. Tamura, and M. Nei (1993) MEGA: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis. Ver. 1.0, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA. Nei wrote a monograph (pp. 130) outlining the scope of the software and presenting new statistical methods that were included in MEGA. The entire set of computer programs was written by Kumar and Tamura. The personal computers then lacked the ability to send the monograph and software electron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masatoshi Nei
(born January 2, 1931) is a Japanese-born American evolutionary biologist currently affiliated with the Department of Biology at Temple University as a Carnell Professor. He was, until recently, Evan Pugh Professor of Biology at Pennsylvania State University and Director of the Institute of Molecular Evolutionary Genetics; he was there from 1990 to 2015. Nei was born in 1931 in Miyazaki Prefecture, on Kyūshū Island, Japan. He was associate professor and professor of biology at Brown University from 1969 to 1972 and professor of population genetics at the Center for Demographic and Population Genetics, University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth), from 1972 to 1990. Acting alone or working with his students, he has continuously developed statistical theories of molecular evolution taking into account discoveries in molecular biology. He has also developed concepts in evolutionary theory and advanced the theory of mutation-driven evolution. Together with W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylomedicine
Phylomedicine is an emerging discipline at the intersection of medicine, genomics, and evolution. It focuses on the use of evolutionary knowledge to predict functional consequences of mutations found in personal genomes and populations. History Modern technologies have made genome sequencing accessible, and biomedical scientists have profiled genomic variation in apparently healthy individuals and individuals diagnosed with a variety of diseases. This work has led to the discovery of thousands of disease-associated genes and genetic variants, elucidating a more robust picture of the amount and types of variations found within and between humans. Proteins are encoded in genomic DNA by exons, and these comprise only ~1% of the human genomic sequence (aka the exome). The exome of an individual carries about 6,000–10,000 amino-acid-altering nSNVs, and many of these variants are already known to be associated with more than 1000 diseases. Although only a small fraction of these p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Likelihood
In statistics, maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) is a method of estimating the parameters of an assumed probability distribution, given some observed data. This is achieved by maximizing a likelihood function so that, under the assumed statistical model, the observed data is most probable. The point in the parameter space that maximizes the likelihood function is called the maximum likelihood estimate. The logic of maximum likelihood is both intuitive and flexible, and as such the method has become a dominant means of statistical inference. If the likelihood function is differentiable, the derivative test for finding maxima can be applied. In some cases, the first-order conditions of the likelihood function can be solved analytically; for instance, the ordinary least squares estimator for a linear regression model maximizes the likelihood when all observed outcomes are assumed to have Normal distributions with the same variance. From the perspective of Bayesian infere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Parsimony
In phylogenetics, maximum parsimony is an optimality criterion under which the phylogenetic tree that minimizes the total number of character-state changes (or miminizes the cost of differentially weighted character-state changes) is preferred. Under the maximum-parsimony criterion, the optimal tree will minimize the amount of homoplasy (i.e., convergent evolution, parallel evolution, and evolutionary reversals). In other words, under this criterion, the shortest possible tree that explains the data is considered best. Some of the basic ideas behind maximum parsimony were presented by James S. Farris in 1970 and Walter M. Fitch in 1971. Maximum parsimony is an intuitive and simple criterion, and it is popular for this reason. However, although it is easy to ''score'' a phylogenetic tree (by counting the number of character-state changes), there is no algorithm to quickly ''generate'' the most-parsimonious tree. Instead, the most-parsimonious tree must be sought in "tree spac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UPGMA
UPGMA (unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean) is a simple agglomerative (bottom-up) hierarchical clustering method. The method is generally attributed to Sokal and Michener. The UPGMA method is similar to its ''weighted'' variant, the WPGMA method. Note that the unweighted term indicates that all distances contribute equally to each average that is computed and does not refer to the math by which it is achieved. Thus the simple averaging in WPGMA produces a weighted result and the proportional averaging in UPGMA produces an unweighted result ('' see the working example''). Algorithm The UPGMA algorithm constructs a rooted tree (dendrogram) that reflects the structure present in a pairwise similarity matrix (or a dissimilarity matrix). At each step, the nearest two clusters are combined into a higher-level cluster. The distance between any two clusters \mathcal and \mathcal, each of size (''i.e.'', cardinality) and , is taken to be the average of all distances d(x,y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neighbor Joining
In bioinformatics, neighbor joining is a bottom-up (agglomerative) clustering method for the creation of phylogenetic trees, created by Naruya Saitou and Masatoshi Nei in 1987. Usually based on DNA or protein sequence data, the algorithm requires knowledge of the distance between each pair of taxa (e.g., species or sequences) to create the phylogenetic tree. The algorithm Neighbor joining takes a distance matrix, which specifies the distance between each pair of taxa, as input. The algorithm starts with a completely unresolved tree, whose topology corresponds to that of a star network, and iterates over the following steps, until the tree is completely resolved, and all branch lengths are known: # Based on the current distance matrix, calculate a matrix Q (defined below). # Find the pair of distinct taxa i and j (i.e. with i \neq j) for which Q(i,j) is smallest. Make a new node that joins the taxa i and j, and connect the new node to the central node. For example, in part ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Code
The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material ( DNA or RNA sequences of nucleotide triplets, or codons) into proteins. Translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links proteinogenic amino acids in an order specified by messenger RNA (mRNA), using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries. The codons specify which amino acid will be added next during protein biosynthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. The vast majority of genes are encoded with a single scheme (see the RNA codon table). That scheme is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply ''the'' genetic code, though variant codes (such as in mitochondria) exist. History Effor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
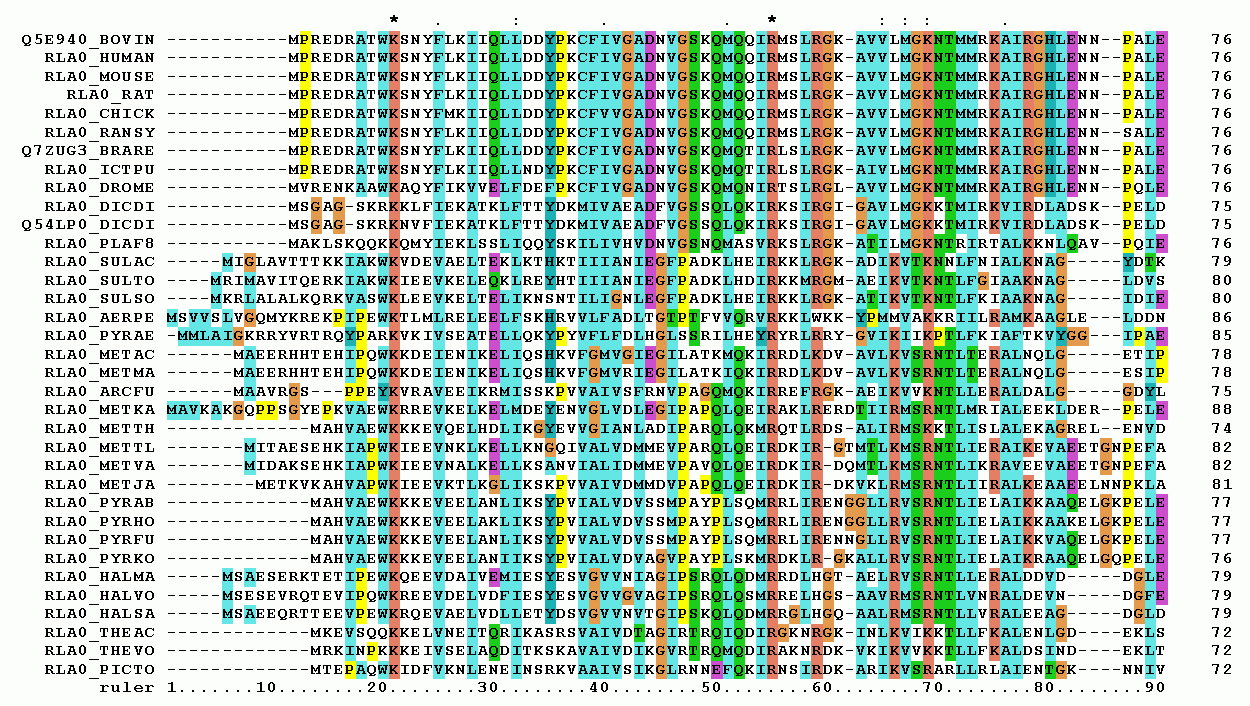
Multiple Sequence Alignment
Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) may refer to the process or the result of sequence alignment of three or more biological sequences, generally protein, DNA, or RNA. In many cases, the input set of query sequences are assumed to have an evolutionary relationship by which they share a linkage and are descended from a common ancestor. From the resulting MSA, sequence homology can be inferred and phylogenetic analysis can be conducted to assess the sequences' shared evolutionary origins. Visual depictions of the alignment as in the image at right illustrate mutation events such as point mutations (single amino acid or nucleotide changes) that appear as differing characters in a single alignment column, and insertion or deletion mutations (indels or gaps) that appear as hyphens in one or more of the sequences in the alignment. Multiple sequence alignment is often used to assess sequence conservation of protein domains, tertiary and secondary structures, and even individual amino aci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
64-bit Computing
In computer architecture, 64-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 64 bits wide. Also, 64-bit CPUs and ALUs are those that are based on processor registers, address buses, or data buses of that size. A computer that uses such a processor is a 64-bit computer. From the software perspective, 64-bit computing means the use of machine code with 64-bit virtual memory addresses. However, not all 64-bit instruction sets support full 64-bit virtual memory addresses; x86-64 and ARMv8, for example, support only 48 bits of virtual address, with the remaining 16 bits of the virtual address required to be all 0's or all 1's, and several 64-bit instruction sets support fewer than 64 bits of physical memory address. The term ''64-bit'' also describes a generation of computers in which 64-bit processors are the norm. 64 bits is a word size that defines certain classes of computer architecture, buses, memory, and CPUs and, by extension, the software t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo Metropolitan University
, often referred to as TMU, is a public research university in Japan. Origin The origin of Tokyo Metropolitan University was Prefectural Higher School, under the old system of education, established by Tokyo Prefecture in 1929 as the third public higher school. The School was modeled on Eton College, with three years of advanced course and four years of regular course. The seven-year system had an advantage to assure the entrance to Imperial universities at the age of Middle School, and the typical passway for academic elites before the end of the Pacific War was to enter Tokyo First Middle School, proceeding First Higher School and Tokyo Imperial University. Since the jurisdiction control of Tokyo First Middle School and First Higher School were different, however, Tokyo First Middle School attempted to originally establish the prefectural higher school, whereas the other Middle Schools opposed to the said attempt. Prefectural Higher School was established in 1929 locating i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple University
Temple University (Temple or TU) is a public state-related research university in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was founded in 1884 by the Baptist minister Russell Conwell and his congregation Grace Baptist Church of Philadelphia then called Baptist Temple. On May 12, 1888, it was renamed the Temple College of Philadelphia. By 1907, the institution revised its institutional status and was incorporated as a research university. As of 2020, about 37,289 undergraduate, graduate and professional students were enrolled at the university. Temple is among the world's largest providers of professional education (law, medicine, podiatry, pharmacy, dentistry, engineering and architecture), preparing the largest body of professional practitioners in Pennsylvania. History Temple University was founded in 1884 by Grace Baptist Church of Philadelphia and its pastor Russell Conwell, a Yale-educated Boston lawyer, orator, and ordained Baptist minister, who had served in the Union ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Computer
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or technician. Unlike large, costly minicomputers and mainframes, time-sharing by many people at the same time is not used with personal computers. Primarily in the late 1970s and 1980s, the term home computer was also used. Institutional or corporate computer owners in the 1960s had to write their own programs to do any useful work with the machines. While personal computer users may develop their own applications, usually these systems run commercial software, free-of-charge software (" freeware"), which is most often proprietary, or free and open-source software, which is provided in "ready-to-run", or binary, form. Software for personal computers is typically developed and distributed independently from the hardware or operating system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |